Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved from an academic concept in the 1950s into a global force driving innovation across industries. Pioneers like Alan Turing and the 1956 Dartmouth Conference laid its foundation, and today AI powers breakthroughs in big data, robotics, automation, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
From diagnosing diseases to enabling self-driving cars and generative tools like ChatGPT, AI is reshaping business and daily life. With 42% of large companies already using AI as of 2024, its influence is undeniable and the next chapter promises even greater transformation.
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
AI has evolved from rule-based systems to data-driven models capable of learning patterns at scale. Advances in computing power, data availability, and algorithms have enabled broader adoption across industries.
In many phases of this evolution, AI development services have supported the transition from experimental models to production-ready systems.
The Birth of AI (1950s–1970s)
The foundations of AI began with Alan Turing’s famous question: “Can machines think?” His Turing Test, proposed in 1950, became the first benchmark for evaluating machine intelligence.
The 1956 Dartmouth Conference, often called the “birth of AI,” brought together pioneers such as John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Allen Newell. They envisioned machines capable of human-like reasoning, sparking decades of research.
During this era, AI systems were rule-based, relying on explicit instructions and symbolic logic. While groundbreaking, these early programs struggled with ambiguity and scalability.
The AI Winters (1970s–1990s)
As expectations soared, progress slowed. Funding cuts and overpromised results led to two major “AI winters”, where interest and investment declined.
Key challenges included:
Limited computing power – technology couldn’t support complex AI models.
Over-reliance on rules – early systems couldn’t adapt to real-world variability.
High costs – AI research required resources most institutions lacked.
The Machine Learning Revolution (1990s–2010s)
The Deep Learning Era (2010s–Present)
The revival came with the rise of machine learning (ML) algorithms that learn patterns from data instead of rigid programming. With better hardware and the internet fueling data availability, AI entered a new era.
Notable milestones:
1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeated chess champion Garry Kasparov.
2011: IBM’s Watson won Jeopardy! against top human contestants
ML expanded AI’s capabilities in speech recognition, recommendation engines, and fraud detection.
Deep learning, powered by multi-layered neural networks, took AI further. These systems excel at processing vast amounts of unstructured data (images, text, audio).
Key breakthroughs:
2012: Deep learning models revolutionized image recognition at the ImageNet competition.
2016: Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated world Go champion Lee Sedol, proving AI’s ability to master highly complex strategy games.
2018–2023: Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and GPT-4 enabled AI chatbots capable of generating human-like text.
Generative AI: Tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and MidJourney brought AI creativity into the mainstream.
Key Technologies Powering AI
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language both spoken and written.
How it works: NLP models analyze syntax, semantics, and context in language, making communication between humans and computers seamless.
Real-world examples:
Chatbots & Virtual Assistants: Tools like ChatGPT, Siri, and Google Assistant understand user queries and provide relevant answers.
Language Translation: Google Translate breaks down global communication barriers.
Why it matters: With NLP, businesses enhance customer experience, improve accessibility, and automate complex tasks like summarizing documents or analyzing sentiment.
Also Read : What is NLP Invoices Processing?
2. Quantum AI – The Next Frontier

Quantum computing has the potential to supercharge AI by processing data exponentially faster.
Applications include:
Drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions.
Global supply chain optimization.
Climate modeling and advanced simulations.
Quantum AI is in its early stages but may define the next generation of technological progress.
3. Computer Vision
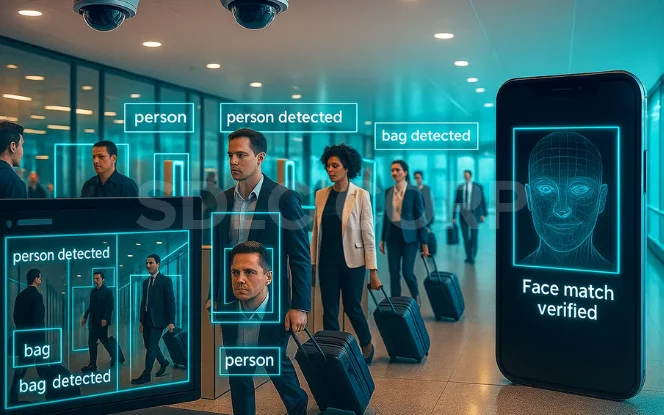

