Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the way Human Resources (HR) operates. Partnering with an AI consulting company can help HR leaders adopt these technologies strategically. From recruitment to compliance, AI is making processes smarter, faster, and more data-driven. To understand the difference between AI and algorithms, it’s important to see how these concepts apply to HR decision-making.
But with opportunity comes responsibility HR leaders must ensure AI adoption balances efficiency with fairness, transparency, and a human touch. In this blog, we explore how AI in HR is being used today, the benefits it delivers, the challenges organizations must manage, and a practical roadmap for responsible adoption in 2025.
Core AI Systems Supporting HR Operations
HR platforms rely on structured data pipelines, secure access controls, and reliable analytics. These foundations are often implemented through broader AI development services that integrate AI features into existing HRMS, ATS, and payroll systems.
Current Adoption and Why AI Matters in HR
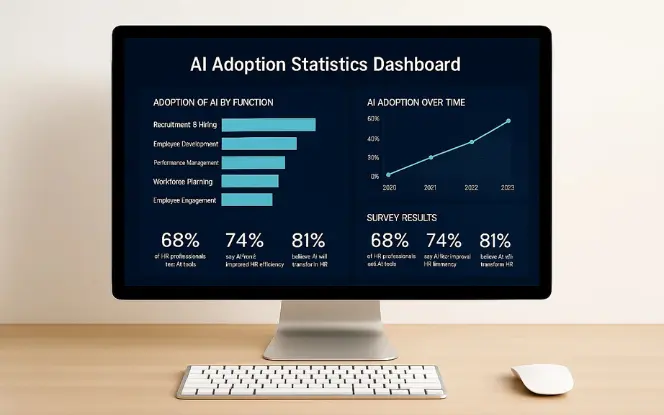
Recent industry research highlights how fast AI adoption is accelerating in human resources:
Around one in four HR managers already use AI-driven HR tools (e.g., for recruiting and automation).
Roughly 7 in 10 professionals believe AI will shape the future of HR over the next five years.
A majority of HR leaders (70%+) are actively exploring AI adoption, with talent acquisition as the primary focus.
However, only a small fraction (less than 5%) have fully integrated generative AI into their HR processes.
This shows enthusiasm but also caution. Most companies begin with recruitment automation, but few extend AI into compliance or performance management. To keep pace, many organizations turn to AI/ML implementation services that can help them adopt scalable solutions. At the same time, HR professionals can stay informed by following the top AI and ML trends reshaping the future to understand how the technology is evolving across industries.
How HR Uses AI Today
AI is no longer just a future concept it’s already embedded in everyday HR functions. From smarter recruitment and personalized onboarding to real-time performance tracking and compliance monitoring, AI is reshaping the entire employee lifecycle. By turning HR data into actionable insights, it helps leaders make faster, fairer decisions and focus more on culture, leadership, and strategy. Below are the key areas where AI is making the biggest impact:
Recruitment and Hiring
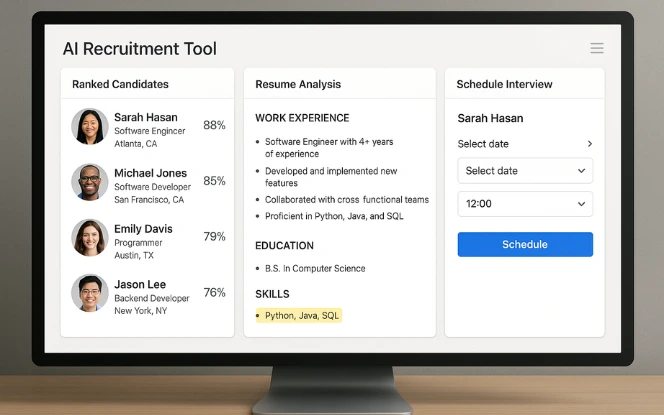
Recruitment is the most common entry point for AI adoption. HR departments use AI to:
Screen resumes and applications: Algorithms quickly scan thousands of applications to highlight the most qualified candidates. To better understand the difference between AI and algorithms, it’s helpful to see how they work together in resume screening.
