Introduction
Artificial intelligence is changing the way we solve problems. One of the latest developments is AutoGPT, a powerful tool built on large language models (LLMs) that can perform tasks with little human input. It’s more than just a chatbot. It thinks, plans, and takes actions based on goals.
This blog gives a complete AutoGPT overview, explains how AutoGPT works, breaks down key AutoGPT features, and shows real-world AutoGPT use cases. It also looks at how it fits into the bigger picture of generative AI agents and its role among open-source AI tools.
Also Read: AI for Small Business: Practical Tools and Strategies
What Is AutoGPT?
AutoGPT is an experimental application that builds on the GPT-4 language model. It connects multiple AI tools and runs them with minimal human instruction. Once a user defines a goal, AutoGPT starts creating plans, executes tasks, checks the results, and repeats until it completes the goal or hits a limit.
Unlike standard chatbots, AutoGPT can act on its own. It does not wait for constant prompts. It manages a sequence of steps, making it an early example of autonomous AI.
AutoGPT first gained attention in the open-source community. It demonstrated that language models can be more than just responsive—they can be proactive.
Related: Learn how AI Agents are Shaping the Future of Business – What is Generative AI?
Why AutoGPT Matters
The value of AutoGPT lies in its ability to chain actions together. It doesn’t just provide answers, it builds solutions. This ability makes it suitable for multi-step tasks like data analysis, report writing, and even coding support.
Most AI tools respond to prompts. AutoGPT sets goals and works toward them. This shift from prompt-response to goal-driven behavior marks a major development in artificial intelligence.
It introduces a different kind of automation, one that is flexible, adaptive, and capable of adjusting its own strategies based on results.
How AutoGPT Works
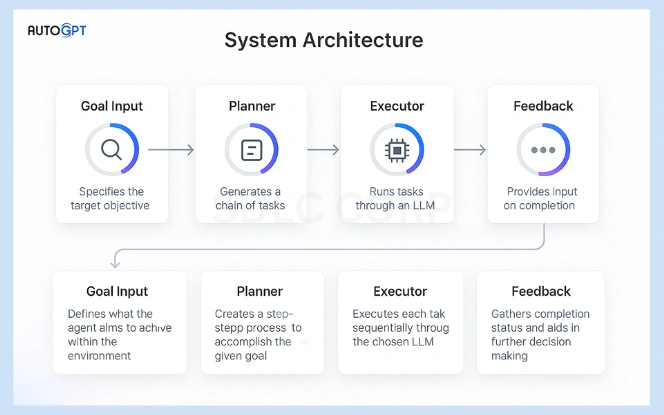
Understanding how AutoGPT works helps reveal its potential. It follows a loop:
- Goal Definition: The user inputs a high-level goal.
- Task Planning: AutoGPT breaks that goal into smaller tasks.
- Execution: It uses external tools or APIs to complete each task.
- Feedback: It reviews outputs and adjusts future steps.
- Memory Use: It stores progress and previous decisions.
This process mimics human-like problem solving. Instead of executing just one task, AutoGPT adapts as it moves toward the final objective.
AutoGPT’s architecture often includes memory components like vector databases. These help it remember past actions and improve long-term performance. Dive Deeper: AI for Logistics
Core AutoGPT Features
Several AutoGPT features make it stand out from typical AI models:
- Autonomous Task Management: It handles multiple steps without new prompts.
- Memory Integration: Stores past context and applies it in future steps.
- Tool Use: It interacts with file systems, browsers, APIs, and more.
- Goal Refinement: If the initial plan fails, it re-evaluates and tries a new path.
- Open Source Flexibility: Developers can modify the code and add plugins.
These features make AutoGPT adaptable across different industries and needs.
You Might Like: Alderney Gaming License: Tech Stack Requirements
AutoGPT in the Context of Generative AI Agents
Generative AI agents are systems that produce new content and act with some level of autonomy. AutoGPT is one of the first public tools to show how such agents can function beyond content creation.
Unlike static models that only generate text, generative agents like AutoGPT combine reasoning, decision-making, and tool interaction.
