Introduction
Cities are growing fast. By 2050, nearly 70% of the world’s population will live in urban areas. Managing this growth demands smarter systems. That is why the idea of smart cities has gained attention. A smart city uses technology, connectivity, and data to make urban living more efficient, sustainable, and citizen-friendly.
Artificial intelligence has long supported smart cities with predictive analytics and automation. Now, generative AI brings a new dimension. Instead of only predicting outcomes, generative AI creates new solutions, models, and insights. With the rise of Generative AI Development Services, cities can adopt advanced tools that enable better design, planning, and decision-making. This blog explores how generative AI can power the next phase of smart cities, highlighting its use cases, benefits, challenges, and future potential.
What Makes a City “Smart”?
A smart city connects infrastructure, people, and services using digital technologies. Sensors gather real-time data on traffic, energy, and public services. Networks share this data with management systems that analyze and act on it.
Traditional AI already plays a role. It predicts traffic patterns, manages energy demand, and powers digital assistants for city services. But these systems often rely on historical data. They tell us what may happen, but they do not imagine new possibilities. That is where generative AI stands out.
How Generative AI Differs from Traditional AI
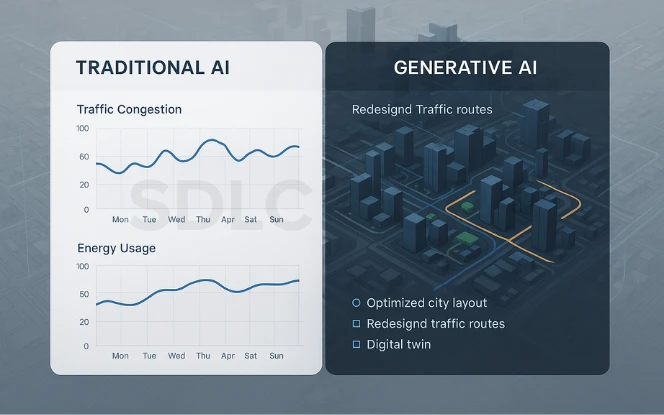
Generative AI is not only reactive. It can create new designs, models, and solutions. Instead of just predicting traffic congestion, it can generate optimized city layouts to reduce congestion. Instead of only automating waste collection, it can design smarter systems for waste reduction and recycling.
This creative capacity makes generative AI vital for urban planning. Cities can test new policies, design infrastructure before building it, and create digital twins that mirror urban life. These simulations help city leaders make better decisions with fewer risks.
Read Also – What is Generative AI?
Key Applications of Generative AI in Smart Cities
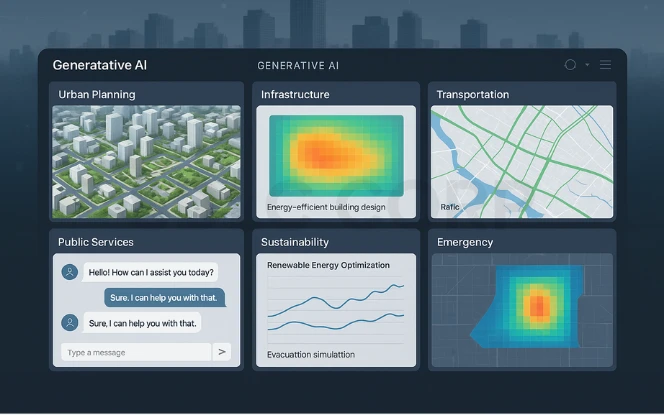
Urban Planning and Decision Support: City planning involves long timelines, regulatory constraints, and competing priorities. Generative AI can help analyse historical data, draft scenario summaries, and support evidence-based planning discussions.
In these cases, a Generative AI consulting company may assist in evaluating use cases, defining governance frameworks, and ensuring outputs are used responsibly in public decision-making.- Smart Infrastructure Design – Buildings consume nearly 40% of global energy. Generative AI can generate designs for energy-efficient structures. From layout optimization to smart material usage, it helps architects and engineers create sustainable infrastructure.
- Transportation Systems – Traffic remains one of the biggest urban challenges. Generative AI can model traffic flows, suggest new transit routes, and help manage autonomous vehicle fleets. This ensures smoother mobility and reduces emissions.
- Public Services and Citizen Engagement – AI-powered chatbots can generate answers to citizen queries. Digital twins of cities can help citizens visualize policy changes—like new zoning laws or green projects—before they happen.
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency – Generative AI supports smart energy grids by simulating demand and optimizing supply from renewable sources. It can design better waste management routes or even generate strategies for reducing food waste.
- Emergency and Risk Management – From floods to wildfires, disasters threaten cities worldwide. Generative AI can generate evacuation models, simulate disaster scenarios, and optimize response strategies to save lives.
