Introduction
AI for Government refers to the application of technologies such as machine learning, automation, and data analytics to create smarter and more efficient governance systems. It enables policymakers to analyze large datasets, make informed decisions, and deliver faster, more transparent services to citizens. For the public, this means reduced delays, better access to resources, and improved quality of life.
Across the world, AI for Government is driving digital transformation. The United States uses it for healthcare and fraud detection, the European Union emphasizes ethical AI and data protection, and China invests in smart governance. Developing nations are leveraging AI to improve agriculture, education, and disaster management. This growing global trend shows that AI is now a key force shaping the future of governance. To explore how AI can empower public institutions.
AI Applications Across Government Operations
Government agencies manage large volumes of data related to public services, infrastructure, policy, and compliance. AI systems help analyze this data to improve planning, service delivery, and operational efficiency. In many public-sector initiatives, AI development services are used to integrate analytics into existing government systems while maintaining transparency and accountability.
1. Benefits of AI for Citizens and Public Services
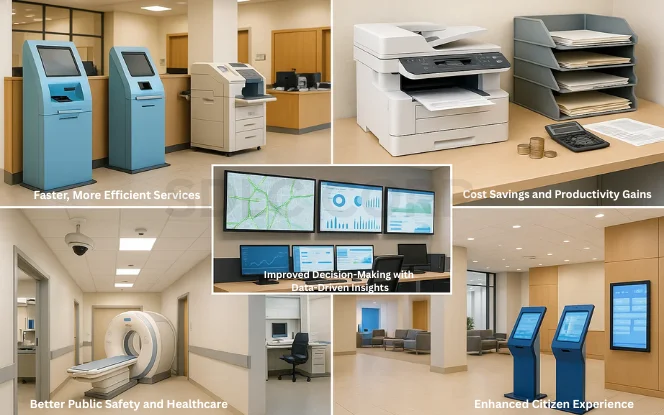

AI is transforming how governments deliver services and interact with citizens. By integrating automation, predictive analytics, and smart tools, public services are becoming more efficient, cost-effective, and responsive to people’s needs.
Faster, More Efficient Services
AI accelerates routine government processes like issuing licenses, processing tax returns, and verifying documents reducing wait times and ensuring timely delivery of citizen services.. Automation reduces long wait times and ensures that citizens get timely services without unnecessary delays.
Cost Savings and Productivity Gains
Governments face constant pressure to do more with limited resources. AI helps reduce administrative costs by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on critical responsibilities. This not only saves taxpayer money but also boosts overall productivity.
Improved Decision-Making with Data-Driven Insights
Policy decisions backed by data are more accurate and effective. AI tools analyze massive datasets from traffic patterns to healthcare trends providing governments with valuable insights. This leads to smarter policies that address real needs rather than relying on guesswork.
Better Public Safety and Healthcare
AI-powered surveillance, predictive policing, and cybersecurity systems enhance safety for citizens. In healthcare, AI supports early disease detection, personalized treatments, and efficient hospital management—improving outcomes and saving lives.
Enhanced Citizen Experience
Modern citizens expect digital-first, hassle-free services. AI-driven chatbots, self-service portals, and personalized communication ensure smoother interactions between governments and the public. This builds trust and makes governance more citizen-centric.
2. AI Use Cases in Government by Sector

AI is being applied across multiple sectors of government, reshaping how public services are delivered and managed. Each area benefits from unique applications that improve efficiency, safety, and citizen well-being.
Healthcare & Public Health
Governments are using AI to strengthen healthcare systems and improve patient outcomes.
- Disease Detection – AI tools can analyze scans and lab reports to identify early signs of illnesses like cancer or heart disease.
- Pandemic Response – During global health crises, AI models help track infection rates and predict hotspots.
- Resource Allocation – Hospitals and clinics use AI to manage staff schedules, medical supplies, and patient flow.
Transportation & Smart Infrastructure
AI helps governments build smarter, safer, and more sustainable cities.
- Traffic Management – AI systems monitor road congestion and optimize traffic light patterns.
- Public Transit – Smart algorithms improve bus and train schedules based on real-time demand.
- Infrastructure Maintenance – AI predicts when bridges, roads, or utilities need repair, preventing costly failures.
Security, Law Enforcement & Defense
AI strengthens national security and enhances public safety.
- Predictive Policing – Algorithms analyze crime data to identify high-risk areas.
- Surveillance – Facial recognition and video analytics help law enforcement monitor public spaces.
- Defense Applications – Military organizations use AI for cyber defense, threat detection, and autonomous systems.
Education, Social Services & Environment
AI ensures that education and social welfare programs reach more people while promoting sustainability.
- Personalized Learning – AI tailors education materials to suit individual student needs.
- Social Services – Governments automate welfare distribution to reduce fraud and ensure fairness.
- Environmental Protection – AI monitors pollution, predicts natural disasters, and supports climate-change initiatives.
3. Case Studies & Global Examples

