Introduction
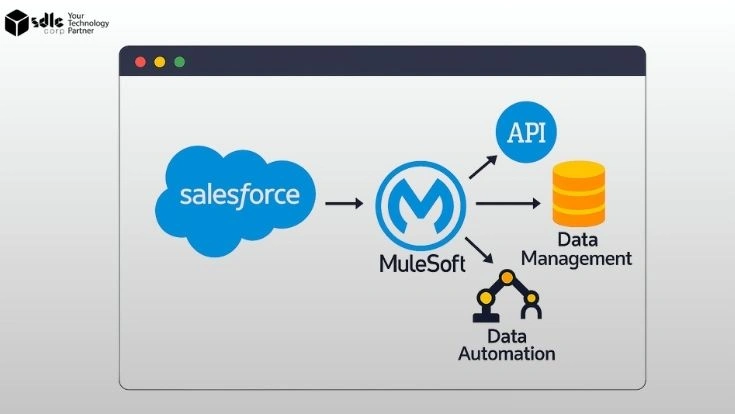
Salesforce MuleSoft Integration Best Practices help businesses connect Salesforce with ERPs, databases, and cloud apps seamlessly. While Salesforce manages customer relationships, MuleSoft ensures secure, scalable data exchange—unlocking the full potential of Customer 360.
Expert Salesforce consulting services guide companies to build robust, reusable integrations that go beyond basic connectivity. The result is faster digital transformation, improved efficiency, and unified customer experiences powered by real-time data.
1. Common Integration Patterns
When starting a Salesforce MuleSoft integration, it helps to follow proven patterns. These patterns guide how data flows between Salesforce and other systems. The five most common are:
1. Migration
Used to move large volumes of data from one system to another. For instance, migrating customer records from a legacy ERP into Salesforce. For instance, MuleSoft handles the batch jobs and transformations needed for this process. (integration example: moving thousands of customer contacts to Salesforce)
2. Broadcast
A one-way sync where data from a source is sent in real time to multiple systems. For instance, when a new lead is created in Salesforce, MuleSoft can broadcast that data to both a marketing platform and a data warehouse.
3. Aggregation

Collects data from multiple systems, combines it, and pushes it into Salesforce. An example is pulling customer info from ERP and support tools, merging them with sales data, and creating a single Salesforce record.
4. Bidirectional Sync
Keeps data aligned between Salesforce and another system. For example, account updates in Salesforce are synced with an ERP, while ERP changes are reflected back in Salesforce.
5. Correlation
Links records across systems without duplicating data. A hospital network, for instance, might correlate patient records across multiple branches only when both systems already have the same patient entry.
These patterns provide a foundation for scalable, secure, and efficient integrations. Choosing the right one depends on business needs and data complexity.
2. Core Best Practices
Successful integrations require both technical precision and business alignment. Below are the most important best practices to follow.
1. Define Clear Business & Technical Requirements
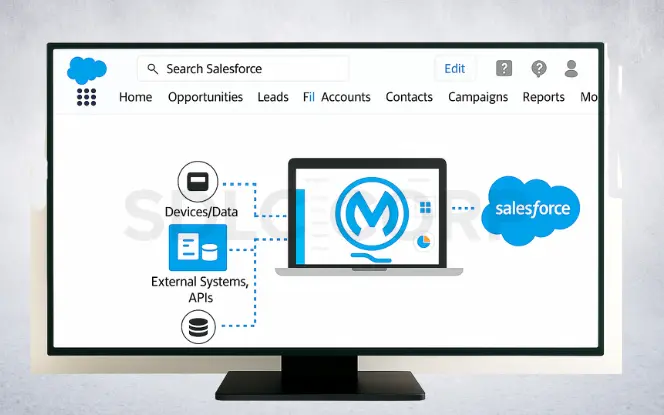
Start with stakeholder workshops to capture use cases, service-level agreements (SLAs), and data needs. Then, Map Salesforce orgs to MuleSoft environments early. This way avoids gaps when multiple teams and systems are involved.
2. Segregate Responsibilities Between Teams
Assign clear roles. MuleSoft should manage data extraction and transformation, while Salesforce handles business logic and workflows. This ensures accountability and prevents overlap.
