Introduction
Hierarchy of Stablecoins
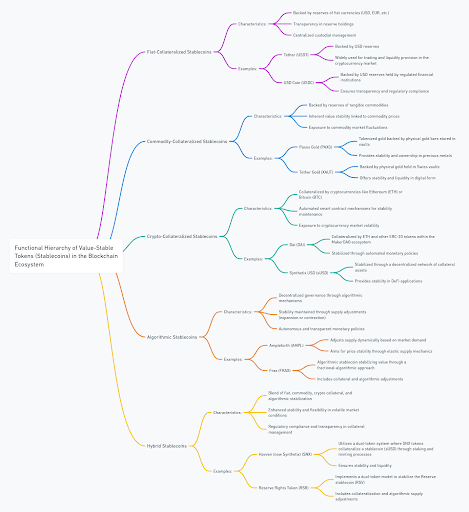
1. Fiat-Collateralized Stablecoins
- haracteristics:
- Backed by reserves of fiat currencies (USD, EUR, etc.).
- Transparent reserve management.
- Centralized custodial oversight.
- Examples:
- Tether (USDT): Backed by USD reserves, widely used for trading and liquidity provision in the cryptocurrency market.
- USD Coin (USDC): Backed by USD reserves held by regulated financial institutions, ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance.
2. Commodity-Collateralized Stablecoins
Stablecoins backed by reserves of commodities such as precious metals (e.g., gold, silver) or other commodities like oil. These stablecoins derive stability from the underlying tangible asset.
- Characteristics:
- Backed by reserves of tangible commodities.
- Stability linked to commodity prices.
- Exposure to commodity market fluctuations.
- Examples:
- Paxos Gold (PAXG): Tokenized gold backed by physical gold bars stored in vaults, providing stability and ownership in precious metals.
- Tether Gold (XAUT): Backed by physical gold held in Swiss vaults, offering stability and liquidity in digital form.
3. Crypto-Collateralized Stablecoins
Stablecoins collateralized by other cryptocurrencies or crypto assets, using over-collateralization to maintain stability and secure smart contract mechanisms.
- Characteristics:
- Collateralized by cryptocurrencies like Ethereum (ETH) or Bitcoin (BTC).
- Automated smart contract mechanisms for stability maintenance.
- Exposure to cryptocurrency market volatility.
- Examples:
- Dai (DAI): Collateralized by ETH and other ERC-20 tokens within the MakerDAO ecosystem, stabilized through automated monetary policies.
- Synthetix USD (sUSD): Stabilized through a decentralized network of collateral assets, providing stability in DeFi applications.
4. Algorithmic Stablecoins
Stablecoins governed by algorithmic protocols adjusting token supply based on demand and market conditions, without direct backing by fiat or assets.
- Characteristics:
- Decentralized governance through algorithmic mechanisms.
- Stability maintained through supply adjustments (expansion or contraction).
- Autonomous and transparent monetary policies.
- Examples:
- Ampleforth (AMPL): Adjusts supply dynamically based on market demand, aiming for price stability through elastic supply mechanics.
- Frax (FRAX): Algorithmic stablecoin stabilizing value through a fractional-algorithmic approach, with collateral and algorithmic adjustments.
5. Hybrid Stablecoins
Stablecoins combining characteristics of multiple stability models (e.g., fiat-backed and algorithmic), offering diversified stability mechanisms and risk management strategies.
- Characteristics:
- Blend of fiat, commodity, crypto collateral, and algorithmic stabilization.
- Enhanced stability and flexibility in volatile market conditions.
- Regulatory compliance and transparency in collateral management.
- Examples:
- Havven (now Synthetix) (SNX): Utilizes a dual-token system where SNX tokens collateralize a stablecoin (sUSD) through staking and minting processes, ensuring stability and liquidity.
- Reserve Rights Token (RSR): Implements a dual-token model to stabilize the Reserve stablecoin (RSV) through collateralization and algorithmic supply adjustments.
stable coin development solution Just @ $5000

Characteristics of Stablecoins
How Stablecoins Work
- Fiat-Collateralized: Backed by reserves of fiat currencies held in bank accounts. Each stablecoin issued is backed 1:1 by the corresponding fiat currency.
- Commodity-Collateralized: Backed by reserves of commodities like gold or other precious metals, ensuring stability through tangible asset backing.
- Crypto-Collateralized: Collateralized by other cryptocurrencies or crypto assets, using over-collateralization to maintain stability and secure smart contract mechanisms.
- Algorithmic Control: Stabilized through algorithmic protocols adjusting token supply based on market demand and conditions, without direct asset backing.
Functionality of Stablecoins
2. Store of Value: Investors use stablecoins to preserve value during market downturns or periods of cryptocurrency price volatility.
Use Cases of Stablecoins
Examples of Stablecoins
- Tether (USDT): Backed by USD reserves, widely used for trading and liquidity provision in the cryptocurrency market.
- USD Coin (USDC): Backed by USD reserves held by regulated financial institutions, ensuring transparency and regulatory compliance.
- Dai (DAI): Collateralized by Ethereum (ETH) and other assets within the MakerDAO ecosystem, stabilized through automated smart contracts.
stablecoin development services Just @ $5000

Why Choose SDLC CORP?
- Expertise: Deep understanding of blockchain technology and tokenization trends.
- Custom Solutions: Tailored token development aligned with client-specific requirements.
- Security: Emphasis on robust security measures and compliance with industry standards.
- Innovation: Continuous innovation in tokenomics and decentralized technologies.
- Client-Centric Approach: Dedicated support and transparent communication throughout the development lifecycle.
Partner with SDLC CORP for cutting-edge crypto token solutions that drive growth, innovation, and value creation in the digital economy. Contact us today to explore how we can transform your blockchain vision into reality.
sablecoin development Just @ $5000

Conclusion
Stablecoins represent a significant advancement in digital asset management, providing stability, liquidity, and reliability in cryptocurrency transactions and investments. Their characteristics, operational mechanisms, functionalities, and diverse use cases illustrate their pivotal role in cryptocurrency adoption, decentralized finance, and global financial inclusion. Understanding stablecoins helps stakeholders navigate digital asset strategies, mitigate volatility risks, and capitalize on innovative financial technologies in the evolving blockchain ecosystem.