Chatbots for candidate support: Virtual assistants answer candidate queries, provide updates, and even schedule interviews. Many of these innovations reflect the top AI and ML trends reshaping the future across industries.
Predictive scoring: AI models assess job fit by analyzing skills, experience, and responses.
Candidate communication: Personalized updates and automated emails improve candidate engagement.
These applications reduce time-to-hire while also making the recruitment process more consistent and candidate-friendly. For organizations ready to scale, partnering with expert AI/ML implementation services ensures these solutions are adopted effectively and responsibly
Onboarding and Training
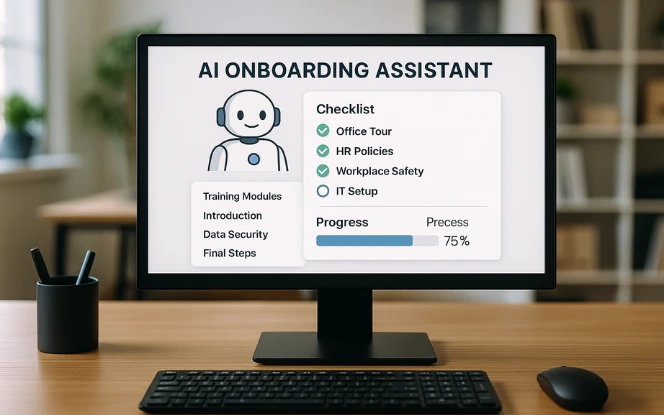
Onboarding often sets the tone for an employee’s experience. AI improves it by:
Guiding new hires through forms, policies, and FAQs via chatbots. This is part of a wider movement where AI in media and entertainment and other industries shows how chatbots and automation enhance user engagement.
Drafting job descriptions, offer letters, and internal documents using generative AI. Organizations looking to adopt this at scale often partner with expert teams to hire generative AI developers who can customize solutions for HR needs.
Customizing training paths based on an employee’s role and skill profile.
Example: Some companies report that AI-powered onboarding platforms improved new-hire experiences by more than 60%, mainly because employees received faster responses and more tailored guidance. This aligns with generative AI for social impact organizations, where personalization and accessibility are also key benefits.
Employee Engagement and Retention
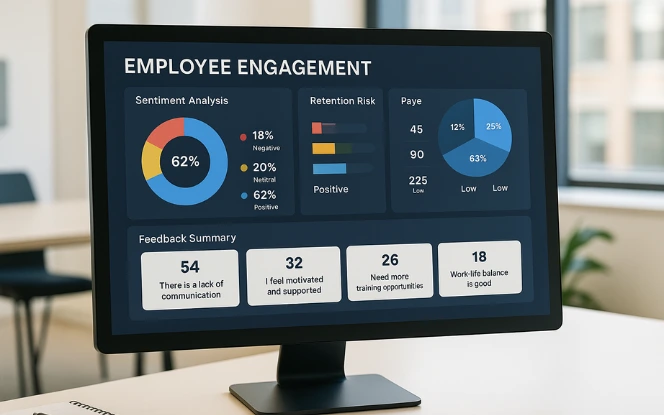
Retention is a growing challenge, and AI helps HR teams predict and prevent attrition.
Data analysis: AI reviews performance scores, feedback, and tenure data to identify employees who may be at risk of leaving. Businesses can learn from the top AI and ML trends reshaping the future to see how predictive analytics is being applied across industries.
Targeted action: Managers can offer personalized support, flexible schedules, or development programs based on these predictions. Many organizations also work with an experienced AI consulting company to design and implement engagement strategies powered by AI.
Wellness personalization: AI systems deliver nudges reminding employees to use benefits or wellness resources.
This shifts HR from reactive to proactive, improving both engagement and retention while ensuring employees feel valued and supported.
