Introduction
Generative AI is changing how industries think about creativity, production, and efficiency. In food technology, or foodtech, this technology is moving beyond buzz and becoming a practical tool. From designing new recipes to reducing waste in the supply chain, generative AI is reshaping how food companies work.
Foodtech is a complex ecosystem that combines agriculture, food science, consumer demand, and global logistics. It faces challenges such as sustainability, personalization, and cost control. Generative AI, supported by advanced generative AI development services, offers data-driven answers to these challenges. Simulating possibilities, predicting outcomes, and generating new ideas give food businesses tools that were once impossible to imagine.
The Role of Generative AI in Food Innovation
Foodtech systems manage data across sourcing, production, logistics, and customer engagement. Generative AI can support these platforms by summarising operational data, generating product descriptions, and assisting with menu or recipe analysis. Many teams rely on AI development services to integrate generative models into existing foodtech systems while maintaining accuracy and system reliability.
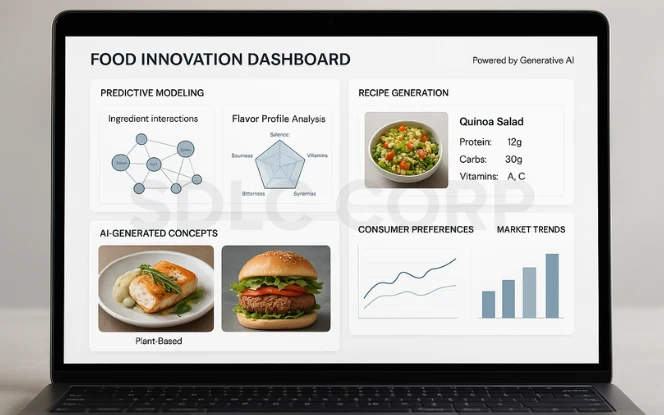
- Predictive modeling in food formulation: AI can analyze flavor profiles and consumer preferences to propose combinations that appeal to specific markets. For example, AI engines have been trained on ingredient databases to generate new plant-based alternatives that mimic the taste of meat or dairy.
- AI-generated food concepts: Image generation models such as GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) can create visual prototypes of dishes. CookGAN, a research model, demonstrated how machine learning can generate realistic images of food items to test concepts before they are made.
- Benefits: Faster product development, reduced research costs, and more innovation. Instead of relying on human intuition alone, companies can evaluate hundreds of possible products virtually before choosing which to make.
Generative AI is not replacing chefs or food scientists. Instead, it augments their work by offering data-driven suggestions and speeding up R&D.
Read Our New Blog –Generative AI for Agriculture
Use Cases Across the Food Value Chain
Generative AI impacts nearly every stage of the food system, from recipe creation to global logistics.
1. Recipe Creation and Personalization
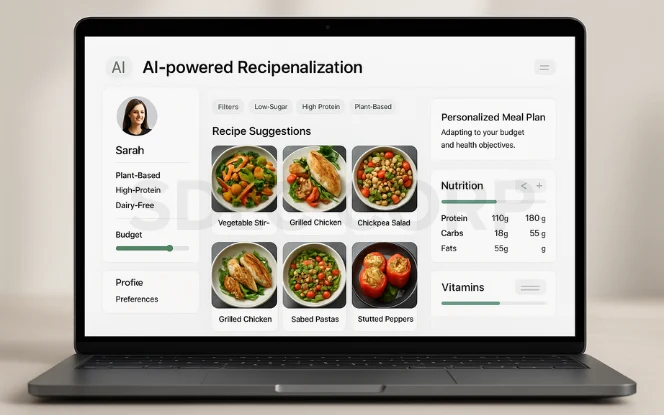
Consumers want food that matches their taste, health goals, and lifestyle. Generative AI makes this possible.
- AI-powered recipe generation: Tools can suggest recipes based on available ingredients, allergies, or nutritional needs. For example, some shopping platforms already offer AI meal planners that adapt to a family’s budget and health goals.
