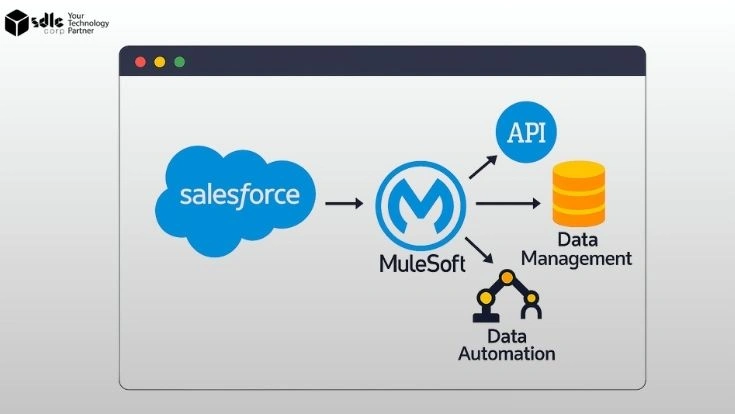
Introduction
The Salesforce Financial Services Cloud Data Model is designed to help financial institutions organize client information, track relationships, and manage accounts more effectively. Banks, insurance firms, and wealth managers use it to build a single view of customers. This structure goes beyond storing transactions. It provides context for customer journeys, making it easier to deliver personal and relevant services.
Unlike general customer relationship management systems, the Financial Services Cloud uses a model that reflects how people, households, and businesses interact with financial products. This approach improves data accuracy and ensures that advisors and service teams work with complete information.
The goal of this article is to explain the model clearly. We will review the Financial Services Cloud entities and relationships, explore the core objects in the Financial Services Cloud data model, examine how FSC data model assets, liabilities, and accounts are tracked, and describe how Salesforce models customer relationships in FSC. This guide will also include practical details to help you understand how Salesforce structures financial data.
For institutions starting digital transformation projects, exploring our Salesforce Implementation Services can provide practical steps for adopting this model effectively.
Why the Financial Services Cloud Data Model Matters
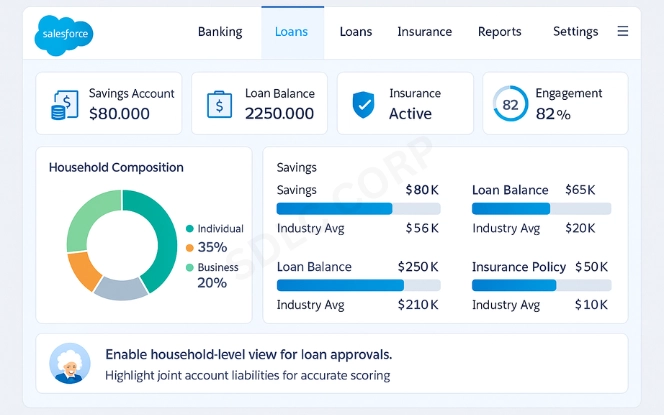
Financial data is complex. A single customer may have checking accounts, credit cards, mortgages, and insurance policies. They may also be part of a household with shared investments or connected to a business with loans and assets. Traditional CRM structures often struggle to capture this complexity.
The Financial Services Cloud data model is built to handle these realities. It ensures that institutions can:
- Consolidate personal and household financial profiles.
- Map accounts to both individuals and groups.
- Track obligations and assets with accuracy.
- Support regulatory requirements for recordkeeping.
- Enable advisors to make better recommendations.
With this framework, financial professionals move beyond raw data. They can interpret relationships and deliver personalized service that aligns with a client’s financial goals.
Key Features of the Data Model
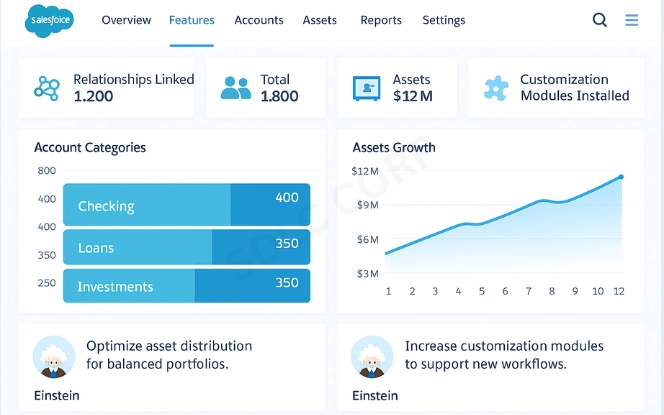
The data model in Financial Services Cloud organizes information into layers. At its core, it relies on objects, relationships, and financial product data. This makes it easier to structure and analyze client records.
