Introduction
Think about how often you use Google Search in a day. You expect it to be fast, relevant, and intuitive. Now imagine if Google gave you results that were slow, cluttered, or irrelevant—you’d quickly lose trust in it.
For Salesforce users, Global Search plays the same role. It’s the first stop for finding records, whether that’s an account, opportunity, case, or custom object. But here’s the problem: out-of-the-box, Salesforce’s global search isn’t always optimized for your business. Users waste precious time scrolling through irrelevant records or missing the right ones altogether.
The good news? You can customize Salesforce global search to make it faster, smarter, and tailored to your team’s needs.
1. What is Global Search in Salesforce?
Global Search is Salesforce’s universal search bar, located at the top of every page. It’s designed to help users quickly find any record they need across standard and custom objects.
Some key features include:
- Autocomplete Suggestions – Salesforce predicts possible matches as you type.
- Object-Specific Results – Results are grouped by objects (Accounts, Contacts, Opportunities, etc.).
- Search Layouts – Admins control which fields display in search results.
- Filters – Narrow down results by record type or field values.
In simple terms, it’s like the “Google” of your Salesforce org. But unlike Google, you get to customize it.
2. Why Customize Global Search?
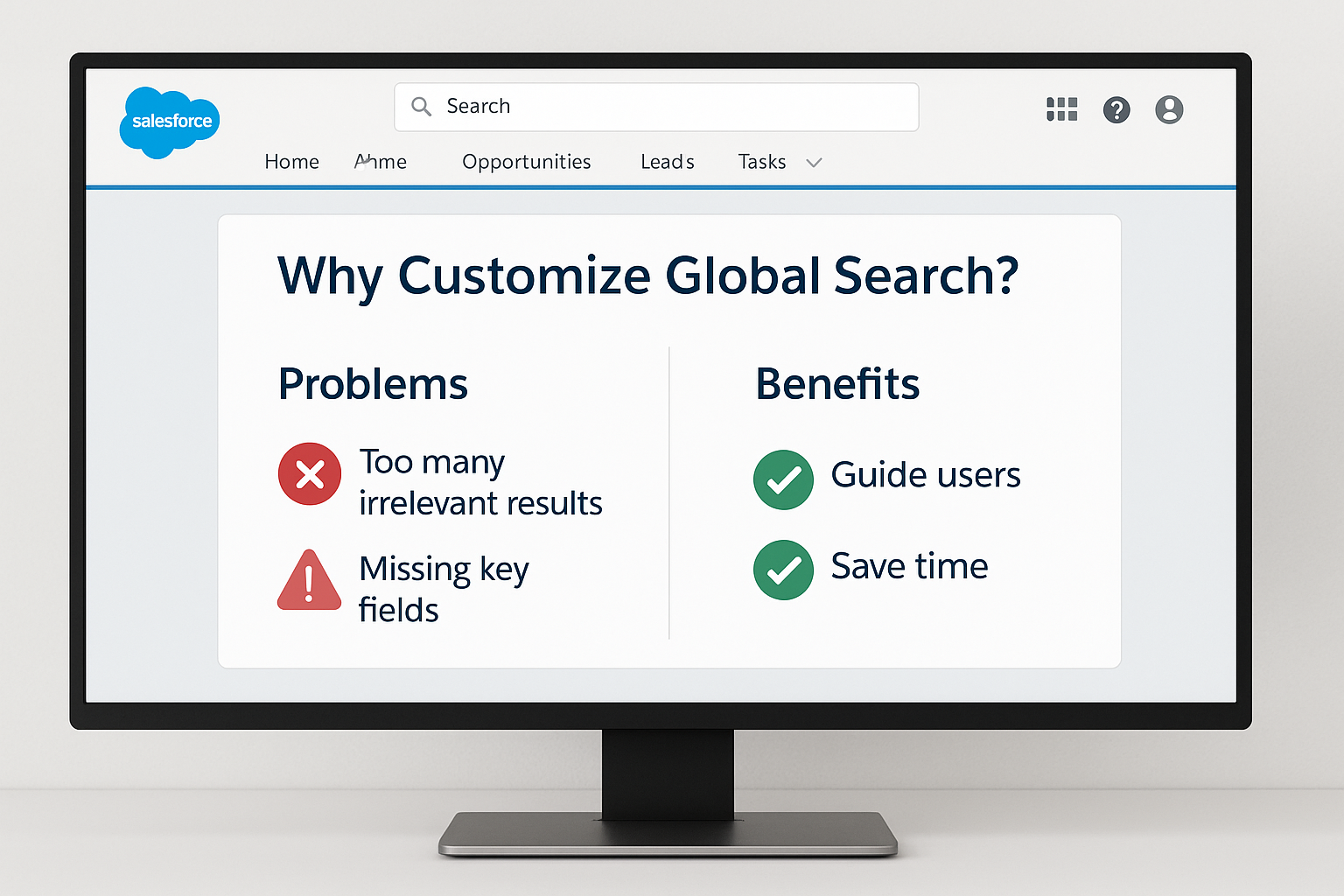
Out-of-the-box, Salesforce search is generic. That might work for small teams, but as your org grows, problems appear:
- Too Many Irrelevant Results – Users waste time scrolling.
- Missing Key Fields – The search preview doesn’t show the info reps actually need.
- Slow Adoption – If search feels clunky, users stop trusting it.
- Productivity Loss – Minutes wasted searching = hours lost across teams each week.
Customizing global search allows you to:
- Prioritize what matters – Show fields like Account Tier or Opportunity Stage right in search results.
- Guide users – Filter out inactive or irrelevant records.
- Save time – Users find the right record in seconds, not minutes.
3. How Salesforce Search Works (Behind the Scenes)