- Personalization at scale: Generative AI allows brands to create customized food offerings. A health-focused consumer may receive recipes designed for low-sugar diets, while another receives plant-based options with high protein.
This personalization creates stronger engagement and loyalty, as customers feel products are designed for them.
2. Manufacturing and Operations
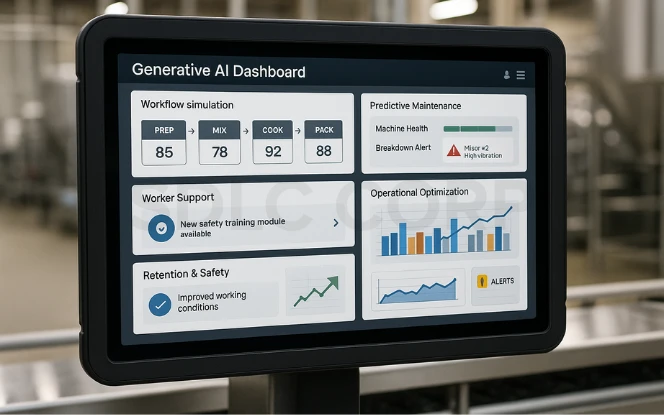
On the production line, generative AI supports efficiency and worker safety.
- Operational optimization: AI models can simulate different workflows and predict machine breakdowns, reducing downtime.
- Connected worker platforms: These AI-driven systems offer real-time support and training, reducing errors and improving safety.
- Retention benefits: By improving working conditions with predictive insights, companies reduce staff turnover, a significant challenge in food manufacturing.
3. Supply Chain and Sustainability
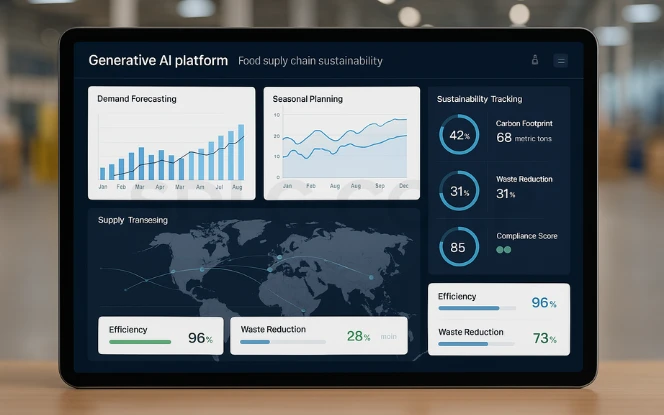
Food supply chains are global and vulnerable to waste and inefficiency. Generative AI offers tools for improvement.
- Waste reduction: AI predicts demand and adjusts production to reduce surplus.
- Seasonal planning: By modeling seasonal supply and climate effects, AI helps companies avoid shortages or price spikes.
- Sustainability goals: Generative AI supports transparency in sourcing, ensuring compliance with environmental standards and helping companies move toward net-zero goals.
4. Agriculture and Quality Control
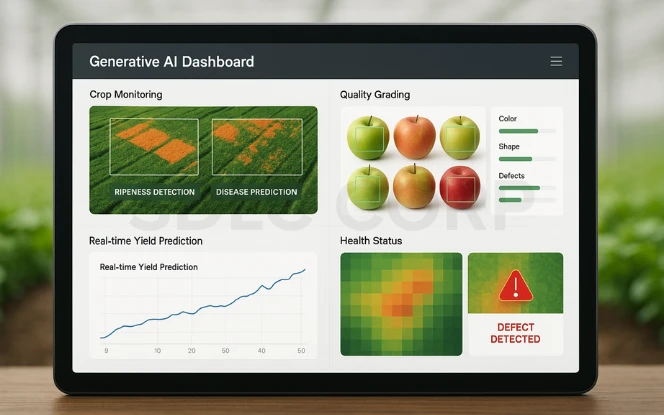
In agriculture, generative AI works with image data to improve yields and detect quality issues.