Central Characteristics
Multi-Level Relationships
Customers can belong to households, which link them to family members and shared financial activities. Businesses can also connect through ownership or partnership records.Unified Account Structures
Accounts are not limited to a single view. The model allows mapping to individuals, households, and organizations. This flexibility reflects real-world finance.Comprehensive Financial Picture
Both assets and liabilities are tracked, offering insight into net worth. Advisors gain a complete perspective on client financial health.Customizable Objects
Institutions can extend the model to match specific industry needs. Whether it’s wealth management, retail banking, or insurance, the framework adapts.
Financial Services Cloud Entities and Relationships
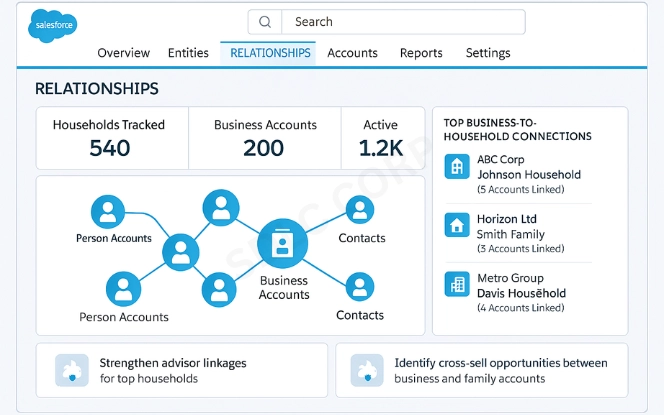
The foundation of the Salesforce Financial Services Cloud is its entity-relationship model. Entities are the major categories of information, while relationships define how those entities connect.
- Person Accounts: Represent individual customers with demographic details, financial accounts, and transaction history.
- Households: Group individuals who share financial responsibilities, like spouses or family members.
- Business Accounts: Capture company data such as credit lines, assets, and ownership structures.
- Relationships: Define how people and businesses are connected with parent-child, employer-employee, investor-client, or joint account holder.
- Contacts: Provide direct information for communication. Each contact ties back to person or business accounts.
Understanding these Financial Services Cloud entities and relationships is essential. They establish the base for customer profiles and allow institutions to link financial activity across individuals and organizations. For detailed insights into similar transformation strategies, visit our CRM Data Migration Solutions page.
Core Objects in Financial Services Cloud Data Model
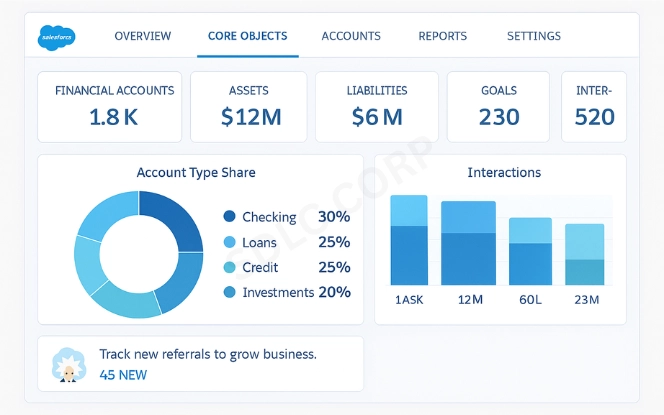
At the heart of the platform are core objects in the Financial Services Cloud data model. These objects represent the building blocks of client data.
- Financial Accounts: Cover banking products like savings, loans, and credit lines.
- Assets and Liabilities: Identify owned property, investments, and debts.
- Goals: Capture financial objectives such as retirement savings or mortgage payoff.
- Interactions: Record meetings, calls, and communications with clients.
- Referrals: Manage leads and opportunities from within or outside the organization.
- Relationships and Roles: Assign specific roles such as “Financial Advisor” or “Joint Account Holder.”
Each object connects to others, creating a network of information. This ensures that when an advisor opens a record, they see the complete context and not just isolated data points. For businesses working with sensitive information, our Financial Data Management Services offer guidance on best practices for secure object handling.