Before customizing, it’s useful to know how Salesforce handles search:
- Indexing – Salesforce builds an internal index of searchable fields.
- Tokenization – When you type, Salesforce breaks down your text into “tokens.”
- Relevance Ranking – Matches are scored based on frequency, field weight, and recent activity.
- Result Display – Records are grouped by object and shown in ranked order.
Knowing this helps you understand why certain results show up higher—and how to adjust them.
4. Step-by-Step: How to Customize Global Search in Salesforce
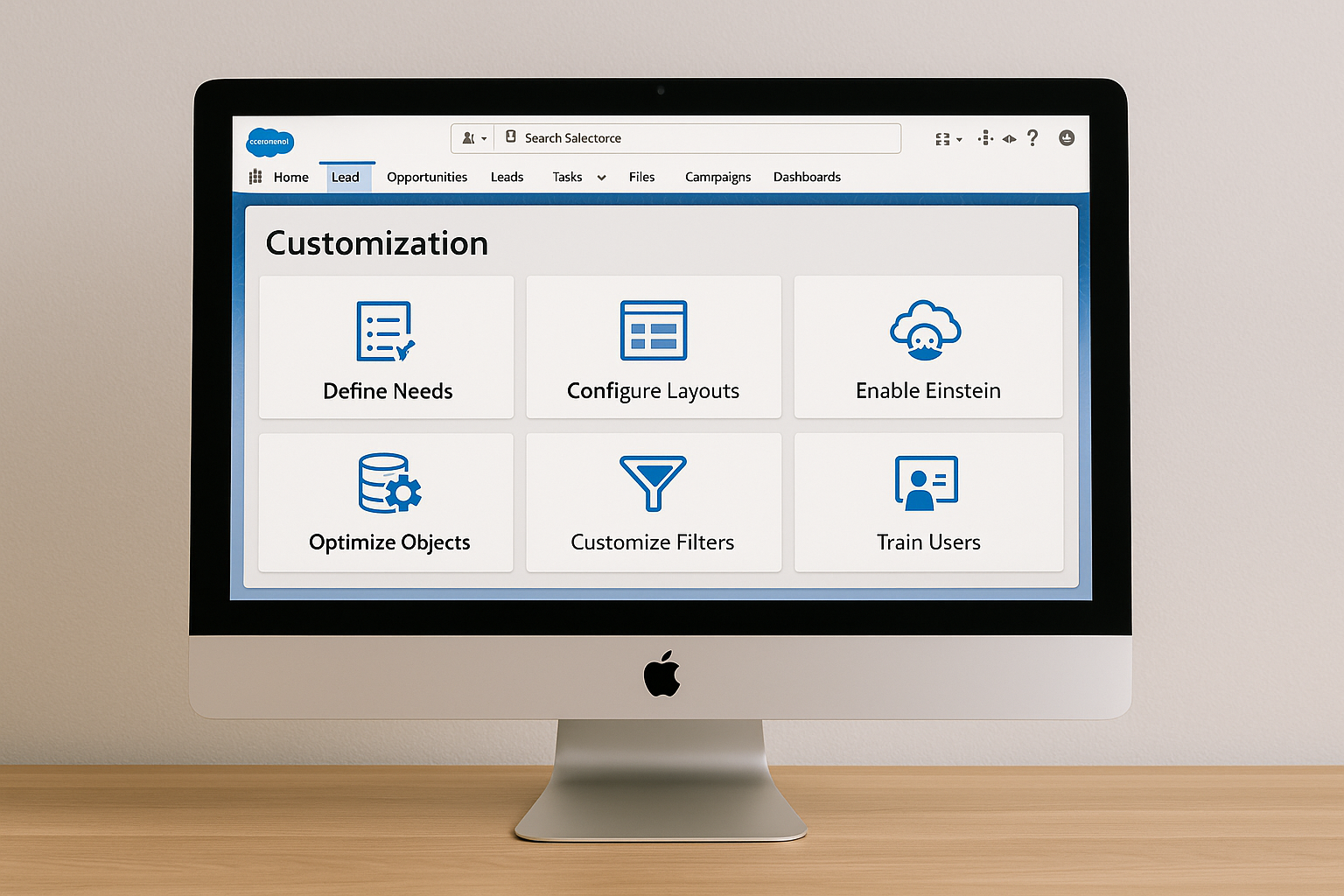
Step 1: Define User Needs
- Interview your sales, service, and marketing teams.
- Ask: “What do you need to see first when searching?”
- Example: Sales may want Account Owner & Industry, while Service cares about Case Priority & Status.
Step 2: Configure Search Layouts
Search layouts determine what fields display in search results.
- Go to Setup → Object Manager.
- Select an object (e.g., Account).
- Click Search Layouts for Salesforce Classic (works in Lightning too).
- Edit the Search Results layout.
- Add fields that matter most (e.g., Account Tier, Region, Owner).
Now, when users search for an account, they immediately see useful info without opening the record.
Step 3: Enable Einstein Search (if available)
Einstein Search uses AI-powered personalization:
- Tailors results based on past behavior.
- Allows natural language search (“Accounts in California”).
- Provides recommended actions (e.g., update a record directly from search).
To enable:
- Go to Setup → Einstein Search Settings.
- Turn on personalization and natural language search.
- Train users on how to use it.
Step 4: Optimize Object Searchability
Not every object needs to be searchable. Too many objects = clutter.
- Go to Object Manager → Object Settings → Search.
- Enable search only for the objects your teams actually use.
- Example: Hide rarely used custom objects from search.
Step 5: Customize Search Filters
Filters let users refine results. Example:
- Accounts: Filter by Industry, Region, Tier.
- Cases: Filter by Priority, Status, Owner.
- Opportunities: Filter by Stage, Close Date.
You can define default filters in Search Layouts so users see them automatically.
Step 6: Train Users on Search Operators & Shortcuts
Salesforce supports search operators like Google. Examples:
- “Exact Phrase” → Finds only exact matches.
- AND / OR → Combine conditions.
- -keyword → Excludes results with that keyword.
Teaching users these tricks can cut search time dramatically.
5. Advanced Customization Techniques

