Introduction
Autonomous AI workflows are reshaping business operations by taking on tasks that once required constant human attention. These systems connect data, decisions, and actions in ways that reduce errors and increase speed.
AI workflow automation allows employees to step back from repetitive jobs and focus on critical goals. Instead of getting slowed down by routine tasks, organizations achieve smoother, more reliable performance.
By combining human oversight with machine-driven execution, autonomous business process AI supports growth and resilience in every industry.
Understanding Autonomous AI Workflows

An autonomous AI workflow is a structured sequence of steps managed by intelligent systems with minimal human oversight. These workflows integrate data sources, predictive logic, and automated execution engines.
For example, when an email request arrives, the system analyzes its content, determines urgency, and routes it to the correct department. The same system can also draft a reply, attach relevant documents, and log the activity in a record system.
This setup highlights the strength of autonomous business process AI. It doesn’t just execute rules; it learns patterns, adapts to context, and reduces dependency on human monitoring.
Why Businesses Need AI Workflow Automation
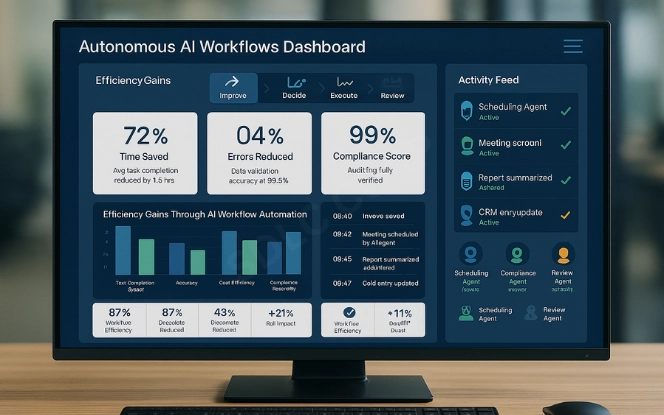
Modern organizations operate in fast, competitive environments. Delays, errors, or inefficiencies cost more than ever. AI workflow automation solves these challenges by keeping processes consistent, scalable, and responsive.
Key benefits include:
- Speed: Tasks that once took hours finish in seconds.
- Accuracy: Systems apply consistent rules across all data.
- Compliance: Auditable workflows reduce regulatory risk.
- Efficiency: Teams focus on strategy instead of repetition.
Moreover, AI-driven task management ensures priorities stay aligned with organizational objectives. When tasks are automatically assigned and tracked, businesses achieve smoother collaboration and better use of resources.
Components of Autonomous Business Process AI
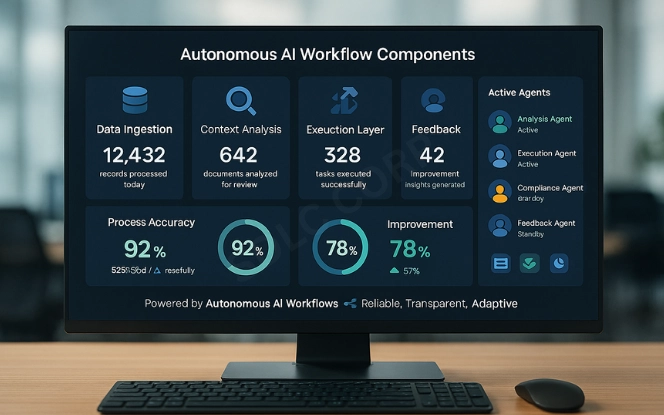
Autonomous business process AI combines several building blocks into a functioning system.
- Data collection: Raw information from emails, documents, sensors, or logs.
- Context analysis: Models interpret input and classify its meaning.
- Execution layer: Automated scripts or bots complete defined actions.
- Feedback loop: Continuous monitoring ensures improvement over time.
Unlike static automation, intelligent process automation with AI adapts when inputs change. This flexibility reduces system downtime and ensures processes remain reliable even as conditions evolve.