FSC Data Model Assets, Liabilities, and Accounts
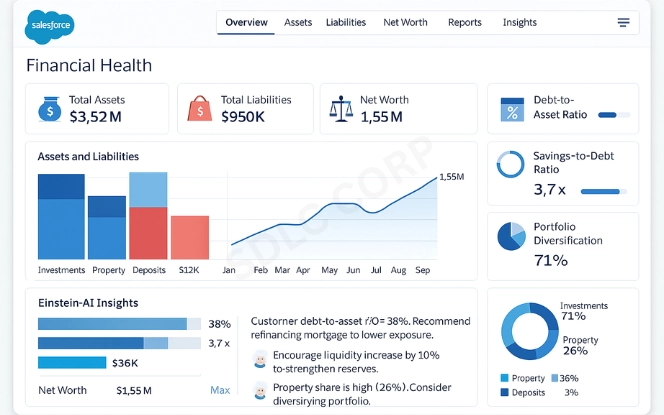
One of the most practical aspects of the data model is its ability to organize FSC data model assets, liabilities, and accounts. These components create a snapshot of financial health.
- Assets: Includes deposits, investment portfolios, properties, and other owned resources.
- Liabilities: Covers mortgages, personal loans, business debt, and obligations.
- Accounts: Provide the framework for tracking financial instruments at both personal and institutional levels.
The data model connects these elements to both individuals and households. For example, a mortgage may appear as a liability for one person but as a joint liability for a household. Similarly, investment portfolios may be shared across family members. This layered view ensures accurate net worth calculations. Organizations can also explore our Enterprise Asset Management Solutions to understand how these principles extend beyond Salesforce.
How Salesforce Models Customer Relationships in FSC
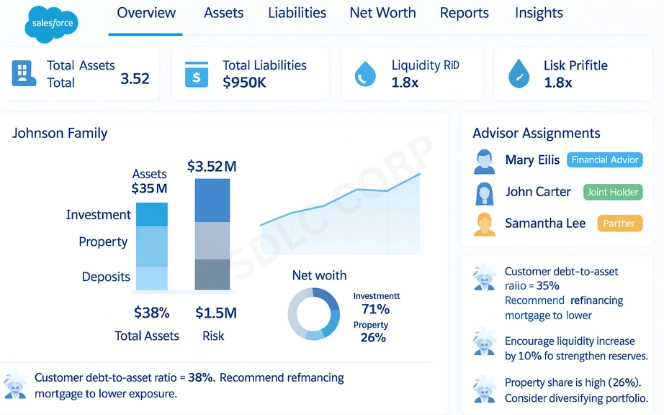
Relationships are the defining feature of this platform. Knowing how Salesforce models customer relationships in FSC helps institutions offer more meaningful interactions.
- Household Relationships: Identify how spouses, parents, and children share accounts or goals.
- Business Relationships: Map investors, partners, and stakeholders to organizations.
- Advisor Assignments: Show which financial professionals are linked to clients and households.
- Cross-Product Links: Connect insurance, loans, and investments to reveal how products affect each other.
By organizing these relationships, Salesforce allows advisors to act as trusted partners. They can anticipate client needs and align financial products with life events.
Benefits for Financial Institutions
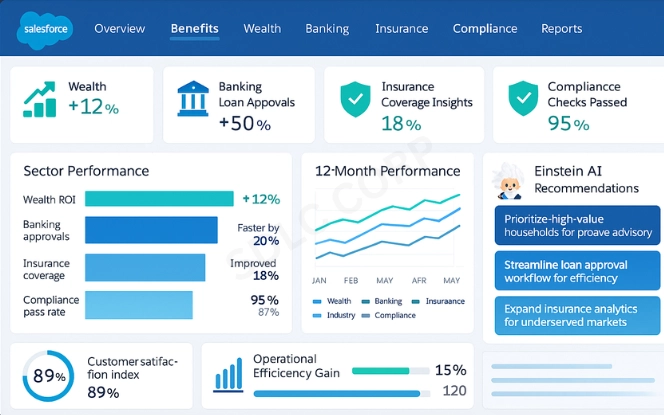
The model delivers clear benefits across the financial services industry:
- Wealth Management: Advisors can view full portfolios and understand household financial goals.
- Banking: Institutions can streamline loan approvals by analyzing liabilities and income together.
- Insurance: Carriers can track customer policies alongside other financial assets.
- Compliance: Records of assets, liabilities, and relationships support regulatory obligations.
The result is stronger customer trust and more effective client management.
Real-World Use Cases
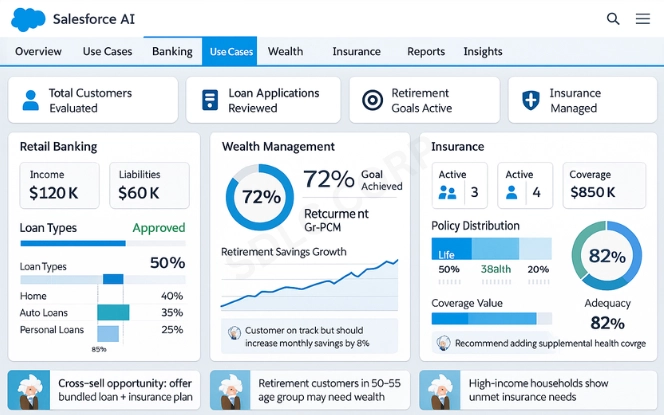
- Retail Banking Example: A couple applies for a home loan. Their household record shows joint income, existing liabilities, and shared assets. The advisor quickly assesses loan eligibility.