1. SOSL vs SOQL for Search
- SOSL (Salesforce Object Search Language) is optimized for full-text searches across objects.
- SOQL (Salesforce Object Query Language) is better for precise queries within one object.
Admins and developers can use SOSL for building custom search tools (e.g., in Apex).
2. Pinning Frequently Used Objects
Admins can configure search result order so the most relevant objects appear first. Example: Put Accounts and Opportunities above Tasks or Campaigns.
3. Custom Search Components in Lightning
With Lightning App Builder, you can create custom search components tailored to specific roles. Example: A service console with case search front and center.
4. Search Performance Optimization
- Remove unused objects from search.
- Limit results to active records.
- Regularly reindex data if performance slows.
6. Best Practices for Customizing Global Search

- Involve End Users – Don’t guess. Ask teams what they need.
- Keep It Clean – Too many fields = clutter. Only show the essentials.
- Use Einstein Search – If available, it’s a game-changer.
- Regular Reviews – Update search layouts as business needs evolve.
- Document Changes – Keep track of which objects/fields are customized and why.
7. Real-World Examples

Sales Teams
A sales rep types “Acme” and immediately sees:
- Account Tier = Platinum
- Region = North America
- Account Owner = Sarah Lee
No need to click into the record—at a glance, they know it’s a high-value customer.
Service Teams
A service agent searches for “Printer Issue” and sees:
- Case Priority = High
- Status = Open
- Last Updated = Yesterday
They can act fast without digging.
Marketing Teams
A marketer searches for a campaign and sees:
- Status = Active
- Start Date
- Budget
This helps them quickly find ongoing campaigns without scanning irrelevant ones.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid

- Showing Too Many Fields – Makes results unreadable.
- Overloading Search with Objects – Clutters results and slows search.
- Not Training Users – Many users don’t know search operators exist.
- Ignoring Mobile – Customize layouts for the Salesforce mobile app too.
Conclusion

Salesforce Global Search is often overlooked, but when customized correctly, it becomes a productivity multiplier. Instead of wasting time digging through irrelevant results, your users can find the right records instantly.
By customizing search layouts, filters, and objects, and enabling Einstein Search where available, you transform Salesforce from a generic database into a tailored, intelligent system that feels built just for your team. Start small—customize one object’s search layout, test it with users, and expand from there. Within weeks, you’ll see the difference in adoption, accuracy, and speed.
Your Salesforce org deserves a search experience as fast and smart as Google—and with the right setup, that’s exactly what you can deliver.
FAQs
Can admins control which fields appear in search results?
Yes. Admins configure this through Search Layouts in Object Manager.
Do search layouts affect reports or list views?
No. They only control how records appear in search results.
Does customizing search affect mobile users?
Yes. Search layouts also apply to the Salesforce mobile app.
How do I improve search speed?
Disable unnecessary objects, simplify layouts, and enable Einstein Search.
Can users personalize their own search?
With Einstein Search, yes. Otherwise, admins control most settings.
How often should I review search customization?
At least twice a year, or whenever business processes change.