Real-World Applications of Autonomous AI Workflows
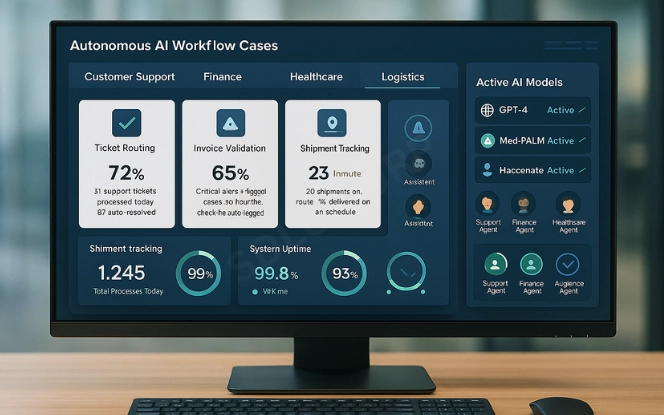
Autonomous workflows now play active roles in daily operations across industries.
- Customer service: Systems classify tickets, generate draft responses, and update support logs.
- Healthcare: Patient records are sorted, appointments are scheduled, and urgent cases flagged.
- Finance: Payments are validated, risk alerts raised, and invoices approved.
- Logistics: Shipments are tracked, exceptions resolved, and supplier reports generated.
Each example reflects the impact of AI agent workflow orchestration, where multiple specialized agents work together to maintain consistency across large, complex systems.
AI-Driven Task Management in Teams
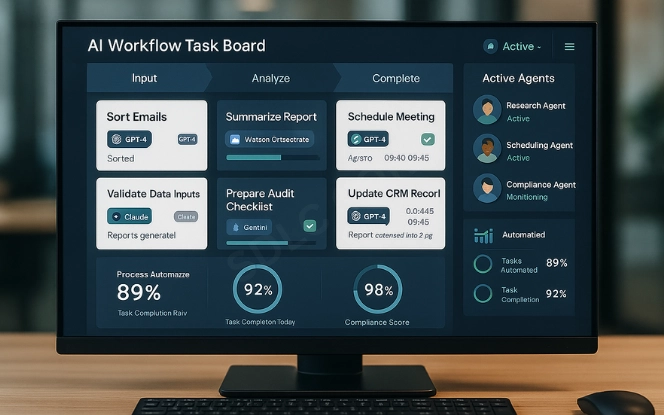
AI-driven task management gives organizations a way to balance workloads without bottlenecks. Instead of manual allocation, AI systems assign tasks to the right person or agent based on urgency and capacity.
For project teams, this creates clarity. High-priority work moves forward automatically, updates are logged instantly, and managers have full visibility without chasing status reports. As a result, teams save time and deliver results with greater precision.
Intelligent Process Automation with AI
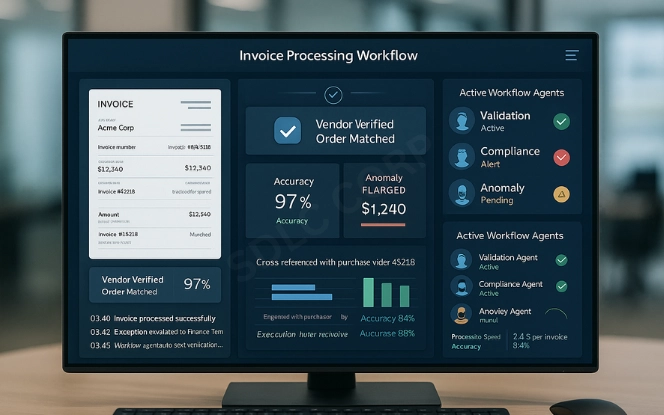
Intelligent process automation with AI goes beyond simple scripts. It uses natural language processing, predictive analytics, and adaptive models to handle complexity.
Consider invoice processing. A basic automation extracts numbers. Intelligent automation cross-validates vendor details, matches entries to purchase orders, and flags anomalies for review. This type of automation supports trust and scalability while reducing operational risks.