Compliance and Risk Management
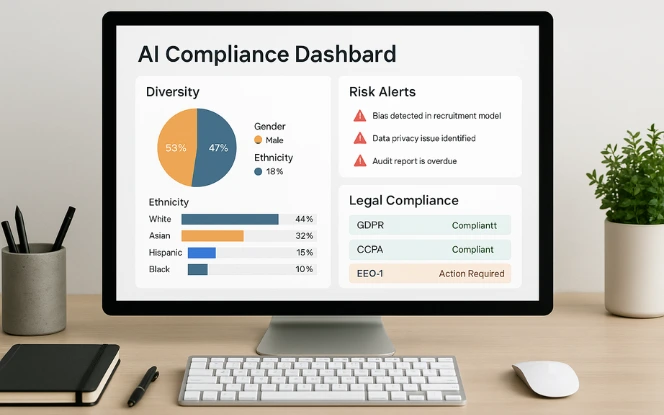
Compliance tasks are often time-consuming, but AI reduces the burden. HR teams use AI to:
Monitor labor law changes automatically. Organizations that adopt AI/ML implementation services can streamline compliance workflows and integrate automation into broader HR systems.
Flag diversity, equity, and pay compliance issues. Similar approaches are being applied in generative AI for social impact organizations, where fairness and transparency are equally critical.
Track training completion for mandatory programs.
Generate audit-ready compliance reports.
By automating these processes, HR reduces human error while keeping pace with evolving regulations.
Performance Management
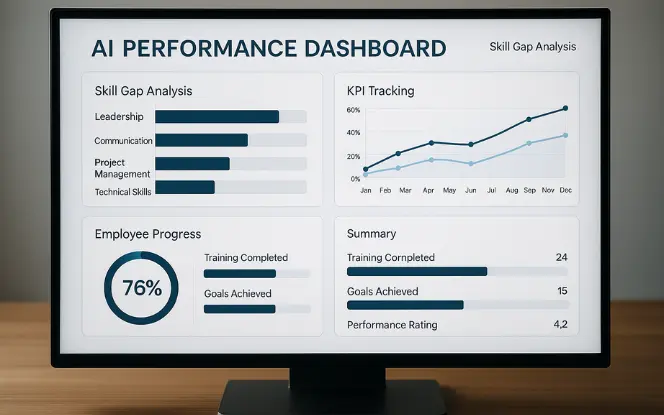
Performance reviews are no longer limited to annual meetings. AI supports continuous performance management by:
Collecting data from projects, collaboration tools, and peer reviews. This mirrors how industries like generative AI in manufacturing startups use data-driven insights to optimize efficiency and outcomes.
Identifying strengths and areas for improvement in real time. By aligning with the top AI and ML trends reshaping the future, HR teams can better understand how predictive and generative models will shape performance tracking.
Recommending personalized training or mentorship programs.
This approach makes performance management more transparent, fair, and future-focused, ensuring employees receive continuous support and growth opportunities.
Offboarding

AI helps with exit surveys, deactivating system access, and managing knowledge transfer. However, HR experts warn against full automation. Offboarding often involves sensitive conversations, where empathy and human judgment matter most.
Benefits of AI in HR
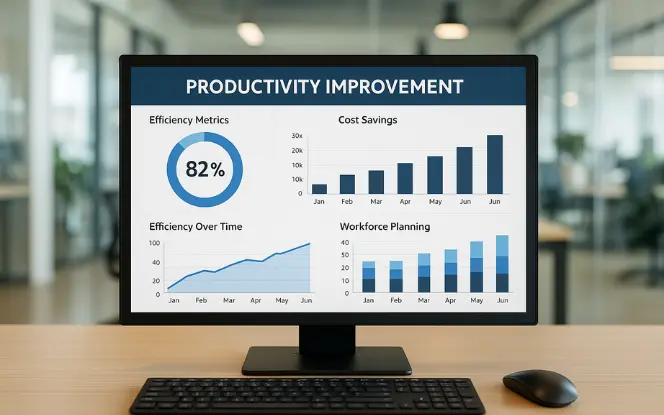
The advantages of AI in HR go beyond time savings. They shape strategy and workforce experience.
