Introduction
Farming has always been the backbone of human survival. Every meal we eat begins with the efforts of farmers. However, modern agriculture is facing more challenges than ever before. Farmers must deal with rising costs, uncertain weather, shrinking farmland, and the urgent need to produce more food for a growing population. Old methods alone are not enough anymore.
This is where technology steps in. Among the many new tools, Generative AI for Agritech is one of the most promising. Unlike regular AI that only looks at old data, generative AI can create new ideas and simulate possible outcomes. It is like having a smart farming partner who suggests the best choices before a seed is even planted. By using this technology, farmers can plan better, reduce risks, and farm in a sustainable way. If you are wondering what is generative AI, it is an advanced type of artificial intelligence that not only analyzes data but also generates predictions and recommendations.
way.
Application of Generative AI in Agritech Systems
Agritech platforms manage data from sensors, satellite imagery, weather feeds, and farm operations. Generative AI can support these systems by summarising field data, generating reports, and assisting with crop planning insights. Many organisations explore Generative AI development services to build models that adapt to agricultural data formats and seasonal variability.
1.How Generative AI for Agritech Works
Generative AI works by studying huge amounts of data and then generating new results from it. When applied to farming, it takes in soil quality reports, crop history, satellite images, and weather patterns. Then, it creates predictions and recommendations.
For example, let’s say a farmer in India wants to plant wheat.
Generative AI can:
- Suggest the right type of wheat seed for the region.
- Predict how much water will be needed at different growth stages.
- Recommend fertilizers and when to apply them.
- Warn about possible pest risks based on past outbreaks.
- Estimate the final yield under different weather conditions.
Because of this, farmers can make informed choices rather than relying on trial and error.
Another way it works is through simulations. AI can create a “virtual farm” and test multiple scenarios without touching the soil. This helps farmers prepare for extreme weather, drought, or even market demand shifts.
2.Real-Life Uses of Generative AI in Farming

Generative AI is already moving from labs into real farms. Here are some real-world uses:
- Precision Farming: In the U.S., some farms use AI sensors to water crops only where needed. This saves millions of gallons of water.
- Weather Predictions: In Africa, AI-powered systems help small farmers know when rain will come. This is life-changing where rainfall is unpredictable.
- Smart Irrigation: AI-based drip systems in Israel help farmers grow more with less water.
- Supply Chain Forecasting: In Europe, AI predicts food demand and helps reduce waste in supermarkets.
- Crop Breeding: Scientists use AI to design stronger crop types that can survive droughts or pests.
These examples show that generative AI is not just theory. It is already making farming more modern and reliable.
3.Benefits of Generative AI for Agritech
The benefits of Generative AI for Agritech are already becoming visible. Farmers, businesses, and even governments are using it to solve long-standing challenges.
3.1 Better Crop Yields
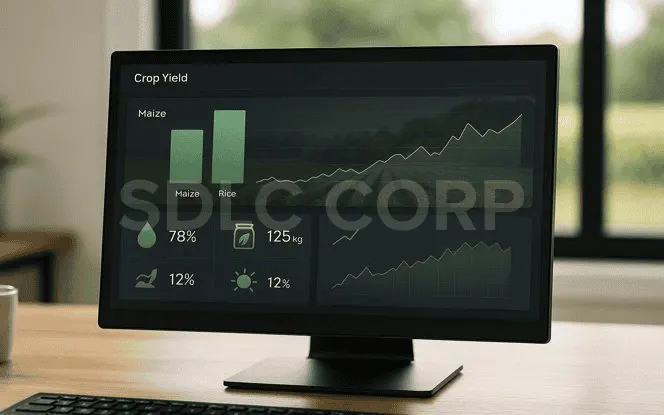
Generative AI helps farmers choose the best crops and methods for their land. For instance, it can show that maize will perform better than rice in a given season. This guidance often leads to higher harvests and more income.cc
3.2 Saving Resources
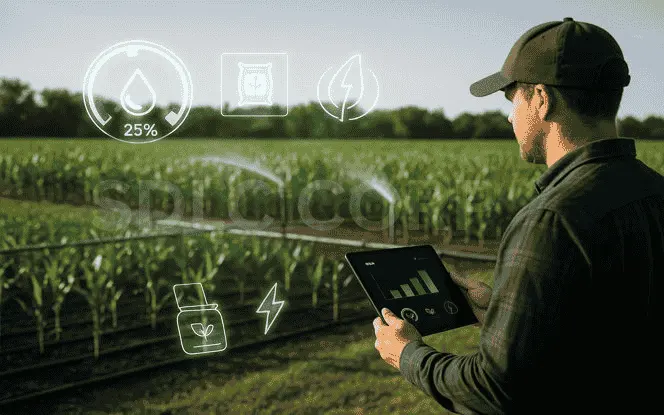

