Introduction
Global Capability Centres (GCCs) are redefining how large enterprises manage operations, technology, and innovation. These centres, also called Captive Centres, act as wholly owned extensions of global businesses that run functions such as analytics, software development, finance, and digital transformation.
In the past, companies viewed GCCs as cost-saving back offices. Today, they are strategic hubs that enable agility, governance, and technological excellence. By uniting global talent and resources, GCCs help organisations improve efficiency and innovate faster.
This blog explores every dimension of GCCs – their definition, evolution, advantages, setup process, operational structure, challenges, and the trends shaping their future.
What Are Global Capability Centres ?
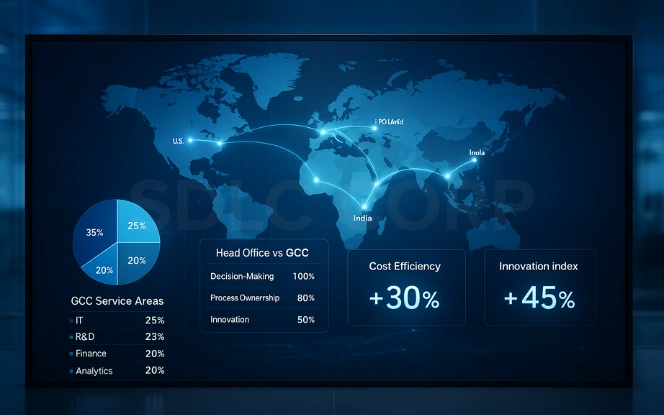
A Global Capability Centre (GCC) is a fully owned offshore or nearshore facility that delivers specialised business and technology services for its parent company. Unlike outsourcing, GCCs provide total control, governance, and cultural alignment. They operate under the same standards and strategic objectives as headquarters, ensuring consistency across functions such as R&D, finance, product engineering, and digital innovation.
Beyond their operational role, GCCs serve as strategic innovation hubs that enable enterprises to experiment, transform, and scale. They are equipped with cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and data analytics to optimise business outcomes. For instance, many GCCs now manage global functions like cybersecurity operations, product lifecycle management, and automation architecture.
In addition, GCCs help organisations attract top-tier global talent, providing access to advanced skill sets and diverse expertise. By building in-house capabilities, enterprises reduce dependency on vendors, gain better process visibility, and ensure business continuity. Ultimately, GCCs empower companies to balance efficiency with innovation – creating a sustainable, future-ready business model that drives growth across global markets.
For a detailed explanation of GCCs, visit What Is GCC?
The Evolution of GCCs: From Support to Strategy
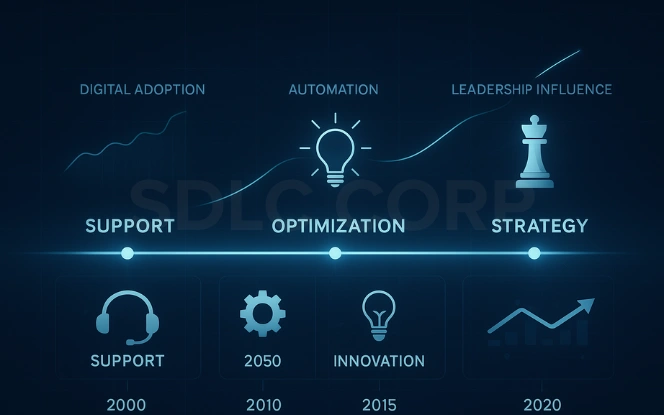
The concept of GCCs has evolved significantly over the last two decades. Initially created to cut costs, these centres have transformed into engines of innovation and capability building.
In the early 2000s, GCCs managed basic back-office tasks such as payroll and IT support. Over time, they began handling complex areas like cybersecurity, data analytics, and product design. Today, they operate as strategic partners that drive growth, automation, and digital transformation.
The Three Phases of GCC Maturity
- Efficiency Phase:
In the beginning, GCCs were focused on process efficiency and labour arbitrage. They handled routine operations at reduced costs without contributing to strategic decision-making. - Capability Expansion:
As global operations matured, GCCs started supporting advanced functions like technology development and analytics. This phase brought higher skill levels and better business integration. - Strategic Evolution:
Modern GCCs act as global innovation hubs. They enable AI-driven product development, digital transformation, and advanced governance, becoming a core part of an enterprise’s competitive advantage.
Through this evolution, GCCs have shifted from being cost-centres to value-creation engines.
Why Organisations Choose Captive Centre Setup
Establishing a captive centre setup provides long-term control, transparency, and strategic growth. Many global enterprises prefer this model over outsourcing to maintain ownership and consistency.
Key Drivers of GCC Adoption
- Strategic Ownership and Compliance:
GCCs allow enterprises to retain control over data, governance, and compliance frameworks. For industries such as finance and healthcare, this ensures adherence to standards like GDPR and ISO 27001, reducing external risks. - Access to Skilled Global Talent:
Locations like India, Poland, and the UAE offer abundant technical and managerial talent. GCCs tap into these pools to build cross-functional teams that combine domain expertise with innovation. - Long-Term Cost Efficiency:
Although setting up a GCC involves initial investment, enterprises achieve 25–35% cost savings over time. These savings come from process automation, in-house knowledge retention, and optimised vendor costs. - Cultural and Strategic Alignment:
Captive centres promote shared culture and values. Because teams operate under the parent organisation’s governance, they maintain quality and brand consistency across regions.
