Introduction
Environmental challenges such as climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss require advanced solutions beyond traditional methods. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful tool for addressing these issues. By leveraging data from satellites, IoT sensors, and advanced algorithms, AI for environmental management enables predictive insights, real-time monitoring, and smarter decision-making.
Partnering with an AI development company enables organizations, governments, and researchers to create customized solutions that conserve resources, mitigate risks, and safeguard ecosystems. From air quality monitoring to optimizing renewable energy, AI is shaping a new era of environmental innovation.
Role of AI in Environmental Management
AI enhances environmental management by predicting risks, monitoring ecosystems, supporting policies, and optimizing resources for sustainability.
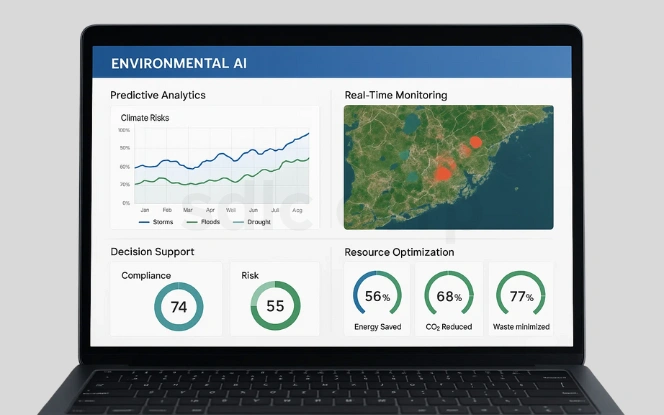
- Predictive analytics for climate risks: Forecast extreme weather events such as floods, storms, and droughts.
- Real-time monitoring: Collect and process environmental data from IoT and satellite sources.
- Decision support systems: Support policymakers by analyzing compliance and risk data.
- Resource optimization: Cut emissions, save energy, and minimize waste across industries.
Technical Approaches in AI for Environment

AI relies on various technical methods that process environmental data, detect patterns, and deliver actionable insights. These approaches enable accurate monitoring, forecasting, and sustainable decision-making.
- CNNs for satellite image classification and deforestation detection.
- LSTMs for forecasting energy demand and weather patterns.
- Gradient Boosting (XGBoost, LightGBM) for carbon accounting.
Computer Vision:
- Detects pollution hotspots from drone and satellite imagery.
- Tracks biodiversity with camera traps and acoustic monitoring.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Extracts rules from environmental regulations.
- Automates compliance and reporting tasks.
Reinforcement Learning:
- Optimizes energy in smart grids and buildings.
- Improves logistics for waste management and recycling.
Key Applications of AI in Environmental Management
Environmental management relies on large datasets from sensors, satellites, climate models, and field reports. AI systems help analyze this data to support monitoring, forecasting, and policy planning. In many initiatives, AI development services are used to integrate environmental data streams and enable evidence-based decision-making.
Climate Change Mitigation
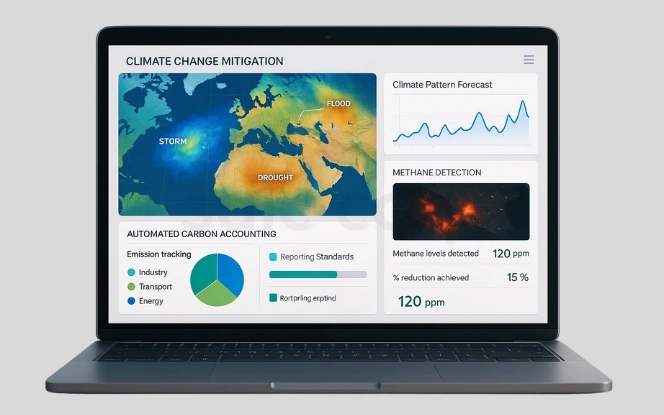
- Weather and climate pattern forecasting
AI models analyze historical and real-time data to predict floods, storms, and droughts, supporting early disaster response. - Automated carbon accounting
Machine learning systems track and calculate emissions, helping organizations comply with global reporting standards. - Methane detection from industrial and natural sources
AI-powered satellite imagery identifies leaks quickly, reducing one of the most harmful greenhouse gases.