Farming requires a lot of water, fertilizer, and energy. AI can calculate the exact amount needed. Instead of flooding fields with water, farmers can irrigate only where necessary. This prevents waste and saves money.
3.3 Early Pest and Disease Control

Pests like locusts or fungal diseases can destroy fields overnight. AI can spot early signs from satellite images or crop photos. It can then suggest treatments before the problem grows. This prevents massive losses.
3.4 Sustainability and Soil Health

Overusing chemicals harms soil in the long run. Generative AI recommends balanced crop rotations and natural fertilizers. This keeps the soil fertile and reduces pollution.
3.5Better Market Access
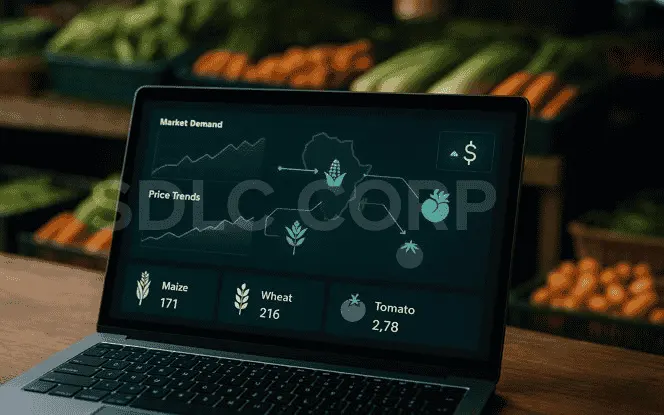
AI does not stop at farming. It also predicts market demand and helps farmers sell at the right time. This reduces wastage and ensures fair prices.
3.6 Decision Support for Crop and Resource Management
Farm operators rely on timely decisions related to irrigation, fertilisation, and harvest planning. Generative AI can help interpret historical data and generate scenario-based recommendations. In these cases, a Generative AI consulting company may support evaluation of model reliability, data quality, and responsible usage, especially when outputs influence operational decisions.
4.Challenges in Using Generative AI for Agritech

While the promise is huge, adopting generative AI is not always easy.
1. Lack of Data
Many farmers do not have soil or weather records. Without good data, AI predictions are less accurate.
2. High Cost
Buying sensors, drones, and AI software can be expensive. Small farmers often cannot afford them. Support from governments and NGOs is important here.
3. Limited Technical Skills
Most farmers are experts in farming, not in using computers. They need training and simple apps that are easy to use.
4. Internet Connectivity
AI often depends on cloud computing. But many rural areas still lack strong internet networks. This slows down adoption.
5. Trust and Awareness
Some farmers are hesitant to trust technology. They may not believe AI can really help. Awareness campaigns and success stories can build trust.
5.Case Studies of Generative AI in Agriculture
Case Study 1: India – Predicting Crop Yields
In India, an AI project used satellite images and weather data to predict rice yields. Farmers who followed AI advice reported up to 20% higher harvests compared to those who didn’t.
Case Study 2: Kenya – Tackling Maize Disease
Farmers in Kenya used a mobile AI app to detect maize disease early. The app used pictures taken by farmers and compared them to a large database. This allowed farmers to save most of their crop.
Case Study 3: Netherlands – Greenhouse Farming
Dutch farmers use AI to manage greenhouses. Generative AI decides how much light, water, and nutrients plants need. This system grows vegetables all year with less energy.
6.Future of Generative AI in Farming

