Introduction
In the rapidly evolving field of Artificial Intelligence, Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 and PaLM are redefining how machines understand and respond to human input. But despite their incredible ability to generate text, they traditionally lack one vital component: the ability to interact meaningfully with the world.This is where the ReAct framework short for Reasoning and Acting comes into play.
Developed by researchers at Princeton and Google, ReAct empowers LLMs to not only think step-by-step but also act in the world, observe the consequences, and refine their thinking. It’s a major advancement in building interactive, transparent, and grounded AI agents.
1.How the ReAct Framework Works
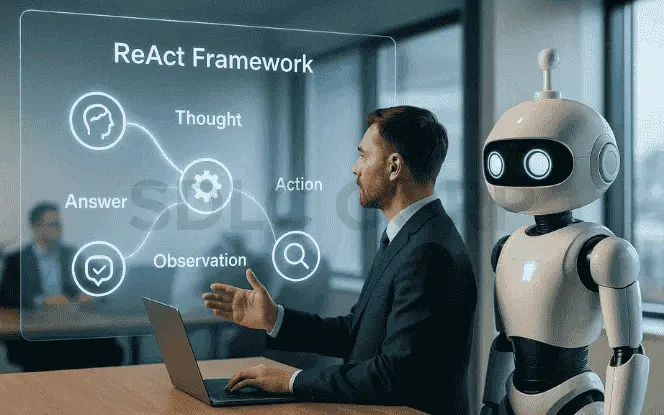
The ReAct framework operates on a structured loop of Thought → Action → Observation → Answer, enabling AI models to merge step-by-step reasoning with real-world interaction. In the Thought stage, the model evaluates the task, identifies information gaps, and plans a logical next step. During the Action stage, it executes a specific task such as querying a database, performing a search, or calling an API. The Observation stage captures and validates the results, extracting only the relevant facts. Finally, in the Answer stage, the ReAct framework synthesizes all gathered information into a final, well-supported output or decides whether another reasoning–action cycle is required.
By continuously looping through these stages, the ReAct framework allows AI systems to adapt dynamically, improve accuracy, and maintain transparency through auditable reasoning trails. This structured process can be enhanced with guardrails like tool access controls, schema validation, and human oversight for sensitive workflows. As a result, the ReAct framework empowers AI agents to think critically, act effectively, and deliver reliable, real-time results across industries.
2.Real-World Applications of ReAct
ReAct is becoming a foundational tool in how AI development services deliver intelligent agents. From customer support to scientific planning, its ability to reason and act makes it a valuable layer in next-gen applications—especially when considered in the broader context of AI alignment strategies that ensure these agents behave in safe and beneficial ways.”
- Search-Augmented QA – Answering questions by retrieving real-time data
Math and Code Solving – Using embedded calculators or Python interpreters
Game-Playing Agents – Solving interactive environments (e.g., ALFWorld)
Automation Bots – Updating databases, generating reports, managing schedules
- Scientific Assistants – Formulating and testing hypotheses using simulations
3.Prompt Engineering Tips
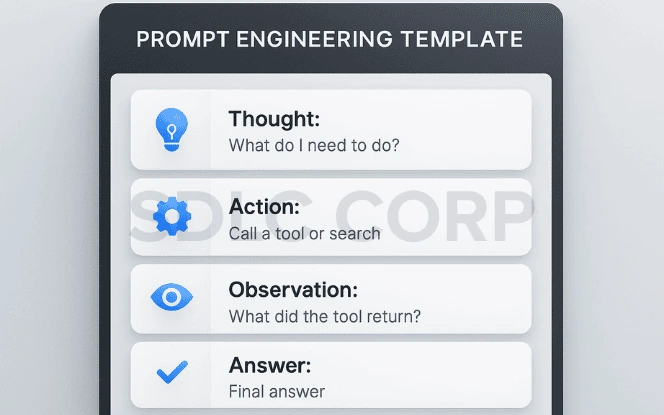
1. Use Structured Prompts
Maintain a clear and consistent format for all prompts to guide the model’s reasoning and tool usage effectively.
Template:
Thought: [Describe reasoning or plan]
Action: [Specify tool or action]
Observation: [Summarize results or findings]
Answer: [Final, well-supported output]
2. Define Available Tools Clearly
List all tools the AI can use in the system message or initial prompt, along with their input/output formats, to avoid confusion or misuse.
3. Provide Fallback Steps
Include contingency actions for tool errors, timeouts, or unexpected results. This ensures the AI can recover and still deliver value.
4. Encourage Step-by-Step Reasoning
Explicitly prompt the AI to break down complex tasks into smaller, logical steps before taking action.
4.Enterprise Use Cases for ReAct
For any modern AI development company, ReAct offers a highly modular, transparent framework for integrating LLM agents into production workflows. Whether you’re building internal bots, enhancing CRMs, or enabling autonomous decision-making, ReAct framework provides the structure needed to ensure reliable outcomes.