Read Also – Generative AI for Hospitality
Benefits of Generative AI for Smart Cities
- Efficiency Gains: Faster planning and testing of new ideas.
- Cost Savings: Less trial-and-error in infrastructure projects.
- Better Citizen Experience: Personalized services and smoother mobility.
- Sustainability Support: Optimized energy, waste, and environmental policies.
- Innovation in Governance: Data-driven policymaking with real-time feedback.
Read Our New Blog – Generative AI for Government
Challenges and Risks

- Data Privacy and Surveillance – Smart cities collect massive amounts of data. If misused, this can invade citizens’ privacy. Generative AI systems need strict safeguards.
- Bias in AI-Generated Decisions – AI reflects the data it learns from. If the data is biased, outcomes may be unfair. Cities must ensure fairness and inclusivity.
- Security Risks – Connected systems are targets for cyberattacks. A hacked smart grid or traffic system could cause chaos.
- Governance and Regulation – Cities must balance innovation with regulations. Without oversight, generative AI may create solutions that conflict with ethical standards.
Real-World Examples and Emerging Projects
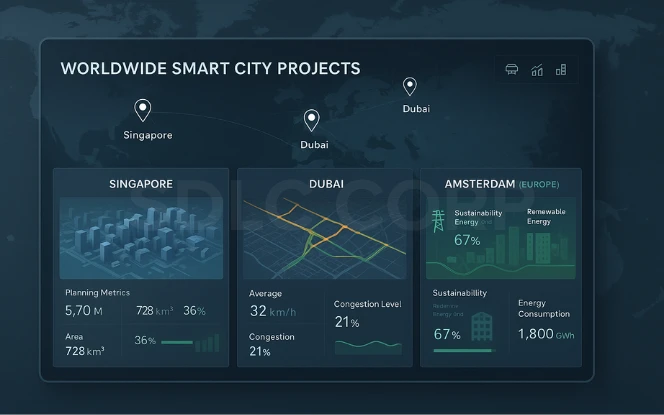
Some cities are already testing generative AI:
- Singapore uses digital twins to plan urban layouts. Generative AI supports these models to predict future needs.
- Dubai is adopting AI for traffic management and smart governance. Generative AI is being explored for new infrastructure projects.
- European Cities such as Amsterdam are piloting AI-driven sustainability projects, from smart energy grids to green building design.
These early projects show how generative AI is moving from concept to practice in urban life.
Future Outlook
Generative AI will deepen its role in smart cities through:
- Digital Twins: Full-scale city replicas where policies and infrastructure can be tested before implementation.
- Metaverse Cities: Virtual environments for citizen engagement and planning.
- AI-Driven Policy Modeling: Testing future regulations for housing, environment, and mobility.
- Scalability: Mid-sized and developing cities will benefit from AI solutions without high costs.
Integration with Existing City Systems
Generative AI tools rarely operate alone. They are often integrated with traffic management systems, energy platforms, and public safety tools. Successful integration depends on stable infrastructure and clear data flows. City authorities and solution providers may rely on AI development services to connect generative models with existing platforms while maintaining reliability and data accuracy.
Conclusion
Generative AI offers more than automation. It allows cities to imagine and design new solutions before they are built. From energy grids to emergency planning, it supports efficiency, sustainability, and resilience.
For smart cities, the challenge is not whether to adopt generative AI, but how to do so responsibly. With careful governance and a focus on fairness, generative AI can help cities grow smarter, greener, and more citizen-centered. To achieve this, many city projects look to hire Generative AI Developers who can build practical, secure, and scalable solutions tailored to urban needs.
FAQ's
What is generative AI in the context of smart cities?
Generative AI in smart cities refers to AI systems that go beyond prediction. They can create new designs, simulations, and solutions for urban planning, infrastructure, transportation, and public services.
How does generative AI differ from traditional AI in smart city projects?
Traditional AI analyzes data and makes predictions, while generative AI creates new possibilities—such as optimized city layouts, energy-efficient designs, and digital twin simulations.
What are the main benefits of using generative AI in smart cities?
Key benefits include efficiency in planning, reduced costs in infrastructure projects, better citizen services, sustainability improvements, and data-driven policymaking.
What challenges come with using generative AI in smart cities?
Challenges include data privacy risks, AI bias, cybersecurity threats, and the need for governance frameworks to ensure ethical and responsible AI use.
Which cities are already using generative AI?
Singapore uses digital twins for urban layouts, Dubai applies AI in traffic management and governance, and Amsterdam explores AI-driven sustainability projects.
How can organizations start implementing generative AI for smart city initiatives?
Organizations can begin by collaborating with AI experts, investing in digital twin platforms, and working with partners who provide Generative AI Development Services to design scalable and secure solutions.