- Harvest detection: Models can analyze images of crops to predict ripeness or detect disease.
- Quality grading: AI can evaluate factors like color, shape, or defects in produce faster and more consistently than manual inspection.
These tools ensure better quality food reaches consumers while minimizing waste at the farm level.
Strategic SEO: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Generative AI is not only transforming food production; it also influences how information about food reaches consumers. With the rise of AI search and recommendation systems, visibility depends on a new discipline:
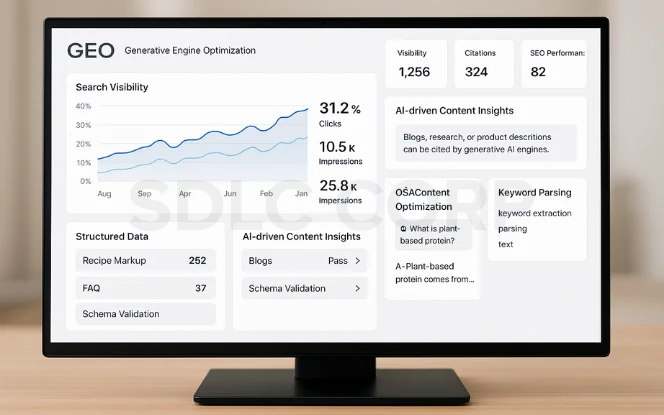
- What is GEO? It is the process of making content easier for generative AI systems to interpret, cite, and recommend.
- How it applies to foodtech: Blogs, research, and product descriptions about generative AI in foodtech must be structured for AI engines. That means clear headings, schema markup, FAQs, and direct answers.
- Best practices:
- Use structured data so AI systems can parse recipes or supply chain data.
- Include Q&A-style sections that AI models can cite directly.
- Avoid jargon unless it is necessary for technical credibility.
- Use structured data so AI systems can parse recipes or supply chain data.
For foodtech companies, mastering GEO means being part of future search results where generative AI plays a key role in content delivery.
Technical Deep Dive: How It Works
Generative AI in foodtech relies on models trained on vast amounts of data. The technical depth explains why this field is credible and effective.
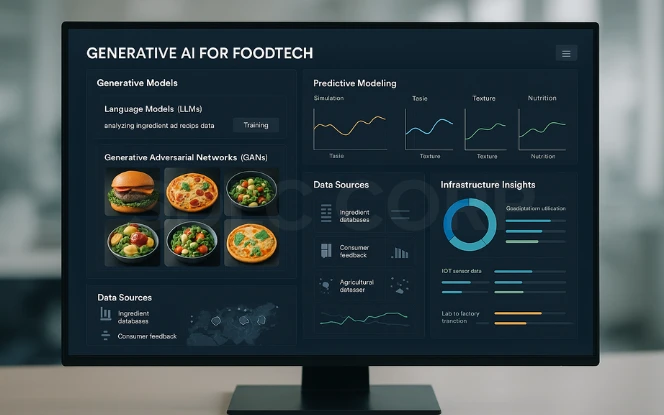
1. Generative Models
- Language models (LLMs): These predict and generate text. In foodtech, they analyze ingredients, recipes, and consumer reviews to propose new products.
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): These models generate images, useful for prototyping food designs or testing marketing visuals.
- Predictive modeling: By simulating ingredient interactions, AI can test taste, texture, and nutritional value before actual production.
2. Data Requirements
Generative AI depends on diverse and high-quality datasets. In foodtech, this includes:
- Ingredient databases with chemical and nutritional profiles.
- Consumer feedback from surveys, social media, and purchase data.
- Agricultural datasets with yield, climate, and soil conditions.
Without reliable data, AI models risk generating biased or impractical results.
3. Infrastructure Needs
- Cloud platforms: Enable scalable training and deployment of models.
- IoT integration: Real-time sensors in factories or farms supply data to AI engines.
