Introduction
Smart Cities integrate data, infrastructure, and digital technologies to improve urban life. At the center of this evolution is AI for Smart Cities, which uses real-time data to optimize services, manage resources, and enhance citizen well-being. From predictive energy use and smart water systems to autonomous transport and AI-powered governance, these technologies make cities more sustainable, efficient, and adaptive. As urbanization grows, AI helps forecast demand, streamline resources, and reinforce public safety creating resilient, future-ready urban ecosystems.
In this article, we explore the benefits, applications, and challenges of AI for Smart Cities, and how it is redefining urban living. Learn more about our AI Development Services.
1. What is a Smart City and How Does AI for Smart Cities Fit In?
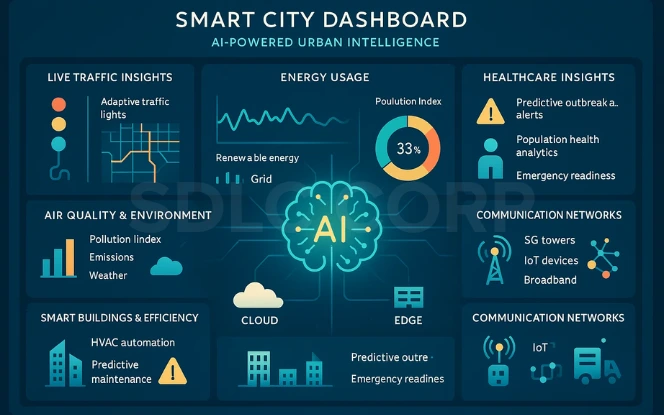
A Smart City is an advanced urban ecosystem where IoT devices, AI-driven platforms, and large-scale data analytics converge to optimize daily operations. While IoT sensors collect massive data streams, AI serves as the brain of Smart Cities, analyzing, interpreting, and transforming this data into actionable strategies. The result is improved urban sustainability, mobility, and intelligent governance.
Core Components of AI-Powered Smart Cities
The ecosystem integrates multiple layers of technology:
- IoT devices: Sensors tracking traffic, pollution, energy usage, and public safety.
- AI-driven decision-making: Algorithms that convert data into real-time insights.
- Data platforms: Cloud and edge systems that store, process, and distribute city-wide data.
- Communication networks: 5G and broadband infrastructure connecting all smart devices.
Together, these elements establish a foundation for intelligent urban management.
AI as the Brain of Smart Cities
AI for Smart Cities acts as the central processing unit that ensures seamless operation across domains. Its role includes:
- Predictive analytics for anticipating energy demand, healthcare needs, and safety risks.
- Automation engines for adaptive traffic lights and public transportation systems.
- Optimization models for resource allocation in energy, water, and waste management.
- Cognitive computing for enhancing decision-making in governance and public policy.
Real-World Applications of AI in Smart City Infrastructure
AI-powered city infrastructure delivers practical benefits across sectors:
- Adaptive traffic lights dynamically adjust signal timings to reduce congestion.
- Smart grids forecast energy loads, integrate renewable power, and prevent outages.
- Predictive healthcare systems analyze population data to identify outbreaks early.
- Urban safety monitoring uses AI to detect anomalies and strengthen surveillance.
- Environmental tracking leverages AI and IoT to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
Resilience and Future Readiness
By merging IoT, AI, and data platforms, cities shift from reactive responses to proactive strategies. This ensures:
- Faster crisis management through early-warning systems.
- Efficient mobility via real-time route optimization.
- Sustainable energy use through smart demand distribution.
- Enhanced citizen services with AI chatbots and digital assistants.
In essence, a Smart City is more than connected infrastructureit is a self-learning ecosystem powered by AI. Through intelligent urban management and AI for Smart Cities, governments create sustainable, scalable, and citizen-centric urban environments.
