Introduction
In 2025, customers expect faster, more transparent, and flexible shopping experiences across online, in-store, and global channels. Managing this complexity requires more than just tracking orders it requires a system that unifies inventory, fulfillment, and customer service into one seamless flow.
Salesforce Order Management (OMS) is a cloud platform that manages the entire order lifecycle—from checkout to delivery to returns—while keeping the customer at the center.
If your business is exploring upgrades, consider expert Salesforce Consulting Services from SDLCCorp to accelerate OMS adoption with architecture design, process automation, and integrations.
In this guide, we’ll cover Salesforce OMS features, architecture, pricing, setup steps, and comparisons helping you decide if it’s the right fit for your business.
1. What Is Salesforce Order Management?
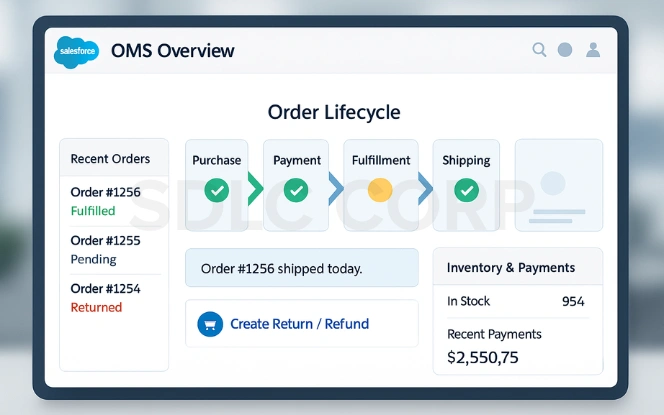
An order management system (OMS) is designed to oversee the full order lifecycle from purchase to payment processing, fulfillment, shipping, and returns. Its main purpose is to ensure smooth, transparent, and timely delivery experiences that match modern customer expectations.
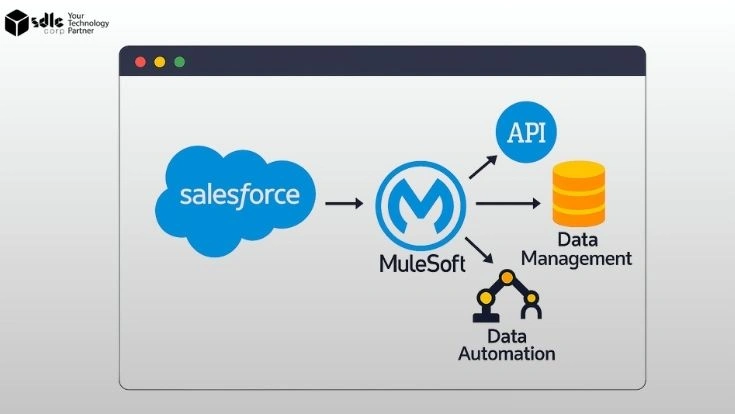
Salesforce OMS, built on the Salesforce Customer 360 platform, goes further. It provides automation, real-time visibility, and customer-centric workflows that connect commerce, service, and fulfillment in one unified solution.
Salesforce OMS vs. ERP OMS
ERP-Based OMS: Traditionally tied to enterprise resource planning software, ERP OMS solutions excel in accounting and supply chain management. However, they are often rigid, slower to adapt, and harder to integrate with customer-facing platforms.
Salesforce OMS: More agile and API-driven, Salesforce OMS is built for omnichannel businesses. It integrates seamlessly with Commerce Cloud, Service Cloud, and third-party apps, making it highly flexible for modern commerce needs.
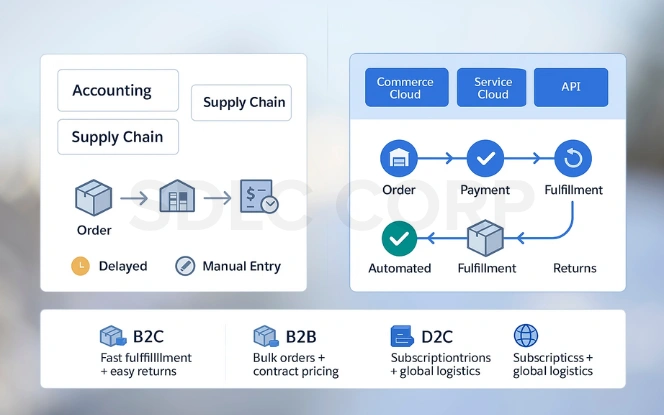
When Salesforce OMS Delivers the Most Value
B2C Retail: Perfect for high-volume transactions where speed, returns management, and cross-channel consistency are essential.