Sustainability Practices
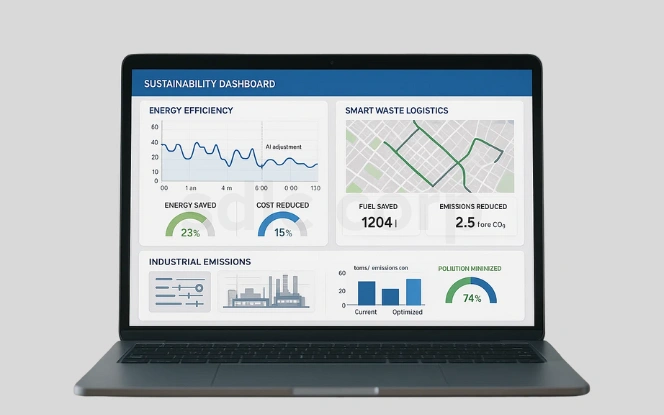
- Energy efficiency in buildings and factories
AI adjusts energy use in real time, lowering consumption and operational costs. - Smart waste management logistics
Predictive systems optimize collection routes, cutting fuel use and emissions. - Reduced industrial emissions via process automation
AI monitors and fine-tunes manufacturing processes to minimize pollution and waste.
Environmental Monitoring
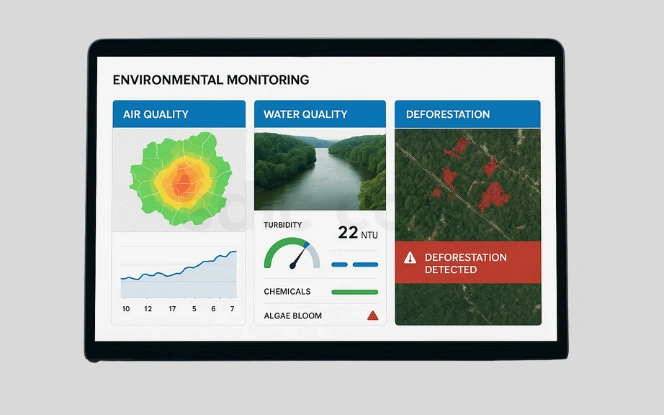
- Air quality prediction using ground and satellite data
AI combines sensor and satellite data to forecast pollution levels, improving public health planning. - Water quality tracking for turbidity and contamination
Machine learning detects algae blooms and chemical changes, protecting aquatic ecosystems. - Deforestation detection with real-time alerts
Computer vision scans satellite images, flagging illegal logging activities for rapid enforcement.
Conservation and Biodiversity
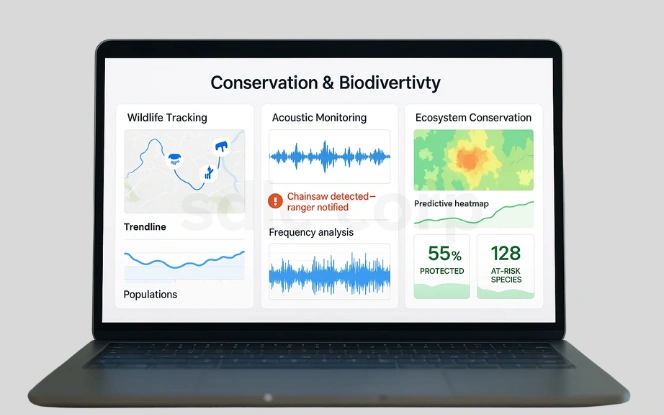
- Wildlife tracking with AI-enabled drones and sensors
AI automates species identification, helping conservationists monitor populations more efficiently. - Acoustic monitoring for poaching detection
AI processes forest sounds to detect gunshots or chainsaws, alerting rangers in real time. - Ecosystem conservation through predictive modeling
Predictive analytics identify at-risk habitats, enabling proactive protection strategies.
Smart Cities and Renewable Energy

- Traffic flow optimization for emission reduction
AI adjusts traffic signals dynamically, reducing congestion and vehicle emissions. - Solar and wind energy forecasting
Machine learning predicts renewable energy output, improving grid stability. - Grid storage and dispatch optimization
Reinforcement learning manages energy storage and distribution, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Benefits of AI for Environmental Management
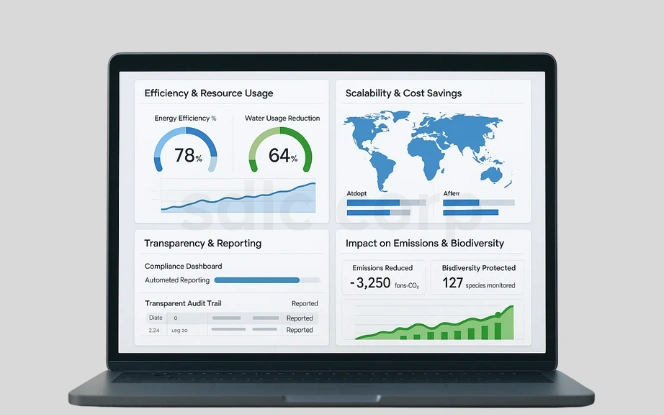
AI provides measurable advantages in tackling environmental challenges by improving efficiency, lowering costs, and enabling sustainable practices across industries and ecosystems.