- Customer Support Agents – Retrieve help articles, interpret intent, and escalate where needed
- Sales Enablement Tools – Enrich CRM records with live searches and summarizations
- Finance Automation – Run calculations, analyze spreadsheet data, and generate audit trails
- Healthcare – Retrieve structured information from medical databases and assist in decision-making
5.Tools and Frameworks That Support ReAct
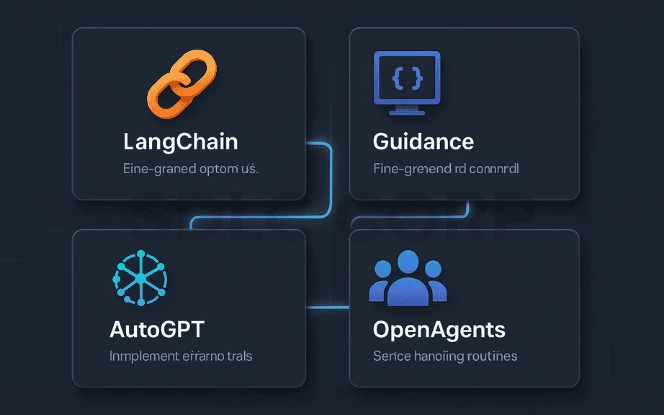
- LangChain
A widely used open-source framework for building applications with LLMs, LangChain excels at integrating reasoning steps with external tools and APIs. It offers modules for prompt management, retrieval augmentation, and chaining complex actions together. - Guidance
Guidance provides a fine-grained way to control LLM output by blending natural language prompts with code-like syntax. It enables precise token-by-token control, making it easier to enforce structured responses and align outputs with strict formats. - AutoGPT
An autonomous agent framework that can chain multiple ReAct-like loops together to achieve long-term objectives. AutoGPT handles planning, task decomposition, and tool invocation without requiring constant user input. - OpenAgents
A flexible platform for creating AI agents that can reason, act, and collaborate. OpenAgents supports multi-agent orchestration, shared memory, and role-based task assignment, enabling complex, coordinated workflows.
6.Challenges and Limitations
- Prompt Complexity – Requires well-structured prompts for effective behavior
- Dependency on Tools – Performance is only as good as the tools being used
- Context Limitations – Long reasoning chains may exceed LLM context windows
- Hallucination Risks – Especially in unverified observations or loosely defined tool outputs
7.Best Practices & Guardrails
- Use validated, reliable tools
Always integrate tools and APIs that are proven in production environments, with high availability and well-documented behavior. Unreliable tools can introduce errors, delay responses, and degrade trust in the AI system. - Clearly define action formats
Ensure every action follows a strict, machine-readable format (such as JSON) so the system can parse and execute it without ambiguity. This minimizes misinterpretations and reduces the risk of failed calls. - Log full Reasoning → Action → Observation trails
Maintain detailed step-by-step logs of the agent’s reasoning, the actions taken, and the results observed. These logs provide transparency for debugging, audits, and improving the AI’s performance over time. - Implement error-handling routines
Design fallback strategies for tool failures, timeouts, or invalid responses. This includes retries with backoff, switching to backup tools, and gracefully returning partial results when needed. - Allow for human oversight in sensitive domains
For tasks involving critical decisions such as medical advice, legal judgments, or financial transactions, introduce a human-in-the-loop process. This ensures that high-impact outputs are reviewed and approved before execution.
Conclusion
The ReAct framework represents a critical evolution in how we design and interact with language models. By integrating reasoning and action, it enables AI systems to:
- Break down complex problems
- Use tools to enhance accuracy
- Reflect on feedback to improve performance
- Explain their decisions step-by-step
This leads to more trustworthy, useful, and autonomous AI agents.
For startups and enterprises alike, especially those led by forward-thinking AI development companies, ReAct unlocks the full potential of agentic AI systems.
FAQ'S
What is ReAct in AI?
ReAct stands for Reasoning and Acting — a method of prompting LLMs to think and interact with tools in a structured loop.
How is ReAct different from Chain-of-Thought (CoT)?
CoT is purely internal reasoning. ReAct adds actions and environment feedback to the loop.
Does ReAct require training?
No. ReAct can be implemented via zero-shot or few-shot prompting with tools.
Can ReAct be used in production?
Yes — especially in combination with robust prompt design, logging, and fallback handling.
What tools can ReAct agents use?
Any tool accessible via code or API — search engines, databases, calculators, CRMs, etc.
How do autonomous agents use memory?
Autonomous agents powered by the ReAct framework use memory to store and retrieve relevant information from past interactions, tasks, and tool outputs. This can include short-term memory for immediate reasoning steps within a session, and long-term memory for retaining facts, preferences, or previous results across sessions. Memory enables agents to maintain context, avoid repeating work, and improve accuracy over time by learning from historical data.
How much does it cost to operate?
The cost of operating an autonomous agent depends on several factors: the underlying language model (e.g., GPT-4, Claude, etc.), the complexity and length of each reasoning–action loop, the number of tool/API calls, and any infrastructure or hosting expenses. For most business workflows, costs can be optimized by batching requests, caching results, and limiting unnecessary tool usage. When well-structured prompts and efficient tools are used, the ReAct framework can deliver high value with controlled operating costs.
What about privacy and compliance?
Privacy and compliance are integral to deploying autonomous agents in production. The ReAct framework can be integrated with secure, vetted tools, data encryption, and access controls to ensure sensitive information is handled safely. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2 is achieved by restricting data storage, anonymizing personally identifiable information (PII), and keeping full audit trails of the reasoning and actions taken. Additionally, human oversight can be incorporated for tasks in regulated or sensitive domains.