B2B Enterprises: Supports bulk orders, contract-based pricing, and approval workflows with flexible fulfillment rules.
D2C Brands: Best for subscription models, global operations, and brands that prioritize direct customer relationships.
2. Salesforce OMS Architecture & Lifecycle
Salesforce Order Management is built on a flexible, event-driven architecture that manages complex order flows while maintaining visibility across systems. It combines standard Salesforce objects with automation tools like Flows, APIs, and event messages.
Core Data Model
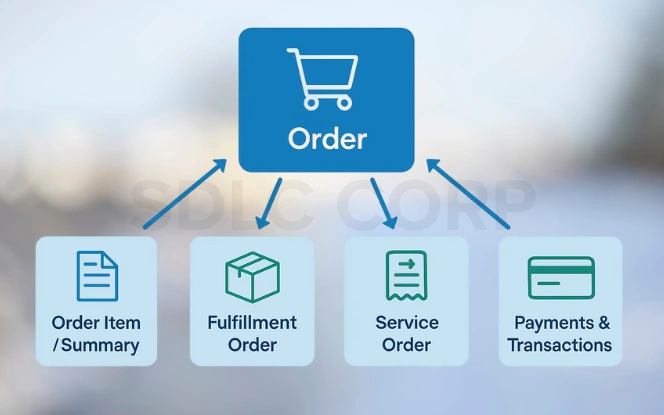
Order: Captures the complete purchase request, including items, pricing details, applied discounts, and order status.
Order Item / Order Item Summary: Breaks the order into individual products or services for easier tracking.
Fulfillment Order: Connects orders to warehouse and logistics operations.
Service Order: Handles returns, exchanges, or repairs.
Payment & Transaction Records: Tracks financial activity from authorization to refunds.
Order Lifecycle Stages
Order Capture – Receives an order from e-commerce, POS, or marketplace.
Payment Authorization – Validates payment info, checks fraud risks, and secures funds.
Order Orchestration – Allocates inventory, splits shipments if needed, and triggers workflows.
Fulfillment – Coordinates picking, packing, and shipping with warehouses or logistics providers.
Delivery & Notifications – Sends real-time updates about status and delivery.
Returns & Service – Manages refunds, exchanges, and customer service cases efficiently.
3. Key Features & Benefits
Salesforce OMS comes with a wide range of capabilities that help businesses streamline operations and deliver a better customer experience. Below is a breakdown of its most important features and the value they bring.
| Feature | What It Does | Business Value |
|---|---|---|
| Order Lifecycle Management | Tracks the entire journey from checkout to delivery and post-purchase service. | End-to-end visibility and fewer errors in processing. |
| Inventory Visibility | Show real-time stock levels across warehouses, stores, and channels. | Prevents overselling, reduces stockouts, and improves forecasting. |
| Split Shipments & Multi-Location Fulfillment | Routes items from different warehouses or ships partial orders. | Faster delivery times and optimized logistics costs. |
| Returns & Exchanges Management | Automates workflows for refunds, replacements, and warranty services. | Increases customer satisfaction and reduces manual work. |
| Customer Service Integration | Connects with Service Cloud, allowing agents to modify, cancel, or refund orders. | Improves customer support and issue resolution speed. |
| Omnichannel Support | Handles orders from web, stores, marketplaces, and mobile apps. | Seamless experience across touchpoints. |
| Automation & Workflows | Uses Flows and event-driven rules for fraud checks, payment capture, and shipping notifications. | Reduces manual intervention, speeds up fulfillment. |
| Scalability | Built on Salesforce platform with API-first design for integrations. | Adapts easily to growing order volumes and complex business models. |
4. Integrations & Reference Patterns
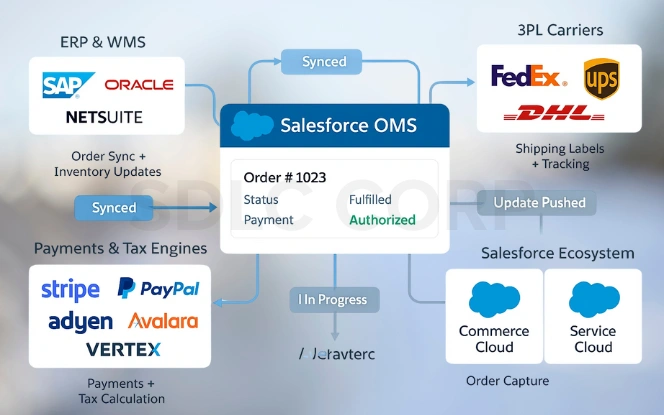
A major strength of Salesforce OMS is its ability to act as a central hub, connecting seamlessly with other commerce systems.