Learn how AI and automation enhance GCC models in AI-First Global Capability Centres (UK)
Key Benefits of a Global Capability Centre
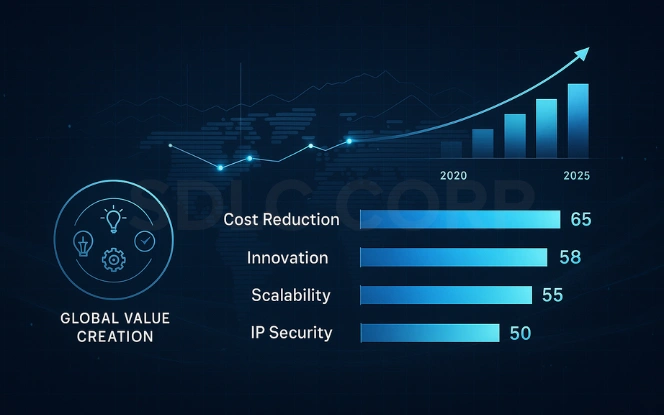
The global capability centre benefits extend well beyond cost optimisation. They enhance innovation, operational efficiency, and workforce capability.
Strategic Benefits of GCCs
- Innovation at Scale:
GCCs operate as centres of excellence for AI, automation, and data analytics. For example, Deloitte’s GCC in India drives global R&D initiatives that support client solutions across industries. These innovation efforts often lead to new revenue streams. - Process Standardisation:
Centralised governance and automation allow GCCs to standardise workflows globally. Tools like RPA and process mining improve accuracy and speed while reducing redundancies. - Data Security and Compliance:
Full ownership ensures complete data control. Implementing Zero Trust Architecture and encryption protocols prevents security breaches and safeguards intellectual property. - Talent Development and Retention:
GCCs create structured learning pathways, certification programmes, and leadership tracks that strengthen employee engagement and reduce attrition. - Resilience and Business Continuity:
Distributed delivery models enable companies to sustain operations during disruptions. During the pandemic, GCCs helped enterprises maintain uninterrupted digital and operational performance.Discover best practices for high-performance GCCs in Build a High-Performance Global Capability Centre (UAE)
Understanding the GCC Operations Model

The GCC operations model defines how a centre’s people, processes, and technology interact to deliver measurable business outcomes.
Key Components of GCC Operations
- Governance Framework:
A structured governance model connects headquarters and the GCC through defined roles and KPIs. For instance, a three-tier system—strategic, operational, and functional—ensures coordination between global and local priorities. - Technology Infrastructure:
GCCs rely on cloud platforms, AI automation, and DevOps pipelines to enable seamless integration with enterprise systems. This infrastructure allows teams across continents to collaborate in real time. - Performance Metrics:
Beyond cost, GCCs measure innovation velocity, service quality, and employee engagement. Real-time dashboards and analytics tools provide visibility into performance and help identify improvement opportunities. - Continuous Improvement:
Frameworks such as Lean Six Sigma and ITIL enable GCCs to refine processes continuously. These models foster a culture of agility and innovation that sustains competitive advantage.
Explore how performance is measured in advanced GCCs in High-Performance Global Capability Centre (USA)
How GCCs Drive Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is central to the modern GCC strategy. These centres combine data, automation, and intelligence to accelerate enterprise innovation.
How GCCs Drive Change
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
GCCs develop predictive models that automate decision-making in areas like supply chain and customer experience. For example, a global retailer’s GCC built an AI-based demand forecasting model that reduced inventory waste by 25%. - Cloud Modernisation:
GCCs lead hybrid and multi-cloud adoption, enabling scalability and reducing infrastructure costs. This shift also improves data accessibility and compliance across regions. - Data Analytics and Business Insights:
Advanced GCCs establish centralised data warehouses that consolidate enterprise data, making insights accessible for faster decision-making. - Cybersecurity Maturity:
Acting as global command centres, GCCs monitor threats and respond proactively. Their in-house security teams strengthen resilience and trust across the enterprise.
As a result, GCCs not only deliver transformation projects but also become strategic enablers of digital-first operations.
Captive Centre vs Outsourcing
While both captive centres and outsourcing aim to optimise performance, they differ significantly in ownership, governance, and long-term objectives. Outsourcing depends on third-party vendors to handle delivery under pre-defined contracts, prioritising short-term cost efficiency. In contrast, Global Capability Centres (GCCs) empower enterprises to retain ownership, develop intellectual property, and build strategic capabilities within their ecosystem.
