Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept in media and entertainment. It is actively shaping how stories are written, how movies are produced, how music is composed, and how content reaches audiences worldwide. From personalized recommendations on Netflix and Spotify to automated dubbing and AI-powered video effects, the entertainment industry is in the middle of a digital transformation with support from an AI consulting company.
AI adoption is not just about efficiency; it is about scale, creativity, and global reach. Yet, this rapid growth also raises questions about originality, ethics, and regulation. To understand where the industry is headed, it is important to also look at the top AI and ML trends reshaping the future. In this blog, we break down the market size, technical applications, risks, and future trends of AI in entertainment.
Role of AI in Media and Entertainment Systems
Media and entertainment platforms manage large volumes of content, metadata, and audience interaction data. AI systems can support these environments by analysing content performance, organising digital assets, and assisting with production workflows. Many organisations rely on AI development services to build solutions that integrate with existing content management and distribution systems.
Market Growth of AI in Entertainment
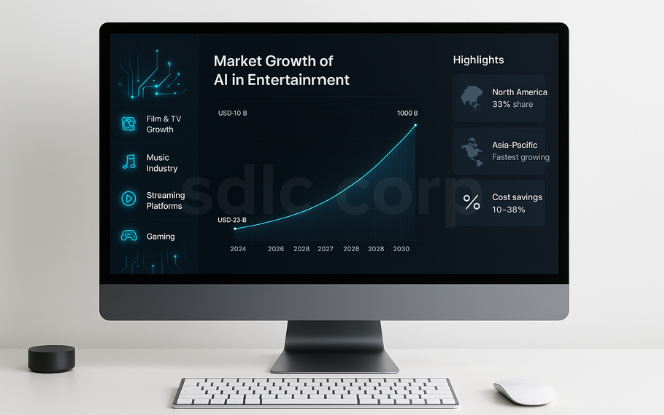
The AI-driven shift in media and entertainment is reshaping how content is created, distributed, and consumed. The market is witnessing strong growth worldwide as studios, streaming platforms, and production houses adopt AI to improve efficiency and creativity.
North America leads the adoption curve, driven by advanced infrastructure and investments from major streaming giants.
Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, with mobile-first audiences and AI-powered localization tools enabling wider global reach.
Cost efficiency is a major driver of adoption, as AI reduces manual workflows in editing, dubbing, and production, helping companies reallocate budgets toward innovation and premium content.
Content personalization is another factor accelerating growth, with recommendation engines and AI-driven analytics keeping users more engaged across platforms.
Overall, the adoption of AI in entertainment is no longer optional it is becoming essential for companies looking to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving global market.
AI Applications in Media and Entertainment
Artificial intelligence is reshaping every segment of the entertainment ecosystem, from film production and music creation to gaming and streaming platforms. Its applications are practical, measurable, and already transforming how content is produced, distributed, and consumed.
From automating video editing and dubbing to generating scripts and visual effects, AI is driving efficiency and creativity at scale. Streaming platforms use recommendation systems to personalize user experiences, while music tools powered by algorithms are changing the way songs are composed and distributed.
Scaling AI Across Media Platforms:
As media companies distribute content across multiple platforms and regions, AI systems must scale reliably. Enterprise-level coordination helps maintain consistency and performance. Practices used by an enterprise AI development company can inform strategies for managing AI across large content libraries and audience bases.
1. AI in Film and TV Production
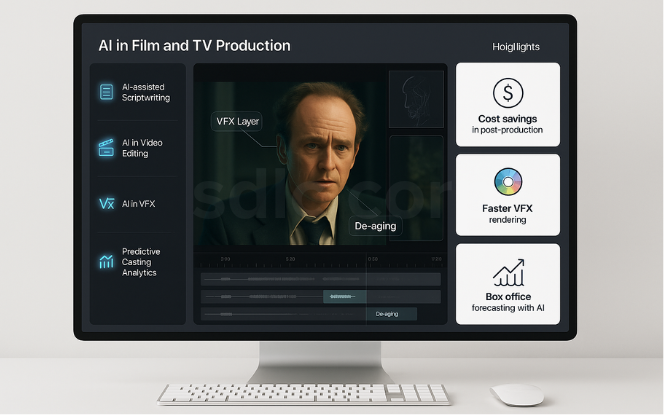
AI is streamlining pre-production, shooting, and post-production.
AI-assisted scriptwriting tools analyze past scripts, audience preferences, and trending genres to suggest dialogue and story arcs.
AI in video editing and VFX reduces production time by automatically generating scenes, de-aging actors, and creating realistic CGI environments.
Studios are also using predictive AI to forecast box-office success and optimize casting choices.scriptwriting.