- ERP & WMS: Syncs orders and inventory with SAP, Oracle, or NetSuite, keeping stock accurate and pushing fulfillment updates back to OMS.
- 3PL & Carriers: Works with FedEx, UPS, DHL, and others to automate labels, tracking, and flexible delivery options like same-day or in-store pickup.
- Payments & Tax Engines: Integrates with Stripe, PayPal, Adyen, Avalara, and Vertex for secure payments, real-time tax calculation, and compliance.
- Salesforce Ecosystem: Natively connects to Commerce Cloud for order capture and Service Cloud for post-purchase support, enabling agents to modify or cancel orders without leaving Salesforce.
As a result, these integrations make Salesforce OMS flexible and extensible, so team can adapt it the existing tech stack without disrupting operations.
5. Salesforce OMS Pricing Explained (with GMV Examples)
Unlike flat subscription models, Salesforce Order Management pricing is tied to Gross Merchandise Value (GMV). This means the more transactions you process, the more you pay—but also the more value you extract as your business scales.
Pricing Tiers
Salesforce OMS pricing is structured around two main tiers, both tied directly to Gross Merchandise Value (GMV).
- Order Visibility (0.25% of GMV): This tier provides basic order tracking and visibility into the lifecycle. It is best suited for smaller businesses that need oversight but may not require advanced automation or orchestration.
- Growth (1% of GMV): This premium tier includes the full suite of OMS capabilities such as orchestration, automated returns and exchanges, and deep integrations with third-party systems. It is designed for larger enterprises and high-volume, omnichannel operations where efficiency and automation are critical.
Example Calculation: Assume annual GMV is $10 million: Order Visibility tier (0.25%), your annual OMS cost = $25,000.
ROI Consideration
6. Implementation Guide
Rolling out Salesforce Order Management isn’t just flipping a switch. Instead, plan setup, integration, and testing to make sure every order flows smoothly across systems.
Pre-Requisites:
- A Salesforce Commerce Cloud or compatible order capture system should be in place to feed orders into OMS.
Connected Salesforce orgs such as Service Cloud or CRM are needed if customer support is part of the process.
Fulfillment and return workflows must be clearly defined to avoid bottlenecks during setup.
Payment gateways and tax engine accounts should be ready for integration to support transactions and compliance.
Proper permission sets must be assigned so the right users can access OMS features securely.
Setup Steps
Enable OMS Features: Begin by activating Salesforce OMS objects and configuring order lifecycle states, ensuring each order moves through structured, automated workflows effectively.
Connect Payment Processors: Integrate trusted gateways such as Stripe, Adyen, or PayPal to manage authorizations, captures, refunds, and ensure secure payment transactions.
Configure Order Flows: Build automation using Salesforce Flows to streamline fraud checks, allocate inventory, split shipments, and accelerate order processing across all channels.
Define Fulfillment Rules: Establish fulfillment logic by mapping warehouses, carriers, and delivery methods, optimizing logistics to reduce delivery delays and operational inefficiencies.
Integrate Tax & Shipping Providers: Connect solutions like Avalara, Vertex, or regional services to automate tax calculations and provide real-time shipping status updates.
Import Historical Orders: Load previous customer orders into OMS to preserve data continuity and ensure accurate reporting, forecasting, and customer service history.
Test End-to-End Journeys: Conduct thorough testing for multiple scenarios, including successful orders, declined payments, product returns, refunds, and split shipment fulfillment.
Timeline
Most mid-sized businesses can expect implementation to take 8–12 weeks, depending on the complexity of integrations and order processes.
By following this structured approach, businesses deploy Salesforce OMS smoothly and achieve quick improvements in visibility, efficiency, and customer experience.
7. Operations & KPIs
After go-live, the main value comes from checking performance and making order processes better. Salesforce includes built-in reports and dashboards, and you can get extra insights with CRM Analytics or third-party BI tools.