AI Agent Workflow Orchestration
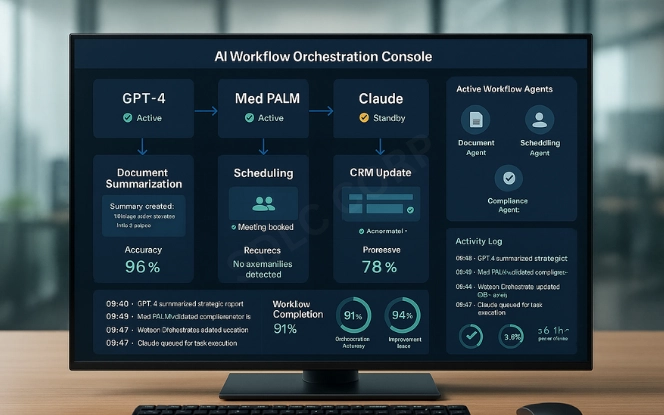
As workflows grow more complex, orchestration ensures coordination. AI agent workflow orchestration assigns responsibilities between different agents—such as scheduling, compliance, or reporting—so they work together without duplication.
This structure guarantees traceability. Each agent’s role is logged, outputs are verifiable, and compliance audits are easier to manage. For industries with strict regulatory requirements, orchestration makes automation usable and trustworthy.
Challenges of Autonomous AI Workflows

The promise of autonomous workflows comes with challenges that require attention.
- Data quality: Poor or incomplete inputs lead to flawed outcomes.
- Over-dependence: Organizations still need human oversight for critical tasks.
- Security: Sensitive data must be protected at all stages.
- Adoption: Staff require training to trust and manage AI-driven systems.
Businesses that address these challenges with structured governance frameworks see the most success.
The Future of Autonomous Business Process AI

The next phase of automation will make systems more context-aware and predictive. Instead of reacting, workflows will anticipate business needs.
Emerging trends include:
- Cross-platform orchestration that spans multiple enterprise systems.
- Embedded predictive insights for decision support.
- Built-in compliance safeguards aligned with new regulations.
- Transparency tools that build user trust.
These developments will make autonomous AI workflows even more central to business operations.
Ethical and Governance Considerations

Ethical deployment is essential. Transparency in workflow design ensures that employees and stakeholders understand how decisions are made. Audit trails and override functions maintain accountability.
Human-in-the-loop mechanisms keep people involved in sensitive or high-stakes processes. This ensures that automation remains a tool for empowerment rather than unchecked control.
By balancing automation with ethical oversight, businesses can scale responsibly.
Conclusion
Autonomous AI workflows are redefining how organizations run. From finance to healthcare, these workflows reduce errors, improve efficiency, and create space for human teams to focus on innovation.
AI workflow automation shows its strength by aligning routine operations with long-term goals. Autonomous business process AI delivers measurable value without sacrificing trust or accountability.
Contact us SDLC corp to learn how tailored solutions can help your organization adopt these systems responsibly. To take the next step, Hire AI Development Services with SDLC Corp and explore how tailored solutions can transform your organization.
FAQs
What Are Autonomous AI Workflows and Why Do They Matter?
Autonomous AI workflows are self-managed processes where AI handles tasks from input to execution. They matter because they combine speed and accuracy, enabling organizations to operate more effectively with fewer errors.
How Does AI Workflow Automation Improve Business Efficiency?
AI workflow automation eliminates repetitive manual work and ensures tasks move faster. By doing so, businesses achieve cost savings, improved compliance, and smoother operations.
What Is Autonomous Business Process AI in Practice?
Autonomous business process AI refers to intelligent systems that manage workflows end-to-end, from analyzing inputs to delivering outputs. This improves accuracy and ensures compliance across industries like finance, healthcare, and logistics.
How Can AI-Driven Task Management Support Teams?
AI-driven task management prioritizes responsibilities, assigns resources, and ensures updates flow across teams. This reduces delays and helps projects progress without bottlenecks.
What Role Does AI Agent Workflow Orchestration Play in Modern Companies?
AI agent workflow orchestration coordinates multiple AI agents, such as scheduling, compliance, or reporting, ensuring processes remain efficient, traceable, and aligned with business objectives.