Smart Buildings and Energy Efficiency
AI is redefining real estate property management through smart building technologies integrated with IoT sensors. These systems optimize resources and improve tenant comfort by enabling:
Real-time energy consumption monitoring and optimization
Automated control of HVAC systems and lighting
Predictive maintenance alerts for equipment and security systems
Personalized tenant experiences through data-driven facility management
AI-powered smart buildings not only reduce operational costs but also support sustainability goals and ESG compliance.
Business Impact: Lower expenses, improved tenant satisfaction, and stronger sustainability credentials.
Explore More : Generative AI for Smart Cities
2. Benefits of AI for Smart Cities
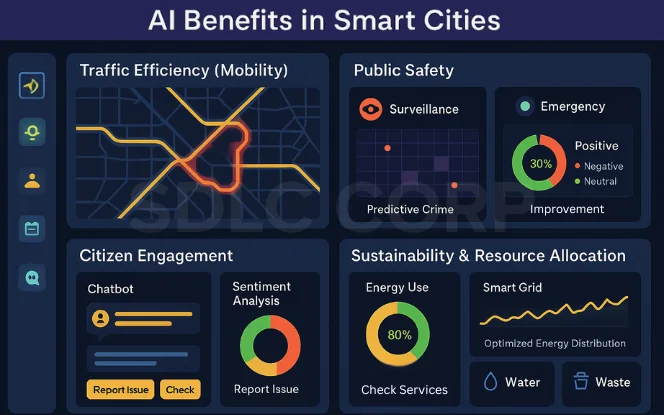
The integration of AI for Smart Cities generates tangible advantages across governance, mobility, sustainability, and citizen experience. By analyzing real-time data and automating decisions, AI systems transform traditional urban infrastructure into adaptive, efficient, and resilient ecosystems. Below are the major benefits that highlight how AI-powered city infrastructure reshapes modern living
AI for Smart Cities in Traffic Efficiency and Congestion Control
AI enhances mobility through predictive analytics and real-time traffic control:
- Adaptive traffic signals reduce waiting times and optimize vehicle flow.
- AI-powered routing directs drivers to less congested roads.
- Predictive congestion modeling prevents bottlenecks before they occur.
- Smart public transport systems adjust schedules dynamically to meet demand.
- Autonomous vehicle integration improves safety and reduces accidents.
Enhancing Public Safety with AI for Smart Cities
AI strengthens surveillance and accelerates emergency interventions:
- Computer vision monitoring detects unusual activities in public spaces.
- Predictive crime mapping identifies hotspots and optimizes police deployment.
- AI-driven emergency dispatching shortens response times.
- Disaster prediction models anticipate floods, fires, or earthquakes.
- IoT-enabled sensors alert authorities to hazardous conditions instantly.
Citizen Engagement through AI-Powered Smart Cities
AI improves the way citizens interact with city services:
- Chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 access to municipal information.
- Smart applications allow real-time reporting of issues such as road damage or waste overflow.
- AI-driven sentiment analysis helps governments understand public concerns.
- Personalized digital services improve inclusivity and accessibility.
- Interactive platforms strengthen transparency and trust in governance.
Resource Optimization and Sustainability in AI-Driven Smart Cities
Sustainability goals become achievable with AI-powered optimization:
- Smart grids balance demand and supply while integrating renewable energy.
- AI in waste management predicts collection routes and reduces fuel consumption.
- Water distribution monitoring prevents leakage and ensures equitable access.
- Energy-efficient building systems lower emissions and reduce costs.
- Predictive maintenance extends the lifespan of infrastructure.