Key Metrics to Track
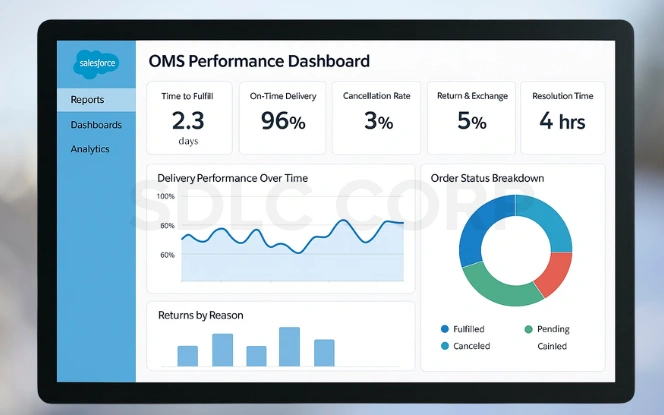
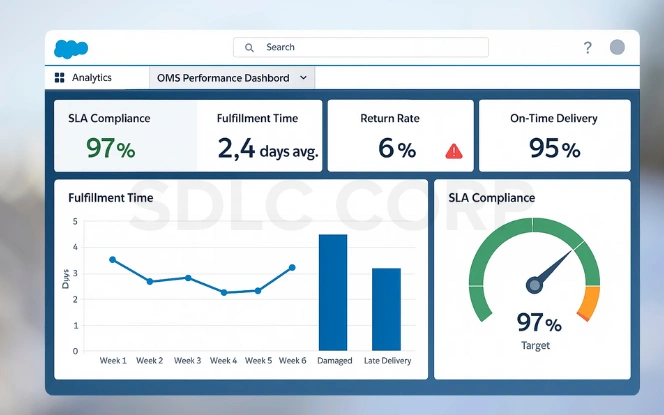
Time to Fulfill: Measure the average time between order capture and shipment, ensuring fulfillment processes remain efficient and customer expectations are consistently met.
On-Time Delivery Rate: Track the percentage of orders delivered within promised timeframes, helping businesses identify delays and improve carrier or warehouse performance.
Cancellation Rate: Monitor how frequently orders are canceled before fulfillment, uncovering potential issues in checkout, payment, or stock allocation processes.
Return & Exchange Rate: Assess how many orders are returned or exchanged, with segmentation by reason to identify patterns and address recurring product issues.
Refund Cycle Time: Calculate the average time required to process refunds or exchanges, ensuring financial operations are responsive and customers remain satisfied.
Customer Service Resolution Time: Track how quickly support agents resolve order-related cases, highlighting efficiency in post-purchase service and overall customer care.
Dashboards & Insights
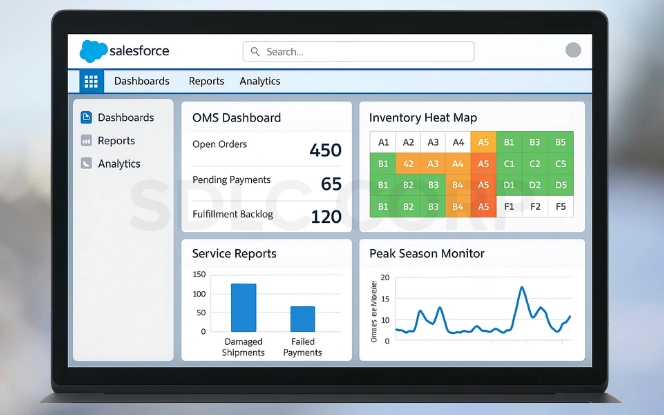
OMS Dashboard: Provides a real-time view of open orders, pending payments, and fulfillment backlogs, allowing managers to take immediate corrective actions.
Inventory Heat Map: Displays stock availability across SKUs and warehouses, highlighting low-stock products to prevent overselling and ensure timely replenishment.
Service Cloud Case Reports: Identifies recurring customer issues such as damaged shipments or failed payments, helping businesses prioritize fixes that reduce friction.
Peak Season Monitoring: Custom dashboards provide real-time insights during high-volume sales events, ensuring resources are allocated properly and delays are minimized.
8. Security, Compliance & Scalability
Security & Permissions
To ensure customer and order data remains safe, Salesforce OMS provides strong access controls, encryption, and monitoring tools.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigns permission sets to agents, administrators, and fulfillment teams, preventing unauthorized access.