1. Efficiency and Productivity
By automating tasks like resume screening, interview scheduling, and compliance tracking, AI frees HR professionals to focus on culture, strategy, and engagement. For example, large firms report reductions in time-to-hire by up to 75% after adopting AI tools.
2. Personalization
Employees receive tailored onboarding content, role-specific training, and customized wellness programs. This makes their experience smoother and more engaging.
3. Data-Driven Decisions
AI transforms HR decision-making. Predictive analytics highlight potential attrition, skill gaps, and top performers. HR leaders gain the ability to act based on data, not guesswork.
4. Scalability
Whether it’s managing thousands of applications during hiring season or monitoring compliance across multiple regions, AI scales processes without requiring large increases in staff.
Challenges and Risks

Despite the benefits, AI in HR introduces critical risks:
Bias and discrimination: AI models trained on biased data can perpetuate unfair hiring or promotion patterns.
Data privacy: Sensitive employee information must be stored securely and used responsibly. Without safeguards, trust is lost.
Ethical concerns: Automating layoffs or promotions without human review risks reputational damage.
Regulatory landscape:
In the U.S., a 2023 executive order requires agencies to assess AI’s impact on privacy, equity, and civil rights.
The EU AI Act, adopted in March 2024, introduces strict rules for “high-risk” applications such as recruitment and employee evaluation. Its provisions will begin taking effect from 2025 onward, making compliance a priority for HR leaders across Europe. [EU Parliament, 2024]
Loss of human touch: Over-reliance on AI risks depersonalizing HR, especially in areas like offboarding and conflict resolution.
Best Practices for Adopting AI in HR
To maximize benefits and reduce risks, HR leaders should follow structured practices:
Define a clear strategy: Identify high-value use cases such as recruiting or onboarding before scaling AI further. Reviewing the top AI and ML trends reshaping the future can help leaders prioritize areas where AI will have the greatest impact.
Choose tools wisely: Select AI systems that integrate with existing HR tech and meet data-protection standards. Partnering with an experienced AI consulting company ensures that chosen solutions align with compliance and business goals.
Train HR teams: Equip staff with AI literacy, covering both technical and ethical use.
Monitor and audit regularly: Ensure fairness and compliance through ongoing audits. This approach mirrors the practices seen in generative AI for social impact organizations, where transparency and accountability are central.
Be transparent with employees: Clearly communicate how AI is used, what data is collected, and why.
Balance automation with empathy: Keep human oversight in sensitive processes like performance reviews and exits.
A 90-Day Roadmap for AI Adoption
A phased roadmap helps HR adopt AI responsibly:
Days 0–15: Define goals, select pilot use cases (e.g., resume triage, chatbot onboarding), and audit data quality.
Days 16–45: Run small pilots, gather user feedback, and refine workflows.
Days 46–75: Evaluate pilot outcomes, conduct fairness and compliance audits, and strengthen data governance.
Days 76–90: Scale adoption to more HR processes, provide staff training, and publish transparent AI-use policies.
This approach reduces risks and ensures smoother integration.
Popular AI Tools in HR
AI adoption in HR is being accelerated by a range of specialized platforms that streamline different stages of the employee lifecycle. For recruitment, tools like HireVue, Pymetrics, and Eightfold AI use predictive analytics and behavioral assessments to identify the best candidates quickly and fairly. Enterprise solutions such as Workday and SAP SuccessFactors bring automation to onboarding, payroll, and performance tracking, helping HR teams work more efficiently while reducing manual errors.
Organizations exploring these solutions often benefit from expert AI/ML implementation services to ensure smooth integration into existing systems.
To strengthen engagement and retention, platforms like CultureAmp and Peakon provide real-time sentiment analysis, enabling proactive action on employee satisfaction. Compliance-focused tools including UKG Pro and ADP DataCloud further support HR leaders by monitoring diversity, equity, and regulatory obligations. Choosing the right mix of these technologies, often with guidance from an experienced AI consulting company, ensures AI adoption in HR is not just efficient but also fair, transparent, and people-centered.