Table: Benefits of AI in Smart Cities (Impact on Urban Life)
| Benefit Area | AI-Driven Impact on Urban Life |
|---|---|
| Traffic Efficiency & Reduced Congestion | Shorter commute times, safer roads, reduced emissions |
| Public Safety & Emergency Response | Faster interventions, proactive crime prevention, disaster resilience |
| Citizen Engagement | Transparent governance, improved inclusivity, accessible digital services |
| Resource Allocation & Sustainability | Lower energy waste, better water use, cleaner environment, cost savings |
3. Key Stakeholders Driving AI for Smart Cities
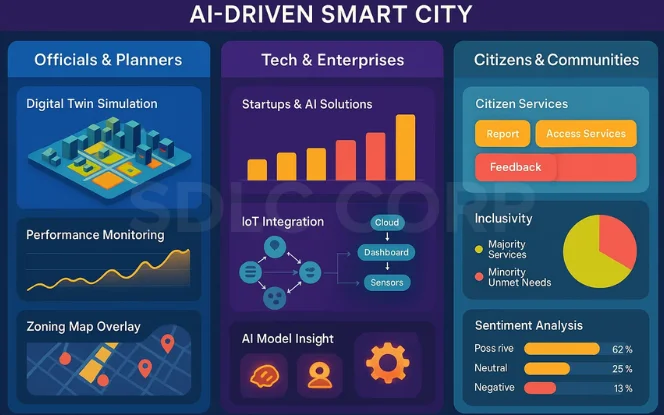
The success of AI for Smart Cities depends on collaboration among diverse stakeholders who shape, implement, and benefit from intelligent systems. Each group plays a critical role in ensuring sustainable growth, efficient governance, and inclusive development.
Urban Planners and Policymakers Using AI for Smart Cities
Urban planners and policymakers act as the strategic drivers of smart city transformation. They rely on AI-powered city infrastructure to make data-informed decisions. Their responsibilities include:
- Data-driven zoning to optimize land use and urban growth.
- Predictive modeling for anticipating transportation, energy, and housing demands.
- Digital twins for simulating infrastructure projects before implementation.
- AI-enabled governance platforms for transparency and resource optimization.
- Performance monitoring dashboards to track city-wide outcomes in real time.
By adopting these tools, officials ensure that planning decisions align with sustainability and mobility objectives.
Learn About : Digital Twins in AI
Role of Technology Professionals and Businesses in AI-Powered Cities
Technology experts and enterprises act as the enablers of intelligent urban management. Their contributions include:
- Startups creating AI-based mobility, energy, and security solutions.
- AI developers building predictive analytics engines and machine learning models.
- Data scientists analyzing urban datasets to generate actionable insights.
- IoT solution providers integrating devices with AI-driven platforms.
- Public–private partnerships enabling cost-effective implementation.
These professionals fuel innovation and ensure scalable, secure deployment of AI for Smart Cities.
How Citizens Benefit from AI for Smart Cities
Citizens represent the most important stakeholders in a smart city ecosystem. Their experiences, feedback, and engagement guide policy and technology development. Key benefits include:
- Better public services delivered efficiently through AI-driven platforms.
- Convenience in daily life with smart mobility, digital payments, and virtual assistants.
- Inclusivity by ensuring equal access to services for marginalized communities.
- Greater transparency through interactive governance portals.
- Participatory engagement in shaping smart city policies.
With citizens at the center, AI-powered city infrastructure ensures that smart cities remain responsive and human-centric.
4. AI for Smart Cities in Traffic Management and Mobility
Efficient mobility is one of the most critical goals of AI for Smart Cities. Urban areas experience growing congestion, longer commutes, and higher emissions as populations rise. By integrating AI-driven solutions with IoT sensors, traffic cameras, and connected vehicles, cities transform transportation networks into adaptive, data-driven systems. The result is smoother traffic flow, shorter commute times, and reduced carbon footprints.
Intelligent Traffic Signals with AI in Smart Cities
AI-powered city infrastructure enables smart traffic lights that adapt dynamically:
- Real-time signal adjustments based on traffic density and pedestrian flow.
- Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication to prioritize emergency vehicles.
- Green wave synchronization for smoother long-distance travel.
- Adaptive algorithms that reduce idle times and lower fuel consumption.
- Continuous monitoring to prevent signal failures.