This blend allows agents to not only generate ideas but also act on them. For instance, AutoGPT can search the web, summarize findings, and create reports without being told each step.
Discover Related Insights: Sweden Gaming License and Responsible AI Use
Real-World AutoGPT Use Cases
There are several practical AutoGPT use cases. Many are experimental, but they show what’s possible:
- Market Research: AutoGPT can search trends, gather data, and summarize insights.
- Content Creation: Drafts blogs, writes reports, or creates outlines based on goals.
- Bug Fixing: It reviews code, identifies issues, and suggests changes.
- Customer Support Bots: Handles inquiries using dynamic decision paths.
- Personal Assistants: Automates calendar updates, sends reminders, or drafts emails.
- E-Commerce Management: Updates product listings, prices, or inventory data.
In each case, the value lies in automation. Users set a goal, and the agent takes care of the execution.Further Reading: AI for Finance
AutoGPT and Open-Source AI Tools
AutoGPT belongs to a growing group of open-source AI tools. This status offers several advantages:
- Transparency: Anyone can inspect the code.
- Customization: Developers adapt it to their specific use case.
- Community Support: Contributions improve the tool’s reliability and scope.
- Security Awareness: Open code helps find and fix vulnerabilities faster.
Compared to closed-source alternatives, open tools like AutoGPT allow broader experimentation and innovation.
Challenges and Limits
Despite its promise, AutoGPT is still early-stage. It faces several limits:
- Hallucination: Like all large language models, it sometimes gives wrong information.
- Cost: Running multi-step processes on GPT-4 can get expensive.
- Lack of Judgment: It doesn’t know when a task doesn’t make sense.
- Security Risks: Without safeguards, it could access sensitive data.
These issues mean AutoGPT is best used under controlled conditions. It can assist, but not replace, human oversight.
Ethics and Responsible Use
AutoGPT’s power raises questions about automation and control. When tasks are delegated to software, who is accountable?
Responsible use means:
- Defining clear boundaries for what AutoGPT can and cannot do.
- Keeping humans in the loop.
- Monitoring outputs to reduce bias and misinformation.
The community behind AutoGPT continues to explore safe ways to deploy generative agents.
Read More: The Role of AI in Providing Personalized Game Recommendations
Future Outlook
AutoGPT is just the beginning. Its release has inspired similar tools that push the limits of automation. Future versions will likely include:
- Better memory systems.
- Stronger safeguards.
- More efficient task planning.
- Integration with new data sources.
As generative AI continues to evolve, tools like AutoGPT will help define how humans and machines work together.
The rise of generative agents points to a shift in software: from tools that follow commands to tools that collaborate on tasks.
What’s Next? Explore:Top 5 AI and ML Trends Reshaping the Future
Conclusion
AutoGPT stands at the edge of a new AI era. It goes beyond prompt-based models to deliver goal-driven, self-updating task performance. This blog offered a complete AutoGPT overview, covered how AutoGPT works, explored essential AutoGPT features, and discussed common AutoGPT use cases. It also placed AutoGPT within the larger world of generative AI agents and open-source AI tools.
AutoGPT is not perfect, but it shows what’s possible. With care and testing, it can be a useful tool for automation, research, and content creation.
If you’re exploring how AI tools like AutoGPT can enhance your business, contact us SDLC corp. Our team helps companies adopt intelligent systems with confidence and control.
FAQs
What Is AutoGPT Used For?
AutoGPT is used for automating multi-step tasks like data analysis, content creation, market research, and customer service.
How Is AutoGPT Different From ChatGPT?
Unlike ChatGPT, which responds to individual prompts, AutoGPT can set goals, create plans, and complete tasks with minimal input.
Is AutoGPT Open Source?
Yes, AutoGPT is an open-source AI tool. Developers can inspect, customize, and improve its code.
Can AutoGPT Be Used in Businesses?
AutoGPT is suitable for automating repetitive tasks in marketing, e-commerce, software testing, and customer support.
Is AutoGPT Safe to Use?
AutoGPT is experimental. It should be used in controlled settings to avoid errors, misjudgments, or security risks.