Computer Vision allows machines to see and interpret the visual world, similar to human sight.
How it works: AI models process and analyze images or video frames using deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
Real-world examples:
Healthcare: AI-driven medical imaging detects tumors or anomalies faster than human radiologists.
Automotive: Self-driving cars rely on computer vision to recognize traffic signs, pedestrians, and road hazards.
Security: Facial recognition is widely used in airports and mobile devices.
Why it matters: Computer Vision is essential for industries where visual accuracy, safety, and automation are critical.
Explore More Insights: Computer Vision in Sports and the Future of Player Tracking
4. Robotics & Automation
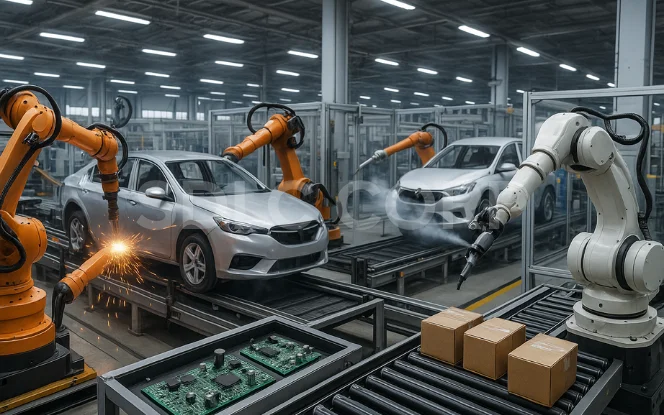

Robotics powered by AI combines physical machines with intelligent decision-making. These systems not only perform tasks but also adapt to changing environments.
How it works: AI integrates with sensors, actuators, and control systems to create robots that can interact with the physical world.
Real-world examples:
Manufacturing: Industrial robots assemble products with precision.
Logistics: AI robots sort and deliver packages (Amazon warehouses use Kiva robots).
Healthcare: Surgical robots assist doctors in performing complex, minimally invasive procedures.
Why it matters: AI-driven robotics improves efficiency, safety, and scalability in industries that require repetitive, high-precision, or dangerous tasks.
Explore More: Generative AI for Home Automation Made Simple
5. Generative AI

Generative AI is one of the most revolutionary AI advancements in recent years. Unlike traditional AI, it doesn’t just analyze data—it creates new content.
How it works: Generative models, like GPT (text), DALL·E (images), and MusicLM (music), learn from vast datasets to generate original text, visuals, audio, or even code.
Real-world examples:
Content Creation: Writing blogs, social media captions, and marketing copy.
Design: Creating logos, product mockups, or entire website layouts.
Entertainment: AI-generated art, videos, and music compositions.
Why it matters: Generative AI is changing how we create, design, and innovate, enabling professionals to work faster, scale creativity, and experiment without heavy costs.
Also Read Our Blogs:
Applications of AI Across Industries
AI in Healthcare
AI enhances diagnosis, drug development, and patient care.
Google DeepMind’s AI detects eye diseases with expert-level accuracy.
AI accelerates drug discovery, saving billions in R&D costs.
Virtual health assistants monitor patients remotely.
Explore more about how AI is transforming healthcare in our blog on AI for Healthcare.
Learn how innovation is driving the future of medicine in Generative AI for Healthcare.
AI in Finance
In finance and banking, AI-powered software helps institutions detect fraud by spotting anomalous transactions in real-time. It can conduct rapid risk assessments and even approve loans by evaluating customer data. Stock traders leverage machine learning to crunch millions of data points and make informed investing decisions quickly. The result is a financial sector that’s faster, more data-driven, and (ideally) more secure.
AI for Finance: See how AI is transforming fraud detection, customer service, and banking efficiency.
Generative AI for Finance: Explore how generative AI is reshaping investments, trading, and risk analysis.
AI in Transportation
Tesla and Waymo are testing autonomous cars.
AI-powered logistics systems optimize routes.
Amazon uses AI robots in warehouses.
AI in Media and Journalism
Journalism is also embracing AI, and its influence will only grow. For instance, The Associated Press uses Automated Insights to generate thousands of earnings reports each year. However, with the rise of generative AI writing tools like ChatGPT, new questions are emerging about their role in journalism.
What’s Next for AI?
Generative AI Everywhere
Generative AI will continue to evolve and expand into nearly every industry:
Content Creation at Scale: AI will generate blogs, marketing campaigns, research reports, and even scripts for film and television.
Design and Creativity: Tools like MidJourney and DALL·E will reshape graphic design, advertising, and product prototyping.
Software Development: AI will increasingly assist developers by writing and debugging code.
Risks and Challenges:
Spread of deepfakes and misinformation.
Questions around intellectual property and originality.
The need for global regulations to ensure ethical use.
Also Read : What Is Generative Ai
Autonomous Vehicles & Robotics
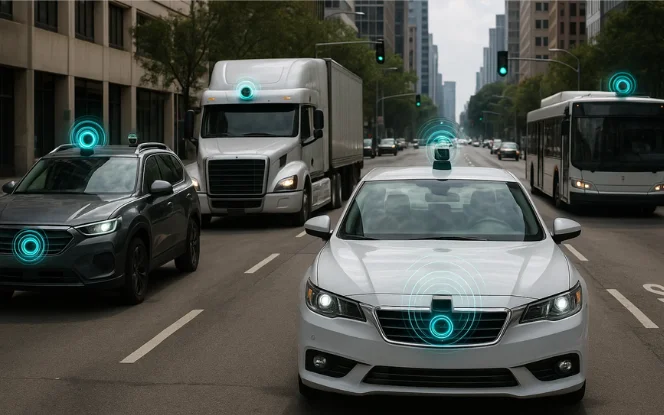