Different countries are leading the way in adopting AI for governance. Their experiences highlight how technology can enhance public services, improve efficiency, and strengthen citizen trust.
Estonia – Digital Government Pioneer : Estonia is recognized as one of the most digitally advanced nations.
- Citizens use e-residency, digital IDs, and AI-powered platforms for healthcare, taxes, and voting.
- AI chatbots handle public queries, reducing administrative workload.
- The country’s small size and proactive policies make it a testing ground for AI-driven governance.
- Takeaway: Estonia proves that even small nations can lead the world by embracing digital-first governance.
Singapore – Smart Nation & AI Assistants : Singapore has launched its Smart Nation initiative to transform governance.
- Virtual assistants like “Ask Jamie” answer citizen queries on government websites.
- AI-powered traffic systems optimize road usage and reduce congestion.
- The government invests heavily in AI research to support long-term sustainability.
- Takeaway: Singapore shows how AI can make governance citizen-friendly while supporting long-term urban sustainability.
United States – Federal AI Use Cases : The U.S. integrates AI into multiple government functions.
- Healthcare – AI helps the FDA analyze drug approvals and monitor safety.
- National Security – AI enhances cybersecurity, intelligence analysis, and defense strategies.
- Public Services – Agencies use AI to detect tax fraud and improve disaster response.
- Takeaway: The U.S. demonstrates how large governments can deploy AI at scale across healthcare, security, and public services.
India – AI for Social Welfare : India uses AI to improve accessibility and social development.
- AI supports crop monitoring and early-warning systems for farmers.
- Welfare distribution systems are automated to reduce fraud and ensure fairness.
- Healthcare initiatives use AI for rural diagnostics and telemedicine.
- Takeaway: India highlights how AI can drive inclusive growth and support large rural populations with limited resources.
United Kingdom – National AI Strategy : The UK emphasizes ethical and transparent AI adoption.
- The National AI Strategy sets guidelines for responsible AI development.
- AI is used in public healthcare (NHS) for early disease detection.
- Smart city projects leverage AI for traffic, energy, and sustainability.
- Takeaway: The UK shows that strong policy frameworks are essential to ensure AI adoption remains ethical and transparent.
China – AI at Scale & Regulation : China is one of the largest investors in AI for governance.
- AI-driven surveillance systems monitor public safety across major cities.
- Smart city projects use AI to manage traffic, pollution, and energy grids.
- The government is also establishing strict AI regulations to balance innovation with control.
- Takeaway: China illustrates the power—and challenges—of deploying AI at massive scale under tight government regulation.
4. Digital Twins vs. Traditional Simulation in Governance

Governments often rely on simulations to predict outcomes and plan policies. With the rise of AI, digital twins—virtual replicas of real-world systems—are taking simulations to the next level. They allow governments to test decisions in a risk-free environment before implementing them in reality.
Definition & Differences
- Traditional Simulation –Relies on fixed models and assumptions to predict outcomes. These models are static, limited in scope, and less adaptive to real-world changes.
- Digital Twins – AI-driven virtual replicas that continuously update in real time. They mirror real systems (such as cities, infrastructure, or healthcare networks) and adapt as conditions change.
Checkout : Digital Twins in AI
Key Advantages of AI-Driven Digital Models
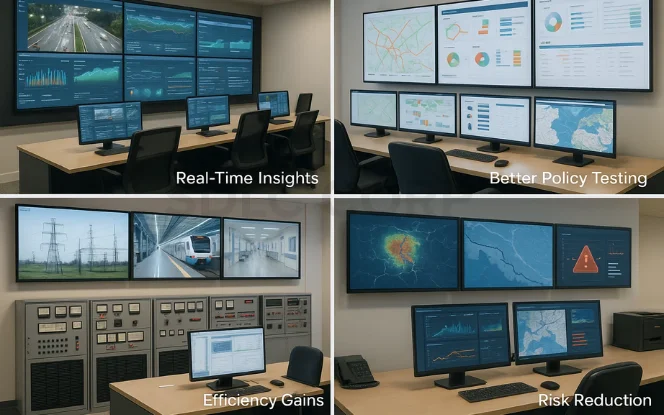