2. AI in the Music Industry
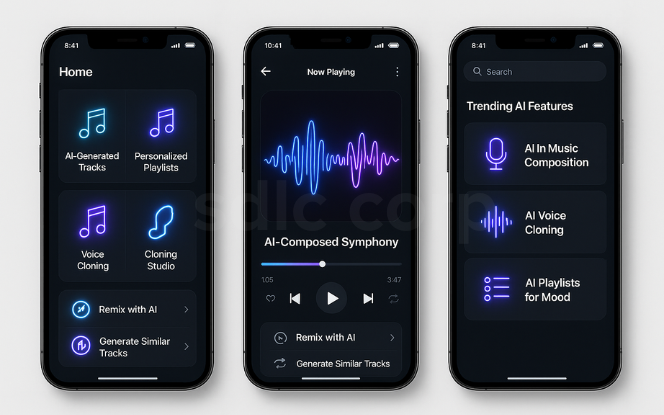
Music creation and personalization are evolving rapidly with AI.
Platforms like AIVA and Amper Music generate royalty-free tracks for films, ads, and games.
AI in composition helps producers experiment with melodies and beats at scale, often supported by AI consulting companies that guide implementation.
Streaming platforms such as Spotify use AI-driven recommendation systems to curate playlists and predict user moods, a trend highlighted in top AI and ML trends reshaping the future.
Voice cloning technology enables artists to release multilingual tracks, but it also raises copyright and ethical concerns.
3. AI in Streaming and Content Discovery
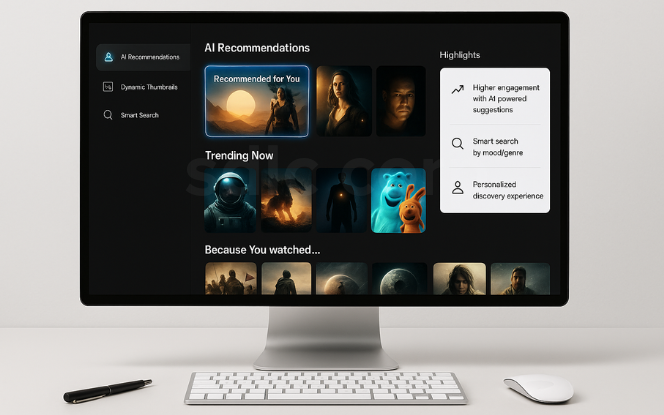
Streaming platforms heavily rely on AI to increase engagement.
Personalized recommendations keep viewers hooked by analyzing watch history and behavior patterns, similar to innovations discussed in top AI and ML trends reshaping the future.
Dynamic thumbnails powered by AI identify which visuals attract more clicks, helping platforms optimize engagement without additional production costs.
Smart search engines allow users to find content with natural language queries like “a thriller with a strong female lead”, an area where businesses often leverage AI and ML implementation services to build advanced search and discovery systems.
4. AI in Localization and Global Reach
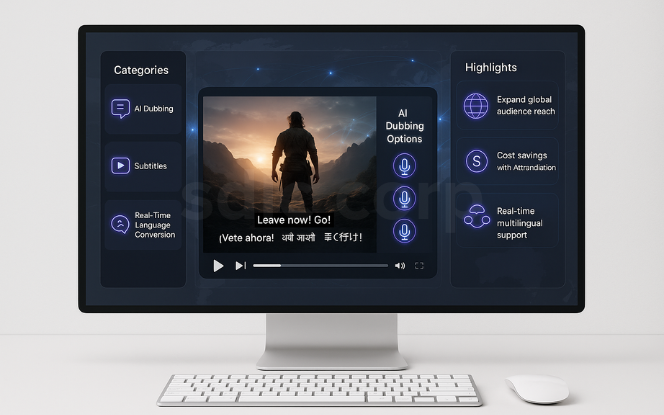
Localization is crucial for global expansion, and AI is making it faster and more affordable.
AI dubbing and subtitles provide near real-time translations, allowing content to launch worldwide simultaneously with support from AI and ML implementation services.
AI-powered localization tools adapt cultural references for different audiences, helping companies expand globally while maintaining relevance.
Example: A platform scaled its reach from 5.5 million to 60 million viewers after deploying AI-driven dubbing across multiple languages a case that highlights how businesses can benefit from expert guidance offered by an AI consulting company.
5. AI in Gaming and Interactive Media
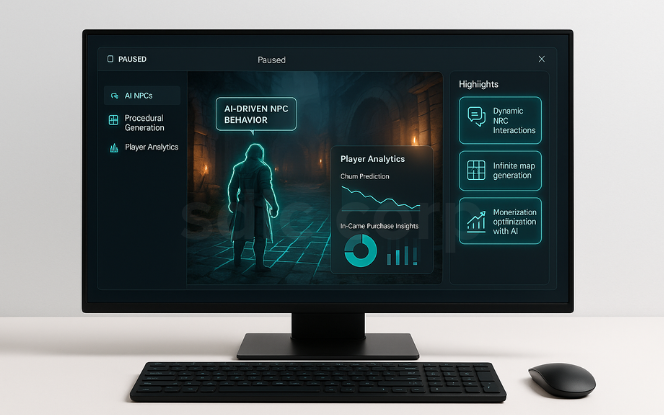
AI is redefining gaming experiences by making them more immersive and dynamic.
AI-driven NPCs (Non-Player Characters) now adapt in real time to player behavior, enhancing gameplay and engagement.