Case in point: Singapore deploys AI-controlled signals to reduce waiting times by nearly 20%, improving both mobility and environmental outcomes.
Predictive Traffic Analytics in AI for Smart Cities
Predictive modeling allows city officials to anticipate congestion before it occurs:
- AI-driven traffic forecasts analyze historical and real-time data.
- Congestion mapping identifies bottlenecks across critical routes.
- Scenario simulation predicts the impact of accidents or weather conditions.
- Dynamic rerouting directs drivers to alternative paths.
- Long-term modeling supports infrastructure investment decisions.
Los Angeles uses predictive analytics in its Automated Traffic Surveillance and Control (ATSAC) system, cutting congestion significantly.
AI for Smart Cities in Public Transit Optimization
AI enhances intelligent urban management of public transportation by:
- Dynamic scheduling that adapts to passenger demand.
- Route optimization for buses, trams, and metro services.
- Predictive maintenance to prevent service disruptions.
- Integrated ticketing systems for seamless multimodal travel.
- Data-driven planning to expand transit capacity in high-demand areas.
These capabilities reduce operational costs while making public transit more reliable.
Smart Parking and Route Guidance in AI-Enhanced Cities
AI-powered parking systems solve one of the biggest urban challenges space scarcity:
- Real-time parking availability detection via IoT sensors.
- AI-powered route guidance to direct drivers efficiently.
- Dynamic pricing models that optimize space usage.
- Mobile applications offering predictive availability updates.
- Reduced vehicle idling that cuts fuel use and emissions.
By adopting these solutions, cities decrease traffic caused by parking searches—often 30% of total congestion.
Benefits of AI in Traffic Management
- Shorter commute times through optimized signals and routing.
- Reduced emissions due to less idling and congestion.
- Improved road safety with predictive modeling and adaptive controls.
- Higher transit efficiency by aligning services with passenger needs.
- Enhanced citizen satisfaction through faster, cleaner, and more reliable mobility.
5. AI for Smart Cities in Public Safety and Security

Public safety is a cornerstone of AI for Smart Cities. By integrating IoT sensors, computer vision, and predictive analytics, city governments improve emergency response, prevent crime, and safeguard infrastructure. However, balancing surveillance with privacy, as well as addressing algorithmic bias, remains crucial for maintaining fairness and trust in AI-powered city infrastructure.
AI-Powered Smart Surveillance in Cities
AI-powered surveillance systems transform how cities monitor public spaces:
- Computer vision algorithms detect unusual behaviors in real time.
- Facial recognition tools identify potential threats at transportation hubs.
- Crowd density monitoring predicts stampedes or unsafe gatherings.
- Automated alerts notify authorities of suspicious activities.
- Drone-based surveillance provides wide coverage in emergencies.
These solutions enhance security but also raise privacy concerns, requiring strict data governance.
Predictive Policing and AI for Smart Cities
Law enforcement benefits from predictive analytics that forecast risks:
- Crime heat maps identify high-risk neighborhoods.
- Behavioral pattern recognition highlights repeat offenders.
- AI-enabled patrol allocation ensures resource efficiency.
- Data-driven decision-making reduces manual errors.
- Partnerships with IoT systems improve situational awareness.
Still, predictive policing must address algorithmic bias, ensuring fairness and avoiding discrimination.
AI in Emergency Response for Smart Cities
AI strengthens response times during crises:
- Real-time incident tracking enables faster coordination.
- AI-powered dispatching prioritizes medical and rescue units.
- Disaster modeling forecasts floods, earthquakes, or fires.
- Traffic rerouting clears emergency pathways.
- Resource allocation algorithms ensure hospitals and shelters remain prepared.
This proactive approach reduces casualties and enhances public confidence.
Infrastructure Safety Monitoring with AI for Smart Cities
AI safeguards critical infrastructure by predicting risks before failures occur:
- IoT-enabled sensors monitor bridges, tunnels, and pipelines.
- Predictive maintenance prevents catastrophic breakdowns.