- Real-Time Insights – Digital twins evolve with live data, giving governments up-to-date predictions.
- Better Policy Testing – Authorities can run multiple scenarios to see the impact before rolling out decisions.
- Efficiency Gains – Helps optimize resources such as energy, transportation, and healthcare.
- Risk Reduction – Identifies potential failures or crises early, allowing proactive responses.
Comparison: Traditional Simulation vs. AI-Enabled Digital Twins
| Aspect | Traditional Simulation | AI-Enabled Digital Twins |
|---|---|---|
| Data Input | Based on fixed, historical datasets | Continuously updated with real-time data |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability | Highly adaptive and scalable |
| Accuracy | Dependent on initial assumptions | Improves continuously with AI learning |
| Use Cases | Basic forecasting and planning | Smart cities, healthcare systems, infrastructure, crisis management |
| Decision Support | Provides estimates | Provides predictive, real-time, and actionable insights |
5. Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns

While AI in government promises efficiency and innovation, it also raises serious ethical and privacy challenges. If not addressed properly, these risks can weaken citizen trust and create long-term governance issues.
Privacy & Surveillance Risks
- Risk: Excessive data collection or misuse can lead to intrusive surveillance.
- Impact: Threatens individual freedoms, civil rights, and public trust in government.
Bias and Fairness in Algorithms
- Risk: Historical data may embed hidden biases in AI models.
- Impact: Can result in discrimination in welfare distribution, policing, or hiring practices.
- Related Insight: These same concerns extend to the justice system, where AI adoption is reshaping legal services. Learn more in our article on AI for the Legal Industry: Transforming Law Firms with AI.
Transparency and Accountability
- Risk: “Black-box” algorithms make it difficult to explain AI-driven decisions.
- Impact: Citizens may lose trust if they cannot understand or challenge government actions.
- Further Reading: Learn more in our article on The Role of Blockchain Developers in Digital Government Platforms to see how blockchain can enhance security and accountability in governance.
Cybersecurity Challenges
- Risk: AI systems are high-value targets for cyberattacks.
- Impact: Breaches can expose sensitive data, disrupt essential services, or compromise national security.
Inclusivity & Digital Divide
- Risk: Vulnerable populations without access to digital tools may be left behind.
- Impact: Deepens inequality, reducing the fairness and inclusiveness of public services.
Key Takeaway: Responsible AI in government requires strong safeguards around privacy, fairness, transparency, and inclusivity to maintain citizen trust.
6. Implementation Challenges in Government AI

Adopting AI in government is not just a matter of technology—it requires addressing structural, legal, and cultural barriers. Without proper planning, even the most advanced systems may fail to deliver expected benefits.
- Data Protection Compliance
- Risk: Mishandling sensitive citizen data can result in privacy violations and legal consequences.
- Impact: Non-compliance with data regulations (like GDPR) erodes public trust and can trigger costly penalties.
- Risk: Mishandling sensitive citizen data can result in privacy violations and legal consequences.
- Legacy IT Systems
- Risk: Many agencies still rely on outdated infrastructure, making AI integration complex and expensive.
- Impact: Slow adoption, higher costs, and limited scalability of AI projects.
- Risk: Many agencies still rely on outdated infrastructure, making AI integration complex and expensive.
- Bias Monitoring & Ethical Oversight
- Risk: Algorithms trained on biased datasets may lead to discrimination in services like welfare, hiring, or policing.
- Impact: Unfair outcomes, reputational damage, and loss of citizen confidence in government AI.
- Risk: Algorithms trained on biased datasets may lead to discrimination in services like welfare, hiring, or policing.
- Workforce Skill Gaps
- Risk: The public sector often lacks professionals skilled in AI, data science, and cybersecurity.
- Impact: Reliance on external vendors, slower innovation, and difficulty maintaining AI systems.
- Risk: The public sector often lacks professionals skilled in AI, data science, and cybersecurity.
- Public Trust & Change Management
- Risk: Citizens and employees may resist AI adoption if systems lack transparency or clarity.
- Impact: Low adoption rates, political pushback, and missed opportunities for modernization.
- Risk: Citizens and employees may resist AI adoption if systems lack transparency or clarity.
7. Future Trends of AI in Government