Procedural content generation creates new levels, maps, and quests automatically, an advancement aligned with generative AI in manufacturing startups that also leverage similar automation principles.
AI in player analytics helps studios predict churn, personalize rewards, and optimize in-game purchases, showing parallels with insights found in top AI and ML trends reshaping the future.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
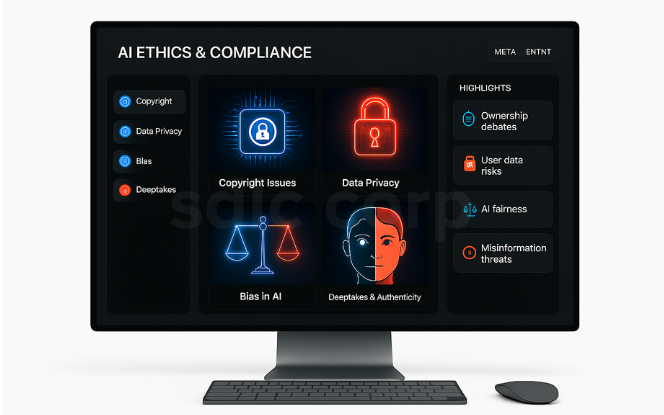
1. Copyright Issues
AI-generated music, scripts, and visuals often rely on copyrighted training data. Lawsuits from authors and musicians demand clearer guidelines on ownership.
2. Data Privacy
Streaming platforms collect vast behavioral datasets. Without strict controls, this creates risks of surveillance, misuse, and regulatory backlash.
3. Bias in AI Models
AI systems may reinforce stereotypes. For instance, facial recognition and voice transcription tools show higher error rates with people of color.
4. Deepfakes and Authenticity
Deepfake technology can create convincing but fake content. While useful in film, it can also spread misinformation if misused.
Regulatory Landscape

- EU AI Act (2024) – The first comprehensive regulation on AI, requiring transparency, risk assessments, and labeling of AI-generated content.
- U.S. State Laws – Tennessee and Utah have introduced rules against unauthorized AI-generated likenesses of performers.
- Industry Standards – Major studios are adopting ethical guidelines for disclosure, watermarking, and responsible AI training.
Future Trends

- Generative AI for Full Content Creation – From script to final cut, AI could soon manage entire production workflows.
- Agentic AI in Media – Autonomous AI agents may run localization, dubbing, and marketing campaigns without human intervention.
- Real-Time Immersive Experiences – Virtual concerts, interactive films, and AR/VR powered by AI will redefine audience engagement.
- Monetization Models – AI will help studios dynamically adjust ad placements, subscription pricing, and content bundles.
FAQs
Q1: What is AI in media and entertainment?
AI in media and entertainment refers to using artificial intelligence to enhance content creation, distribution, and personalization. Examples include AI video editing software (Runway, Adobe Sensei), AI dubbing tools (Papercup, Deepdub), and recommendation engines used by Netflix and Spotify.
Q2: How is AI used in film and TV production?
AI is streamlining film and TV workflows by automating editing, script generation, dubbing, and special effects. Tools like Synthesia (AI video creation), Runway (AI-powered editing and VFX), and Adobe Sensei (smart editing and tagging) are widely adopted in production pipelines.
Q3: What role does AI play in streaming platforms?
AI powers personalized recommendations, A/B testing of thumbnails, and viewer engagement strategies. Platforms like Netflix and Spotify use machine learning for playlist curation, while AI also assists in ad targeting, viewer churn prediction, and content performance analytics.
Q4: How does AI improve localization in entertainment?
AI makes global content distribution faster and more affordable. It supports AI dubbing (Papercup, Deepdub), real-time translation, and cultural adaptation so that jokes, idioms, and references resonate with regional audiences. This helps platforms scale worldwide with minimal delays.
Q5: What are the risks of AI in entertainment?
The risks include copyright challenges, data privacy issues, and deepfake misuse. There are also concerns about job displacement among writers, musicians, and editors. Ethical adoption requires disclosure practices, strong copyright frameworks, and regulations to protect creators.
Q6: What is the future of AI in entertainment?
The future of AI in entertainment lies in generative AI for content creation, immersive AR/VR storytelling, and new monetization models powered by audience data. AI will also play a key role in interactive media and hyper-personalized experiences while maintaining a balance with human creativity.
Q7: Can AI replace human creativity or writers?
AI can assist with writing scripts, generating music, or creating visual effects, but it cannot fully replace human creativity. Storytelling, emotional depth, and cultural nuance still require a human touch. The most successful applications of AI in entertainment come from collaborations between humans and AI tools, where machines handle repetitive tasks and humans focus on originality and vision.
Q8: Which AI tools are used in entertainment today?
Popular AI tools in entertainment include:
Runway (AI video editing and VFX)
Synthesia (AI video generation with avatars)
Adobe Sensei (smart editing and tagging)
Papercup / Deepdub (AI dubbing and translation)
AIVA / Amper Music (AI music composition)
Netflix & Spotify AI engines (recommendations and personalization)
These tools show how AI supports different aspects of content production, distribution, and user engagement.