AI-powered autonomy is set to dominate the physical world:
Self-Driving Vehicles: Cars, trucks, and buses powered by AI will reduce human error and improve traffic safety.
Agriculture: Autonomous tractors, harvesters, and drones will increase crop efficiency while reducing labor costs.
Logistics and Delivery:
Drones for rapid package delivery.
Warehouse robots streamlining order fulfillment (e.g., Amazon).
Healthcare Robotics: Robots assisting in surgeries and patient care, improving precision and outcomes.
Industrial Automation: Smarter factory robots that can work alongside humans in collaborative environments.
Also Read : Autonomous AI Workflows
Workforce Transformation
AI will significantly reshape the global workforce:
Job Automation: Repetitive, manual, and rule-based tasks will increasingly be automated.
New Careers: Rising demand for roles in:
AI ethics and governance
Data science and machine learning engineering
AI product management and human-AI collaboration
Upskilling Needs: Workers will require ongoing training in digital literacy, data analytics, and human-AI collaboration.
Impact on Industries:
Customer support → AI chatbots handling queries.
Healthcare → AI-assisted diagnostics.
Finance → AI-driven risk assessment and fraud detection.
Ethical AI and Regulation
As AI systems become more powerful, ethical use and oversight are critical:
Key Concerns:
Algorithmic bias leading to unfair outcomes.
Data privacy violations through unregulated use of personal information.
Lack of explainability in complex models.
Regulatory Developments:
Governments introducing AI Bills of Rights and AI-specific legal frameworks.
The EU’s AI Act setting global standards for accountability.
Industry-wide push for transparency and fairness testing.
Corporate Responsibility: Companies embedding ethics-by-design and ensuring AI tools are tested for inclusivity.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Quantum AI may redefine the limits of computation:
Why Quantum Matters: Quantum computers can process massive datasets simultaneously, far surpassing classical computing.
Potential Applications:
Medicine: Simulating molecular interactions for drug discovery.
Logistics: Optimizing global supply chains and resource allocation.
Climate Science: Modeling complex weather and environmental systems.
Cybersecurity: Developing unbreakable encryption (and posing new risks).
Current Limitations:
Quantum hardware is still in experimental stages.
High costs and limited availability restrict mainstream use.
Future Outlook: When combined with AI, quantum systems could solve problems previously deemed intractable, ushering in a new technological revolution.
Risks and Dangers of AI
Job Losses
Data Privacy
Automated Weapons
Superior Intelligence to Humans
Major AI Milestones in History
GPT-5 Release (August 2025)
First Global AI Safety Summit (November 2023)
ChatGPT Launch (November 2022)
Conclusion
AI evolution is shaped by regional infrastructure, regulation, and investment priorities. References to AI development services in the US illustrate how regional ecosystems influence AI deployment strategies and innovation trajectories.
Conclusion
From its humble beginnings in the 1950s to today’s smart assistants and self-driving cars, the evolution of artificial intelligence has been extraordinary. With technologies like machine learning, deep learning, and generative AI, it now influences industries as diverse as healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment. Looking forward, AI will become more creative, autonomous, and seamlessly integrated into daily life. At the same time, ethical challenges, data privacy, and workforce adaptation must be addressed responsibly.
As someone who has closely studied and written about AI trends, I believe the key lies in responsible innovation ensuring AI empowers people, enhances industries, and advances society without compromising trust. The future of AI is not only about technological breakthroughs, but also about how wisely we choose to guide them.
Related Blogs You Should Explore:
FAQ'S
How has artificial intelligence evolved over time?
What are the main technologies driving AI today?
Key technologies include:
Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Computer Vision
Robotics
Generative AI
Quantum AI
What does the future of AI look like?
How does AI compare to human intelligence?
AI will automate many repetitive and routine tasks, but it is also expected to create new roles in AI development, data science, robotics, and ethics. Instead of replacing humans, AI will augment skills and transform the nature of work.
How does AI compare to human intelligence?
What is the future of AI in 2025 and beyond?
AI will become more integrated into daily life and industries. We will see:
Smarter virtual assistants
Wider use of autonomous vehicles
Growth of AI in healthcare for personalized treatments
Advances in Quantum AI for faster problem-solving
Stronger focus on AI ethics, privacy, and governance