- AI anomaly detection identifies structural weaknesses early.
- Energy grid surveillance ensures resilience against cyberattacks.
- Automated inspection drones improve efficiency and worker safety.
By integrating these systems, cities create safer, more resilient environments.
Balancing Safety, Privacy, and Fairness
While AI for Smart Cities enhances public safety, it requires:
- Ethical governance frameworks to balance security with civil liberties.
- Transparency in algorithms to prevent misuse of surveillance data.
- Bias mitigation strategies to ensure fair treatment across communities.
Sustainable safety is achieved only when AI systems combine efficiency with accountability.
Advisory and Governance for Smart City AI
Smart city AI systems often affect public services and citizen data, making governance essential. Advisory input helps define accountability, transparency, and data protection standards. An AI consulting company may support city authorities in establishing governance frameworks and ethical AI policies.
6. Challenges and Ethical Considerations of AI for Smart Cities
While AI for Smart Cities offers transformative benefits, it also presents complex challenges. Ethical concerns, technical limitations, and public acceptance remain key barriers to adoption. Addressing these issues with transparency, accountability, and citizen involvement is critical to building sustainable and inclusive AI-powered city infrastructure.
Data Privacy and Security Challenges in AI for Smart Cities
AI-driven urban systems generate massive amounts of personal and behavioral data. Without strict safeguards, risks emerge:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive citizen data.
- Cyberattacks targeting IoT networks, traffic systems, or smart grids.
- Data misuse for surveillance without proper oversight.
- Cross-border data flows that complicate compliance.
- GDPR violations if privacy rights are not respected.
Cities must adopt encryption, anonymization, and compliance frameworks such as GDPR to safeguard trust.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
Bias in AI systems undermines equitable urban governance:
- Discriminatory policing models targeting certain communities.
- Biased facial recognition with inaccurate identification across demographics.
- Skewed predictive analytics leading to unfair service allocation.
- Opaque decision-making limiting accountability.
- Lack of fairness audits for algorithmic outputs.
Implementing ethical AI policies, fairness audits, and diverse datasets ensures inclusivity and equity.
Integrating Legacy Infrastructure with AI for Smart Cities
Smart City adoption faces technical and financial hurdles:
- Outdated transportation networks incompatible with AI systems.
- High integration costs for IoT sensors and digital platforms.
- Fragmented governance slowing large-scale deployments.
- Data silos across agencies preventing seamless collaboration.
- Limited technical expertise in municipal organizations.
Public–private partnerships and phased modernization strategies reduce these integration barriers.
Public Trust and Acceptance
Citizen confidence determines Smart City success.
Trust issues arise from:
- Concerns over constant surveillance.
- Limited transparency in how data is collected and used.
- Fear of job displacement due to automation.
- Insufficient community engagement in decision-making.
- Mistrust of opaque algorithms managing civic services.
Solutions include:
- Transparent communication on AI use cases.
- Citizen involvement in governance and planning.
- Ethical frameworks aligned with fairness and accountability.
- Independent audits to validate AI systems.
7. Future Outlook of AI for Smart Cities and Urban Innovation
Notable projects include SingularityNET (AGIX), Fetch.ai (FET), Ocean Protocol (OCEAN), and Numerai (NMR)—each combining AI with blockchain for unique applications.
The future of AI for Smart Cities lies in deeper integration with emerging technologies, stronger ethical frameworks, and global collaboration. By leveraging 5G, IoT, edge computing, autonomous mobility, and digital twins, cities will evolve into highly adaptive, inclusive, and sustainable ecosystems. Open standards and international cooperation will be essential to ensure scalability and fairness across regions.
Read Also : AI for Telecommunications
AI + 5G, IoT, and Edge Computing in Smart Cities
The convergence of AI with next-generation connectivity reshapes urban intelligence:
- 5G networks enable ultra-low latency for real-time data transfer.