Key Differences
- Control:
GCCs provide full decision-making authority, enabling direct alignment with corporate vision and culture. Outsourcing, however, restricts oversight since execution lies with the vendor, which can lead to inconsistent quality and limited agility. - Security:
Captive centres ensure enterprise-grade data protection and strict compliance with global standards like GDPR and ISO 27001. Vendor-managed setups often expose businesses to data security risks and governance challenges. - Scalability:
GCCs scale dynamically with business needs, allowing faster adaptation to new markets or technologies. Outsourcing usually requires contract renegotiations and lacks flexibility during expansion or crisis. - Strategic Value:
Captive centres strengthen internal expertise, nurture innovation, and create reusable assets that drive long-term advantage. Outsourcing focuses mainly on transactional efficiency, limiting innovation and cultural integration opportunities.
By choosing GCCs, enterprises invest in sustainable capability-building rather than temporary cost-cutting, ensuring greater resilience and continuous innovation.
Building a GCC: Implementation Framework
Setting up a GCC requires a detailed roadmap that combines strategic foresight with operational excellence.
Phases of GCC Implementation
- Define Vision and Purpose:
Establish the GCC’s role—whether it will serve as a digital innovation hub, shared service centre, or technology development unit. Clear vision ensures alignment with corporate objectives. - Select the Right Location:
Evaluate factors such as cost efficiency, talent availability, infrastructure, and government incentives. Emerging cities like Pune and Krakow are gaining traction for their scalability and skilled workforces. - Design Governance and Leadership:
Build a leadership team capable of bridging global and local expectations. A strong governance model ensures accountability and smooth collaboration. - Integrate Technology and Processes:
Implement cloud platforms, automation tools, and collaboration systems to enable seamless operations. Define standard operating procedures to maintain quality and compliance. - Optimise and Scale:
Once stabilised, GCCs can expand their service portfolio, introducing automation, AI, and advanced analytics to enhance overall efficiency.
A structured approach ensures that the GCC evolves from setup to self-sustaining excellence.
Challenges in Managing GCCs
Despite their proven value, GCCs face several management challenges that require proactive strategies.
Common Challenges
- Talent Retention:
Retaining skilled talent is difficult in competitive markets. Companies counter this through mentorship programmes, hybrid work models, and leadership training. For example, IBM’s GCCs run rotational leadership initiatives to build loyalty and engagement. - Rising Costs:
Operational and compliance costs can rise as centres mature. Many organisations offset this by expanding into tier-two cities or using automation to optimise resource allocation. - Governance Alignment:
As GCCs scale, maintaining strategic alignment with headquarters becomes vital. Regular governance reviews and digital dashboards help bridge communication gaps. - Regulatory Complexity:
Each region has unique legal frameworks. Collaborating with local legal and compliance experts helps GCCs stay compliant and avoid costly penalties.
With the right frameworks, these challenges become opportunities to strengthen governance and innovation.
The Future of GCCs
The future of GCCs is dynamic, data-driven, and sustainable. As digital ecosystems evolve, GCCs will play a central role in shaping enterprise competitiveness.
Emerging Trends
- AI-Powered Operations:
GCCs will leverage AI and automation for predictive insights, code generation, and intelligent process orchestration. This will increase productivity while reducing human error. - Sustainability and ESG Goals:
Next-generation GCCs will implement energy-efficient operations and paperless processes, aligning with global carbon-neutral targets. - Expansion to Tier-Two Cities:
Tier-two locations such as Coimbatore, Krakow, and Cebu offer a balance between cost, infrastructure, and skilled talent. This decentralisation promotes inclusivity and cost control. - Cybersecurity Command Centres:
Many GCCs are evolving into 24/7 global cybersecurity hubs, protecting data assets across multiple geographies through predictive monitoring. - Hybrid Operating Models:
The GCC of the future will combine captive ownership with selective outsourcing, allowing agility while preserving governance.
These trends point to a future where GCCs become innovation-driven ecosystems that enable long-term enterprise transformation.
Conclusion
Global Capability Centres have become the backbone of modern enterprises. They bring together talent, technology, and governance to create self-sustaining ecosystems that foster continuous innovation.
Unlike outsourcing, GCCs focus on ownership, cultural alignment, and value creation. They enable companies to stay agile, secure, and competitive in an increasingly digital world.
If your organisation is ready to build or scale a GCC, partner with Contact Us SDLC Corp for end-to-end expertise in design, setup, and performance management.
FAQs
What Is the Definition of Global Capability Centres (GCCs)?
A Global Capability Centre (GCC), or Captive Centre, is a fully owned facility that handles global operations, IT, and R&D for its parent company. It provides cost efficiency, control, and innovation under one structure.
How Does a Captive Centre Setup Support Business Growth?
A captive centre setup allows companies to build scalable, technology-driven teams that accelerate digital transformation, improve efficiency, and protect intellectual property.
What Are the Main Benefits of a GCC?
The global capability centre benefits include innovation, process efficiency, cost savings, talent retention, and enhanced data security. GCCs also strengthen resilience and business continuity.
How Does the GCC Operations Model Improve Efficiency?
The GCC operations model ensures alignment between strategy and delivery. It leverages automation, cloud tools, and KPIs to improve performance across multiple geographies.
Why Do Companies Prefer Captive Centres Over Outsourcing?
When comparing captive centre vs outsourcing, companies choose GCCs for ownership, transparency, and strategic flexibility. This control allows them to innovate faster and maintain data integrity.