3. Ensure Strong Security
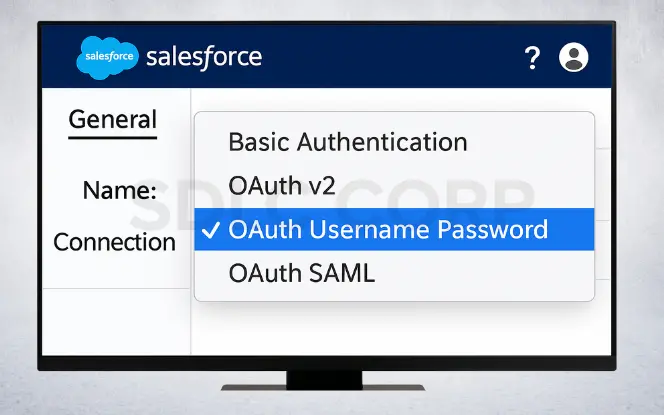
Use OAuth 2.0 instead of basic authentication for the Salesforce connector. In addition, encrypt sensitive properties such as passwords, and enforce API authentication policies. Finally, always involve the Infosec team to approve integration security.
4. Use Integration Patterns & Anypoint Platform Features
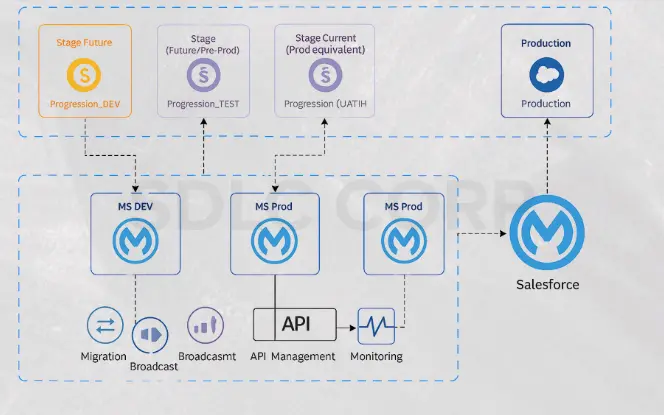
Apply standard patterns like Migration or Broadcast where they fit best. Leverage Anypoint Platform capabilities such as connectors, API management, and monitoring to simplify integration and improve reusability.
5. Plan for Scalability & Future-Proofing
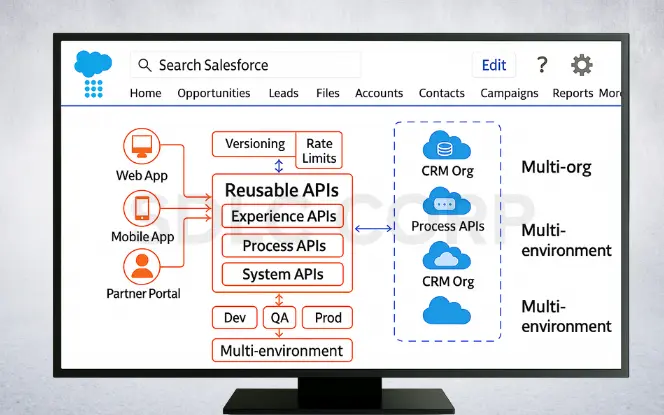
Design APIs to be reusable across multiple applications. Anticipate growth by preparing for multi-org and multi-environment Salesforce setups.
6. Configuration Best Practices
Keep all global elements in a dedicated global.xml file. Similarly, use environment-specific property files (dev, test, prod) instead of hardcoding. As a result, This makes the integration easier to maintain.
7. Business Logic & Transformation Placement
Keep business logic inside Salesforce, where it can be managed through metadata and admin tools. Handle data transformations in MuleSoft to ensure consistency and reuse across systems.
8. Testing & Performance Validation
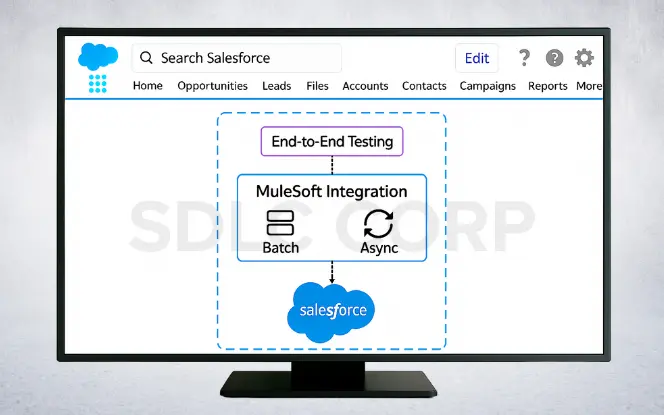
Perform thorough end-to-end testing. Use batch processing and async jobs to meet SLAs and reduce API call limits. Validate performance with real-world data loads.
9. Logging & Monitoring
Log key integration events inside Salesforce for visibility to admins. Use MuleSoft logs for technical troubleshooting. Implement proactive monitoring to detect issues early and ensure smooth operations.