- IoT devices capture granular insights into energy, mobility, and environment.
- Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing bandwidth costs.
- AI-driven coordination ensures seamless communication between devices.
- Distributed smart systems increase resilience against failures.
Together, these technologies create the foundation for scalable and adaptive AI-powered city infrastructure.
Autonomous Mobility (AVs, Drones)
Autonomous mobility will redefine transportation and logistics in smart cities:
- Self-driving cars reduce accidents and congestion.
- Autonomous buses optimize mass transit efficiency.
- AI-powered drones support emergency response and deliveries.
- Connected vehicle networks improve route optimization.
- Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates all modes of travel into one platform.
These solutions align with intelligent urban management and sustainable mobility goals.
Digital Twins for Smart City Simulation and AI Forecasting
Digital twins simulate entire city ecosystems with real-time AI models:
- Urban planning simulations test infrastructure before construction.
- Crisis modeling predicts flood, fire, or traffic emergencies.
- Energy demand forecasting improves grid efficiency.
- Population growth scenarios aid long-term planning.
- Continuous feedback loops refine services dynamically.
This technology ensures predictive and adaptive governance.
Ethical AI and Sustainable Development
The future requires embedding ethics into urban transformation:
- Fairness-driven algorithms to eliminate bias.
- GDPR-compliant governance to protect citizen data.
- Open standards to ensure interoperability across cities.
- Citizen participation models to strengthen inclusivity.
- Sustainability-first policies to align AI with global climate goals.
Global collaboration between governments, businesses, and communities ensures that AI for Smart Cities evolves responsibly, creating inclusive, resilient, and sustainable environments.
Enterprise-Scale Platforms for City Operations
Large metropolitan areas manage AI systems across transportation, utilities, and public services. Enterprise-scale platforms provide centralized analytics while supporting department-specific needs. Architectural practices used by an enterprise AI development company are often referenced when designing scalable smart city platforms.
Conclusion
The rise of AI for Smart Cities is reshaping urban life, making environments more sustainable, efficient, and citizen-focused. By combining IoT data, predictive analytics, and intelligent automation, cities improve mobility, enhance public safety, and boost citizen engagement. From adaptive traffic systems to AI-powered emergency response, the impact is far-reaching. Collaboration among policymakers, tech leaders, and communities is vital to ensure inclusivity, resilience, and trust. Ethical AI practices, transparency, and data privacy remain central to widespread adoption.
Looking ahead, innovations such as autonomous vehicles, digital twins, and AI-driven infrastructure will make cities more adaptive and sustainable. By adopting AI-powered urban solutions today, governments can create smarter, safer, and more inclusive cities for the future. Learn more about our AI Development Company.
FAQs
1. How Does AI Improve Traffic Management In Smart Cities?
AI for Smart Cities improves traffic management through adaptive signal control, predictive analytics, and smart parking systems. By analyzing real-time IoT data, AI reduces congestion, shortens commute times, and lowers emissions.
2. What Role Does AI Pay In Enhancing Public Safety?
AI-powered city infrastructure enhances safety through smart surveillance, anomaly detection, predictive policing, and emergency response optimization. These systems allow faster interventions while balancing privacy and fairness.
3. Why Is AI Important For Sustainable Urban Development?
AI supports sustainability by optimizing resource allocation, managing smart grids, reducing energy waste, and enabling predictive maintenance of infrastructure. In this way, AI for Smart Cities aligns urban development with climate goals.
4. What Challenges Exist In Adopting AI For Smart Cities?
Key challenges include data privacy risks, algorithmic bias, integration with legacy systems, and public trust issues. Compliance with GDPR, transparency in AI governance, and citizen engagement help overcome these barriers.
5. What Is The Future Outlook Of AI In Smart Cities?
The future of AI-powered city infrastructure involves deeper integration with 5G, IoT, edge computing, autonomous mobility, and digital twins. Ethical AI and global collaboration will ensure sustainable and inclusive growth.