The future of Generative AI for Agritech is exciting. With rapid advances, it will become cheaper and more widely available. Here’s what we may see:
- AI-Powered Marketplaces: Farmers will know in advance what crops are in demand and choose accordingly.
- Autonomous Farms: Robots, drones, and AI systems will plant, water, and harvest with little human effort.
- Climate Resilience: AI will simulate extreme weather and guide farmers on how to adapt.
- Global Food Security: Governments will use AI to plan food supplies and prevent shortages.
As AI becomes more user-friendly, even small family farms will benefit. The dream of “smart farming” is becoming a reality.
System Development and Model Maintenance
Deploying generative AI in agritech requires careful implementation and ongoing updates as conditions change. Models must handle new data sources and evolving farm practices. Some teams choose to hire generative AI developers to implement, test, and maintain these systems while ensuring they remain aligned with real-world agricultural workflows.
Integration with Broader Agricultural Platforms
Generative AI often operates alongside predictive analytics, automation tools, and monitoring systems. Integrating these components requires stable infrastructure and clear data flows. Agritech providers may rely on AI development services to connect generative models with existing platforms while maintaining system performance and data integrity.
Conclusion
Generative AI for Agritech is more than just technology—it is hope for the future of farming. It helps farmers grow more food with fewer resources, fight pests early, and protect the environment. While there are challenges like cost, data gaps, and connectivity issues, the benefits are far greater.
As governments, businesses, and communities invest more in AI-driven farming, this technology will only grow stronger. It will not only feed billions but also make agriculture sustainable for generations to come. In short, generative AI is not just transforming fields; it is reshaping the future of food.
FAQ'S
What is generative AI in agriculture?
Generative AI in agriculture refers to advanced artificial intelligence that can create predictions, simulations, and models to guide farming decisions. Instead of only analyzing past data, it generates new insights about crop yields, soil health, irrigation needs, and climate impacts. For example, it can simulate how different weather patterns affect crop growth, helping farmers prepare for challenges in advance.
How does generative AI help farmers?
Generative AI helps farmers by turning raw data into practical farming advice. It can:
- Predict rainfall and temperature changes for better planning.
- Suggest the right amount of fertilizer and water needed.
- Identify early signs of crop diseases or pests.
- Improve yields by recommending the best crop varieties.
In short, it reduces risks, saves resources, and boosts farm productivity while cutting down unnecessary costs.
Is it useful for small farmers?
Yes, generative AI can be useful for small farmers, though affordability is sometimes a challenge. With the rise of mobile apps, government subsidies, and cooperative platforms, small farmers can now access simplified AI tools. For instance, smartphone-based AI apps can guide them on when to plant, water, and harvest, making advanced farming more accessible even for those with limited land and budget.
Can it improve sustainability?
Absolutely. Generative AI plays a key role in sustainable agriculture. It:
- Reduces chemical waste by suggesting precise fertilizer use.
- Promotes soil health with crop rotation advice.
- Optimizes water usage through smart irrigation.
- Lowers carbon emissions by preventing over-farming.
By combining profitability with eco-friendly practices, it helps farmers protect the environment while maintaining strong harvests.
What is the future of generative AI in agritech?
The future of Generative AI in Agritech looks very promising. In the coming years, we can expect:
- Robot-run farms where drones and AI-powered machines handle planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
- AI marketplaces where farmers can check demand forecasts before choosing crops.
- Climate-resilient strategies that simulate droughts, floods, or heat waves and guide farmers to adapt.
- Global food security systems where governments use AI to predict shortages and distribute resources better.
This future will make farming not only smarter but also more resilient and sustainable worldwide.