- Wealth Management Example: A client sets a retirement goal. Their profile already includes investment accounts, property values, and liabilities. The advisor suggests a savings strategy aligned with that goal.
- Insurance Example: A family adds an insurance policy. The system links it to their existing household accounts and assets, providing a complete view of coverage.
These scenarios demonstrate how the Salesforce Financial Services Cloud Data Model supports decision-making in real time.
Challenges in Implementation
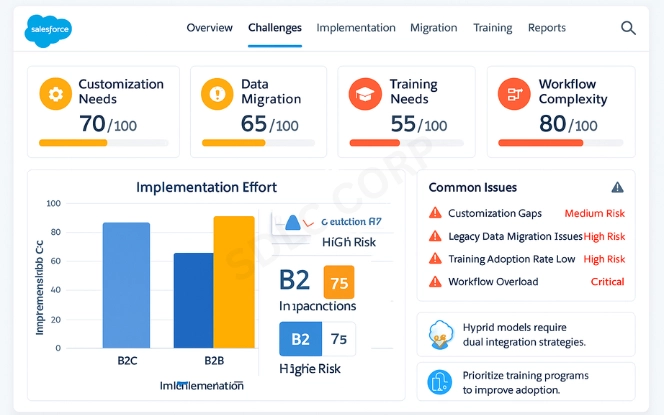
While powerful, the model does present challenges:
- Customization Needs: Institutions often need to tailor objects and workflows to match unique processes.
- Data Migration: Moving legacy data into Salesforce requires careful mapping.
- User Training: Staff must learn how to navigate objects and relationships.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Financial products and compliance rules evolve, requiring updates.
Institutions that invest in planning and training overcome these challenges and achieve long-term benefits.
Future Outlook
The future of the Salesforce Financial Services Cloud Data Model will emphasize automation and intelligence. Einstein AI and predictive analytics will deliver insights into customer behavior. Institutions will also see more integrations with external systems, allowing real-time updates from banking platforms and insurance carriers.
Cloud-based compliance tools will ensure that recordkeeping stays aligned with new regulations. As financial technology evolves, the FSC data model will continue to expand, offering broader coverage of digital wallets, cryptocurrencies, and new asset classes.
Conclusion
The Salesforce Financial Services Cloud Data Model provides financial institutions with a framework that matches real-world needs. It organizes people, households, and businesses while tracking assets, liabilities, and accounts. By structuring Financial Services Cloud entities and relationships, institutions gain clarity on customer journeys. With core objects in the Financial Services Cloud data model, they capture the details that matter. Through FSC data model assets, liabilities, and accounts, they calculate financial health. And by learning how Salesforce models customer relationships in FSC, they create stronger connections with clients.
If your organization is exploring Salesforce solutions, Contact us SDLC Corp for expert advice and implementation support. Our team can design a model tailored to your institution’s needs.
For those looking to enhance digital transformation, Hire Salesforce Developer with SDLC Corp and leverage intelligent automation alongside the Financial Services Cloud. With the right foundation, you can improve client experiences and prepare for the future of finance.
FAQs
What Is The Salesforce Financial Services Cloud Data Model?
The Salesforce Financial Services Cloud Data Model is the framework used to organize client information, accounts, assets, and relationships. It helps financial institutions create a single source of truth for customer data.
How Do Financial Services Cloud Entities And Relationships Work?
Financial Services Cloud entities and relationships define how people, households, and businesses are linked. This includes individuals with personal accounts, households with shared assets, and companies connected through ownership or contracts.
What Are The Core Objects In Financial Services Cloud Data Model?
The core objects in the Financial Services Cloud data model include financial accounts, assets, liabilities, goals, interactions, and referrals. These objects work together to build a complete financial profile for each customer.
How Are Assets, Liabilities, And Accounts Managed In FSC Data Model?
The FSC data model assets, liabilities, and accounts section helps track customer net worth. Assets like investments are linked with liabilities such as mortgages, while accounts provide a structured record of all products.
How Salesforce Models Customer Relationships In FSC?
Understanding how Salesforce models customer relationships in FSC shows how connections between households, businesses, and advisors are mapped. This allows institutions to deliver personalized services based on accurate relationship data.