3. Step-by-Step Example
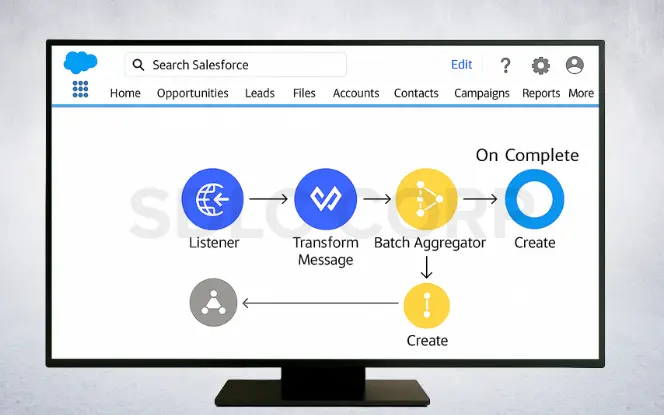
One common MuleSoft Salesforce integration example step by step is syncing leads from a database into Salesforce. This use case shows how MuleSoft extracts data, transforms it, and inserts it into Salesforce.
1. Set up the HTTP Listener
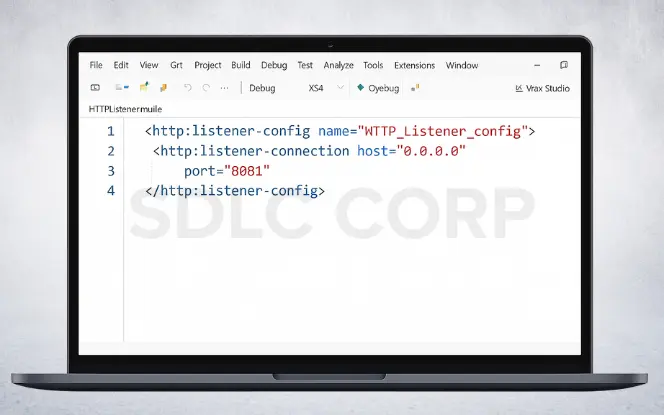
In Anypoint Studio, create a new Mule project and add an HTTP Listener on port 8081 with the path /salesforce. This endpoint triggers the flow.
2. Connect to the Database
Add a Database connector and configure it with MySQL credentials. Use a query such as:
SELECT * FROM contacts:
This pulls lead information including (first name, last name, email, company).
3. Transform Data with Data Weave
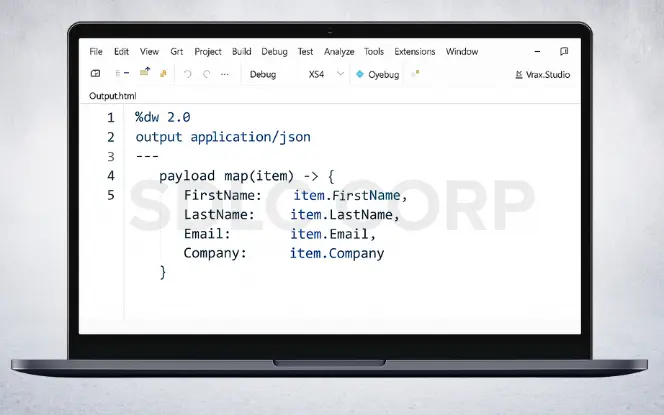
Use a Transform Message component to map database fields into Salesforce lead fields.
4. Insert Data into Salesforce
Drag a Salesforce Create connector into the flow. Configure it with Salesforce credentials (username, password, and security token). Under Type, select Lead, and set Records to [payload].
5. Batch Processing (Optional)
Add a Batch Job scope to process large volumes of records efficiently, reducing API call consumption.
Once deployed, posting to http://localhost:8081/salesforce will read contacts from the database and insert them as leads into Salesforce.
Overall, this simple flow demonstrates how MuleSoft handles extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) in a Salesforce integration.
4. Common Pitfalls to Avoid
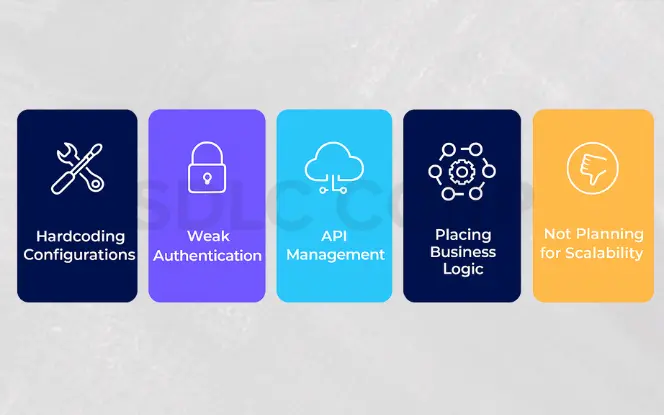
Even with the right plan, Salesforce MuleSoft integration projects can fail if certain mistakes are overlooked. Here are the most common pitfalls:
1. Hardcoding Configurations
Storing values like endpoints, credentials, or ports directly in the code makes integrations fragile. Always use environment-specific property files and encrypt sensitive values.