- Improved efficiency in energy and resource usage.
- Scalability across global ecosystems and industries.
- Cost savings from optimized logistics and processes.
- Transparency in monitoring and reporting.
- Measurable impact on emissions reduction and biodiversity protection.
Challenges in Adopting AI for Environment
Despite its potential, the adoption of AI in environmental management faces significant hurdles, ranging from technical and financial barriers to ethical concerns.
- High infrastructure and implementation costs.
- Gaps in reliable environmental datasets.
- Risk of bias in AI models across diverse ecosystems.
- Ethical challenges, including surveillance and privacy issues.
Reducing the Environmental Footprint of AI
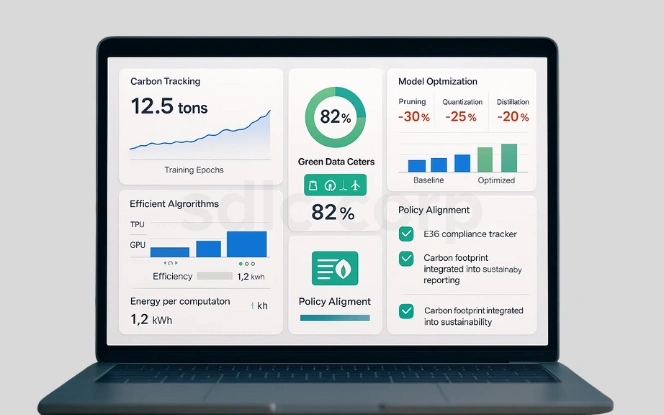
While AI contributes to environmental protection, it also consumes significant energy. Addressing AI’s environmental impact is essential.
- Carbon Tracking: Tools like CodeCarbon monitor emissions during model training and deployment.
- Model Optimization: Techniques such as pruning, quantization, and distillation reduce computational load.
- Green Data Centers: Running AI workloads on cloud providers powered by renewable energy.
- Efficient Algorithms: Adoption of low-energy architectures and hardware acceleration (e.g., TPUs, GPUs).
- Policy Alignment: Including AI’s carbon footprint in sustainability reporting and ESG frameworks.
Strategic Future Outlook
The future of AI in environmental management will focus on responsible adoption, greater transparency, and scalable solutions to address global sustainability challenges.
- Broader adoption of carbon-aware AI practices.
- Expansion of open, standardized environmental datasets.
- Integration of blockchain for transparent emissions tracking.
- Stronger governance and MLOps frameworks for responsible deployment.
Advisory and Governance for Environmental AI
Environmental AI systems often influence public policy and regulatory decisions. Governance frameworks help ensure transparency, accountability, and scientific integrity. An AI consulting company may support organizations in defining oversight mechanisms and aligning AI usage with environmental regulations.
Enterprise-Scale Platforms for Environmental Intelligence
Large organizations and agencies manage environmental data across regions and ecosystems. Enterprise-scale platforms centralize analytics while supporting localized insights. Architectural practices used by an enterprise AI development company are often referenced when designing scalable environmental intelligence systems.
Conclusion
AI for environmental management is no longer experimental; it is essential. With applications in climate change adaptation, pollution control, biodiversity conservation, and renewable energy, AI is driving measurable sustainability outcomes. The next phase of progress lies in scaling adoption while actively reducing the environmental footprint of AI itself. Partnering with the right technology partner or choosing to hire AI developers ensures organizations can implement responsible innovation that supports long-term ecological integrity and global climate goals.
Related Blogs You Should Explore:-
FAQ'S
How Does Ai Support Environmental Management?
AI supports environmental management by forecasting climate risks, monitoring air and water quality, optimizing resource usage, and improving compliance with environmental regulations.
What Are The Main Applications Of Ai In Environmental Management?
Key applications include climate change mitigation, sustainability practices, pollution control, renewable energy optimization, smart city development, and biodiversity conservation.
Can Ai Help Reduce Carbon Emissions?
Yes, AI reduces emissions by improving energy efficiency, optimizing industrial processes, forecasting renewable energy, and detecting methane leaks through satellite data.
What Challenges Exist In Adopting Ai For Environment?
Challenges include high infrastructure costs, gaps in reliable environmental data, bias in AI models, and ethical concerns related to surveillance and privacy.
How can the environmental footprint of AI be reduced?
The footprint can be reduced through model optimization techniques such as pruning and quantization, using low-carbon data centers, and tracking emissions with tools like CodeCarbon.
What Is The Future Of Ai In Environmental Management?
The future will focus on carbon-aware AI practices, open datasets, blockchain-based transparency, and stronger governance frameworks to ensure responsible and sustainable deployment.