The Future of AI in HR
Over the next five years, AI will evolve from automating routine tasks to supporting strategic HR decisions. Generative AI will create HR communications at scale, predictive analytics will guide workforce planning, and AI “co-bots” may work alongside employees.
HR professionals will need new skills, including:
Data literacy and AI governance to oversee technology responsibly.
Ethical leadership to ensure fairness and transparency.
Empathy and communication to balance automation with human relationships.
Rather than replacing HR, AI will elevate it. HR professionals will focus less on paperwork and more on shaping workforce strategy and culture.
What Employees Gain from AI in HR
AI in HR doesn’t just benefit managers it also enhances the employee experience. Chatbots can instantly answer payroll, leave, and policy-related questions, reducing frustration and wait times. AI-powered onboarding platforms provide step-by-step guidance to new hires, ensuring a smoother start and faster integration into the workplace. These applications mirror the impact of generative AI for social impact organizations, where fairness, inclusion, and accessibility are central to adoption.
Employees also gain from personalized career development supported by AI. Intelligent systems recommend training programs, mentorship opportunities, and internal job openings based on individual skills and career goals. Wellness platforms even send nudges about benefits and health resources, helping employees feel supported and valued. Organizations looking to build tailored employee-centric solutions can hire generative AI developers to design custom tools that boost engagement, growth, and satisfaction.
Enterprise-Scale HR AI Solutions
Large organisations require AI systems that operate across departments and regions. Solutions informed by an enterprise AI development company help support role-based access, cross-location analytics, and standardised HR reporting.
Conclusion
AI is redefining HR in 2025. From recruitment to compliance, it saves time, improves decision-making, and personalizes employee experiences. Its promise lies in freeing HR professionals to focus on strategy, leadership, and culture. Exploring the top AI and ML trends reshaping the future can help HR teams stay aligned with how technology is evolving across industries.
Yet, AI is not without risks. Bias, privacy concerns, and over-automation can damage trust and compliance if not managed carefully. Partnering with a trusted AI consulting company ensures organizations adopt AI responsibly with governance, fairness, and ethical use at the forefront.
Done thoughtfully, AI will not replace HR it will strengthen it, creating workplaces that are efficient, fair, and people-centered. For HR leaders ready to take the next step, working with expert teams to hire generative AI developers can accelerate innovation and deliver tailored solutions for tomorrow’s workforce.
FAQs
1. What is AI in HR?
AI in HR refers to the use of technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and generative AI to support HR functions. It is applied in recruiting, onboarding, training, compliance, performance management, and employee engagement.
2. How is AI currently used in recruitment?
AI tools scan resumes, rank candidates, answer initial queries through chatbots, and schedule interviews. They reduce time-to-hire and make hiring more consistent while improving the candidate experience.
3. Can AI improve employee engagement?
Yes. AI analyzes performance data and feedback to detect early signs of disengagement or attrition. Based on insights, managers can offer personalized support, flexible work options, or targeted development opportunities.
4. What are the biggest risks of AI in HR?
The most common risks include bias in decision-making, data privacy issues, lack of transparency in automated decisions, and over-reliance on automation that reduces human empathy in HR processes.
5. Will AI replace HR professionals?
AI will not replace HR but will change its focus. Routine tasks like resume screening or compliance reporting can be automated, freeing HR professionals to concentrate on strategy, leadership, and culture. Empathy, communication, and ethical decision-making remain uniquely human strengths.
6. How can organizations adopt AI in HR responsibly?
Adoption should start with a clear plan, choosing the right tools, training HR staff, auditing outputs for bias, and being transparent with employees about data use. Balancing automation with human oversight ensures responsible use.
7. What is the future of AI in HR?
In the next five years, AI will move beyond automation into strategic HR. Generative AI will create HR communications, predictive analytics will guide workforce planning, and HR teams will need new skills in AI governance, data literacy, and ethical leadership.