- Data Masking & Encryption: Encrypt sensitive fields such as payment tokens both at rest and during transfer.
- Audit Trails: Record every access or modification to order data, ensuring accountability across the organization.
Fraud Prevention: Integrates with fraud detection tools to identify suspicious activity before fulfillment takes place.
Compliance Considerations
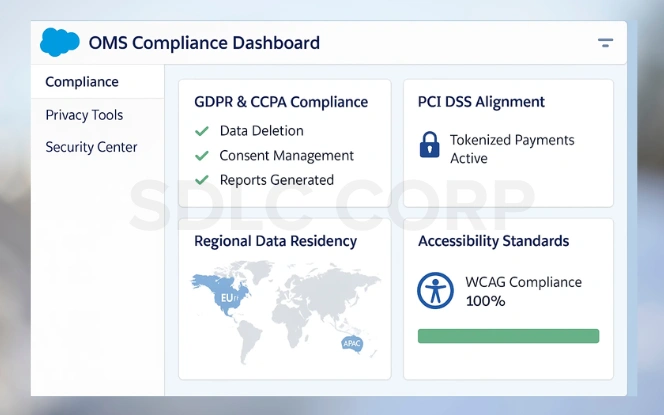
Additionally, modern businesses must meet strict regulatory requirements, and Salesforce OMS offers built-in tools to simplify compliance with global regional .
- GDPR & CCPA: Supports data deletion, consent management, and reporting to meet privacy law obligations.
- PCI DSS Alignment: Enables tokenized payments so raw card data is never stored within the system.
- Regional Data Residency: Provides hosting options in specific regions to comply with local data storage laws.
- Accessibility Standards: Meets WCAG accessibility requirements to support inclusive use of the platform.
Scalability
Salesforce OMS scales easily, enabling businesses to expand globally and maintain high performance during peak seasons.
Cloud-Native Performance: Uses Salesforce’s multi-tenant cloud infrastructure to process large spikes in traffic and transactions.
Elastic Architecture: Handles thousands of concurrent orders during peak events without performance bottlenecks.
API-First Design: Simplifies integration with other systems, making scaling efficient without major overhauls.
Global Support: Provides multi-currency, multi-language, and tax localization for international expansion.
9. B2C vs B2B vs D2C Considerations
| B2C (Business-to-Consumer) | B2B (Business-to-Business) | D2C (Direct-to-Consumer) |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Conclusion
Order management today goes beyond shipment tracking—it’s about giving customers seamless, clear, and reliable experiences across every channel. Salesforce Order Management (OMS) brings together commerce, service, and fulfillment in one flexible system that grows with your business.
As a result, with real-time inventory, smart workflows, and deep Salesforce connections, OMS cuts friction and boosts customer satisfaction. In addition, for tailored setup, integrations, or migration support, Salesforce Consulting Services make sure your OMS fits business goals and delivers clear ROI.
Related Blogs You Should Explore:
FAQ's
How Is Salesforce OMS Different From CRM?
A CRM manages customer relationships, while OMS manages order processes. Salesforce CRM helps you track leads, opportunities, and service cases. Salesforce OMS ensures that once a purchase happens, the order flows smoothly through payment, inventory, shipping, and post-purchase support.
How Much Does Salesforce OMS Cost?
Salesforce OMS is priced based on Gross Merchandise Value (GMV):
- Order Visibility tier: 0.25% of GMV.
Growth tier: 1% of GMV.
Costs scale with order volume, so businesses should calculate ROI based on sales and complexity.
How Long Does It Take To Implement Salesforce OMS?
Typical implementations take 8–12 weeks for mid-sized businesses. Timelines depend on integration complexity, data migration needs, and training requirements.
Can Salesforce OMS Handle Returns And Exchanges?
Yes. Salesforce OMS supports returns, refunds, and exchanges through Service Orders. These processes can be automated with Flows and integrated with warehouses and payment systems to reduce manual work.
Is Salesforce OMS Suitable For B2b Businesses?
Absolutely. It supports bulk orders, negotiated pricing, approval workflows, and split shipments features often required in B2B commerce.
Does Salesforce OMS Integrate With Third-party Systems?
Yes. Salesforce OMS has an API-first design and integrates with ERP systems, WMS, 3PL providers, tax engines, and payment gateways to create a connected commerce ecosystem.