2. Weak Authentication
Using basic authentication instead of OAuth 2.0 exposes systems to unnecessary risks. Secure APIs with proper authorization and review security settings with the Infosec team.
3. Placing Business Logic in MuleSoft
Business rules should stay in Salesforce, where they can be managed through metadata and admin tools. MuleSoft should focus on data transformation and integration flows.
4. Not Planning for Scalability
Point-to-point connections may work at first; however, they fail as systems grow. Use API-led connectivity and design for multi-org and multi-environment scalability.
Avoiding these pitfalls will keep your integrations secure, maintainable, and future-proof.
5. Future-Proofing Salesforce MuleSoft Integration
Strong integrations are not just about solving today’s needs. They must be designed to scale and adapt as the business grows. Future-proofing your Salesforce MuleSoft integration involves building flexible APIs, supporting multiple environments, and adopting modern DevOps practices.
API-First Approach
Design APIs as reusable building blocks rather than one-off connectors. This allows faster rollout of new services, reduces duplication, and keeps integrations consistent across systems.
Multi-Org and Multi-Environment Readiness
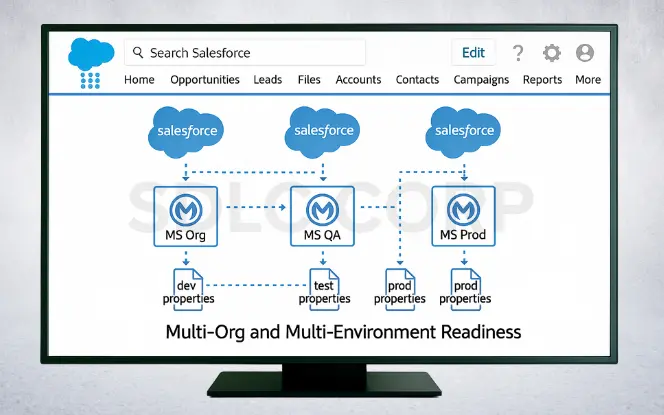
Many companies use more than one Salesforce org or work across dev, test, and production environments. Plan for this from the start by mapping environments, avoiding hardcoding, and using environment-specific property files.
CI/CD and DevOps Alignment
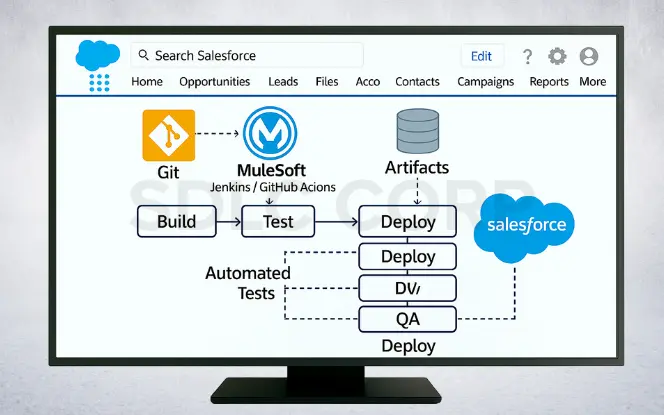
Automate deployments using CI/CD pipelines. Consequently, this ensures faster releases, better version control, and fewer manual errors. Moreover, MuleSoft projects should integrate with common DevOps tools to streamline builds, tests, and deployments.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Integration work does not end at go-live. Use MuleSoft’s monitoring tools to track API health, error rates, and performance metrics. Regularly review logs and apply optimizations so the integration remains reliable and secure.
Future-proofing ensures that Salesforce-MuleSoft integrations stay secure, scalable, and ready for evolving business requirements.
Conclusion
Strong Salesforce MuleSoft integration depends on more than just connecting systems. It requires clear business alignment, secure and scalable design, and disciplined technical practices. From defining requirements and separating responsibilities to applying integration patterns, testing, and monitoring, every step shapes long-term success.
The key is balance: Salesforce should manage business rules, whereas MuleSoft handles data integration and transformation. With this approach, companies not only avoid common pitfalls but also deliver unified, reliable customer experiences.
By following these best practices, teams can ensure integrations remain secure, flexible, and ready to scale as business needs evolve. Partnering with experts in Salesforce implementation and support ensures that MuleSoft integrations deliver long-term value and a unified customer experience.
Related Blogs You Should Explore:
FAQ'S
How Do I Customize Global Search Layouts In Salesforce?
What Fields Are Searchable In Salesforce?
What Is The Difference Between Sosl And Soql?
Is Einstein Search Free In Salesforce?
Yes, Einstein Search is included in most Salesforce editions that support Lightning Experience.