- Lab-to-factory transition: AI insights must be tested in controlled environments and then scaled to mass production.
This blend of data, models, and infrastructure allows generative AI to deliver value at both experimental and industrial levels.
Challenges and Considerations
While promising, generative AI in foodtech faces hurdles that businesses must address.
- Data Quality and Bias – If input data is incomplete or biased, AI results may be inaccurate. For example, a model trained only on Western cuisines may overlook regional or cultural variations.
- Ethical and Privacy Concerns – Personalized nutrition requires sensitive health data. Companies must handle this data responsibly, ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations.
- Human Oversight – AI suggestions must be validated by food scientists, nutritionists, and chefs. Automation alone cannot guarantee safety or taste. Human expertise remains central.
- Adoption Barriers – High implementation costs and lack of expertise are real barriers for small and mid-sized businesses. Training staff and investing in AI infrastructure can be resource-intensive.
Generative AI must be introduced with a balanced approach, respecting both innovation and responsibility.
Future Outlook for Foodtech
The future of generative AI in foodtech points toward personalization, sustainability, and smarter consumer experiences.
- Personalized nutrition: AI will deliver meal plans aligned with DNA analysis, lifestyle data, and real-time health metrics. Smart appliances may prepare meals automatically based on these insights.
- Sustainability: Generative AI will help companies meet net-zero goals by cutting waste and ensuring transparent supply chains.
- Smarter visibility: As GEO becomes essential, content about foodtech must adapt to generative search. This will redefine how consumers discover products and information.
Generative AI will not replace humans in food innovation but will serve as a co-creator, accelerating discovery while respecting cultural and ethical boundaries.
Quality Control and Operational Insights
Maintaining consistency and safety is critical in foodtech. Generative AI can assist by analysing inspection reports, drafting compliance documentation, and identifying patterns in quality data. In such cases, working with a Generative AI consulting company helps organisations assess feasibility, manage data quality, and define clear boundaries for model use in regulated environments.
Conclusion
Generative AI is emerging as a cornerstone of the foodtech revolution. It transforms recipe development, streamlines manufacturing, reduces waste, and strengthens sustainability. At the same time, it raises important questions about data quality, ethics, and human oversight.
The real opportunity lies in using AI as a collaborator rather than a replacement. Food businesses that embrace generative AI responsibly will not only gain efficiency but also build trust with consumers.
For companies exploring how generative AI can enhance their operations, the message is clear: the technology is ready, and its potential is vast. The key is to adopt it with precision, responsibility, and long-term vision — and in many cases, to hire generative AI developers who can align technical expertise with industry-specific needs.
FAQ's
What is generative AI in foodtech?
Generative AI in foodtech refers to the use of AI models that can create new recipes, simulate ingredient interactions, optimize food production processes, and improve supply chain management by generating predictive insights.
How does generative AI help in recipe creation?
Generative AI can analyze ingredient databases, consumer preferences, and nutritional requirements to generate personalized recipes. It can also suggest plant-based alternatives and create dishes tailored to health goals or dietary restrictions.
Can generative AI improve food manufacturing operations?
Yes. Generative AI supports operational optimization by predicting machine breakdowns, simulating workflows, and providing connected worker platforms that improve safety, efficiency, and employee retention in food production.
How does generative AI contribute to sustainability in foodtech?
AI models help reduce waste by predicting demand accurately, support seasonal planning by modeling climate impacts, and improve transparency in sourcing — enabling companies to move toward net-zero sustainability goals.
What challenges does generative AI face in foodtech?
Key challenges include data quality and bias, ethical and privacy concerns in personalized nutrition, the need for human oversight, and high adoption barriers for smaller businesses due to cost and technical expertise requirements.
Why should food businesses consider adopting generative AI?
Generative AI enables innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. By simulating possibilities and predicting outcomes, it helps businesses cut costs, reduce waste, and build trust with consumers — while keeping human expertise central to decision-making.