AI in governance is moving from experimentation to large-scale adoption. As technology evolves, governments worldwide are preparing to embed AI deeper into policies, services, and infrastructure. The future will be shaped by both innovation and ethical responsibility.
Accelerating Global Adoption
More countries are integrating AI into healthcare, taxation, urban planning, and defense. Smaller nations are also leveraging AI through international collaborations and cloud-based solutions.
- Timeline Marker: Expected to accelerate steadily through 2025–2027.
Stronger Governance & AI Policy Frameworks
To ensure trust, governments are creating clear policies for ethical AI use. Regulations around privacy, fairness, and accountability will play a central role in global AI governance.
- Timeline Marker: New frameworks expected to be widely adopted between 2026–2028.
Generative AI for Citizen Services
Generative AI will transform how citizens interact with governments. From automated document generation to advanced chatbots handling complex queries, services will become faster and more personalized.
- Timeline Marker: Projected mainstream adoption by 2027.
- Further Reading: For deeper insights, explore our detailed guide on
AI for Policy Simulation & Decision Support
Digital twins and predictive AI models will help governments simulate economic, healthcare, or environmental policies before real-world execution, reducing risks and improving outcomes.
- Timeline Marker: Expected to scale globally between 2027–2029.
Smart Cities and IoT Integration
AI combined with the Internet of Things (IoT) will drive the development of intelligent urban infrastructure. From traffic flow optimization to energy-efficient buildings, governments will rely on AI to build sustainable smart cities.
- Timeline Marker: Broad adoption expected by 2028.
Focus on Ethics, Transparency & Inclusion
As adoption grows, ethical concerns will remain central. Governments will emphasize inclusivity, ensuring AI benefits all citizens, while maintaining transparency in decision-making processes.
- Timeline Marker: Strengthened emphasis projected between 2029–2030.
Overall Key Takeaways
- AI is reshaping governance globally by improving efficiency, transparency, and citizen services.
- Benefits are visible across sectors including healthcare, transportation, education, defense, and smart cities.
- Ethical risks and privacy concerns remain critical, requiring safeguards for fairness, inclusivity, and trust.
- Implementation challenges exist—governments must modernize infrastructure, invest in skills, and ensure compliance.
- The future of AI in governance will be defined by global adoption, stronger policy frameworks, generative AI services, and AI-driven smart cities.
Advisory and Governance for Public-Sector AI
AI adoption in government requires strong governance frameworks to address fairness, accountability, and public trust. Advisory input helps define oversight structures, evaluation standards, and compliance processes. An AI consulting company may support government bodies in designing governance models aligned with public-sector mandates.
Conclusion
AI for Government is revolutionizing how public institutions operate by increasing efficiency, transparency, and citizen satisfaction. From healthcare to education and public safety, AI is helping governments make smarter decisions and deliver better services.
Large government organizations operate across departments, regions, and service areas. Enterprise-scale AI platforms support centralized analytics while allowing local customization and control. Architectural approaches used by an enterprise AI development company are often referenced when building scalable public-sector AI systems.
FAQs
1. What is AI in government?
AI in government refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies—such as automation, data analytics, and machine learning—to improve decision-making, service delivery, and public safety.
2. How does AI benefit citizens in governance?
AI makes public services faster, reduces costs, improves healthcare, enhances security, and creates more transparent, citizen-friendly systems.
3. What are the main challenges of AI in government?
Challenges include data privacy concerns, cybersecurity risks, algorithmic bias, legacy IT systems, and the need to maintain citizen trust.
4. Which countries are leading in AI adoption for governance?
Estonia, Singapore, the United States, India, the United Kingdom, and China are pioneers in implementing AI for governance and public services.
5. What is the future of AI in government?
The future includes generative AI for citizen services, digital twins for policy simulations, smart city integration with IoT, and stronger ethical frameworks to ensure fairness and inclusivity.