Introduction
In today’s hyper-connected world, speech-to-text conversion has become a technology we interact with almost daily, often without realizing it. Whether you’re dictating an email on your smartphone, asking a virtual assistant to set a reminder, or watching real-time captions during a webinar, you’re experiencing speech recognition technology in action.
Also called automatic speech recognition (ASR), it transforms spoken language into written text using Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning. The result is a tool that enhances productivity, boosts accessibility, and streamlines workflows across industries.
1.What Is Speech-to-Text Conversion?
At its core, speech-to-text conversion is the process of turning spoken words into written form through automatic speech recognition systems. These systems can process live speech or recorded audio, delivering instant or near-instant transcriptions.
This technology powers everything from personal assistants like Siri and Alexa to cloud-based transcription services such as Google Speech-to-Text and Amazon Transcribe. It also underpins accessibility tools that help those with hearing impairments stay connected in real time.
Because human speech is complex, filled with accents, slang, pauses, and varying speeds, machine learning in speech recognition and NLP are critical. They allow the software to learn from massive datasets and adapt to different speakers and environments.
Related Read: Curious about converting visuals into written content instead? Here’s what are 3 easy methods for turning an image into text.
2.How Speech-to-Text Conversion Works
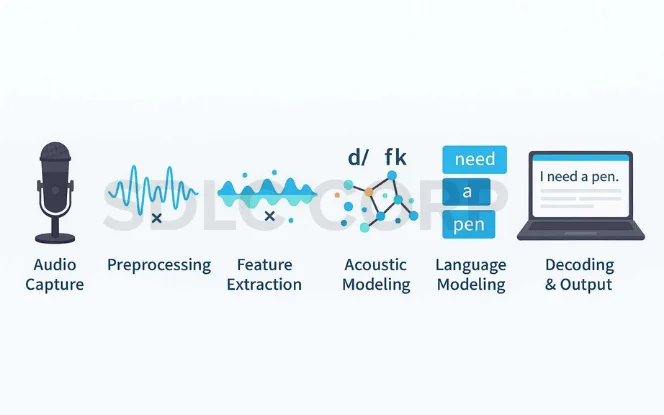
Step 1: Audio Capture
The process begins when a microphone records speech, converting sound waves into digital signals. Since clear audio is the foundation of speech-to-text accuracy, using a high-quality microphone in a quiet environment is crucial. In addition, directional microphones help focus on the speaker’s voice while minimizing surrounding noise.
Step 2: Preprocessing
Before transcription can begin, the system prepares the audio. This involves reducing background noise, removing echoes, and normalizing volume levels so that every word is equally clear. As a result, the ASR system has a cleaner signal to analyze, which directly improves output quality.
Step 3: Feature Extraction
At this stage, the audio is transformed into a set of measurable data points called “features.” These capture details like pitch, tone, and energy levels. Because human speech is complex, these features allow the system to identify subtle patterns that distinguish one sound from another.
Step 4: Acoustic Modeling
The acoustic model takes these features and maps them to phonemes—the smallest units of sound in speech. By comparing patterns against trained datasets, the model begins forming the building blocks of words.
Step 5: Language Modeling
Next, the language model predicts the most likely sequence of words based on grammar rules, probability, and context. Therefore, it can choose “I need a pen” instead of “Eye knead a pin.”
Step 6: Decoding and Output
Finally, the ASR engine combines both models to produce the transcription, often in real time. Because of these optimizations, modern tools like Otter.ai and Rev can deliver highly accurate results within seconds.
Related Read:
Curious about converting visuals into written content instead?
Here are 3 easy methods for turning an image into text.
3. Key Components of Speech Recognition Technology

For a speech recognition application to function effectively, several components work in harmony:
- Acoustic Models – Convert audio waveforms into phonemes.
- Language Models – Predict logical word sequences.
- Pronunciation Dictionaries – Store pronunciation patterns for words.
- NLP Algorithms – Ensure the transcription is coherent and grammatically correct.
- Machine Learning Models – Continuously improve results with new data.
Advanced systems also integrate deep learning neural networks, which outperform older statistical models by recognizing patterns across massive datasets. This is why voice-to-text software today can understand casual speech, interruptions, and even overlapping voices better than ever before
4. Types of Speech-to-Text Systems
Speech to text systems come in different forms, each tailored to specific needs and environments. The two primary categories, cloud based and offline, offer distinct advantages in terms of performance, accessibility and security. Understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right solution for your workflow.
Cloud-Based Systems
- Operate on powerful remote servers.
- Provide high accuracy and scalability.
- Examples: Google Speech-to-Text, Amazon Transcribe, Microsoft Azure Speech.
- Ideal for organizations that require fast, high-volume transcription.
Offline Systems
- Run locally without internet access.
- Offer strong data privacy.
- Ideal for legal, defense, and medical environments.
- May require high-performance hardware for complex tasks.
Some hybrid solutions use edge computing to process part of the workload locally and send the rest to the cloud, balancing speed, accuracy, and security.
5. Applications of Speech-to-Text

Healthcare
Doctors and other healthcare professionals use audio transcription tools to update patient records, which allows them to focus on patient care rather than manual documentation. Furthermore, systems like Nuance Dragon Medical integrate specialized medical vocabularies, ensuring terms such as “angioplasty” or “myocardial infarction” are recognized correctly. In addition, these tools can integrate with electronic health record (EHR) systems, streamlining the process even further.
Customer Service
Call centers rely on automatic speech recognition (ASR) to automate call logging, detect keywords, and even analyze caller sentiment. As a result, agents can respond more effectively, and managers can monitor performance in real time. Moreover, automated systems can guide agents during calls by suggesting responses or providing instant information.
Education
In classrooms and online learning platforms, real-time transcription services make lectures accessible to students with hearing difficulties or language barriers. Additionally, recorded lectures can be transcribed for study materials, allowing learners to review content at their own pace.
Media & Journalism
ournalists benefit from instant transcription of interviews, press conferences, and speeches. Consequently, this reduces turnaround times for articles, enabling faster news delivery. Some media houses even integrate ASR into live broadcasts for immediate captioning.
Accessibility
For individuals with hearing impairments, real-time captioning ensures they can participate fully in conversations, events, and media consumption. Furthermore, voice-to-text features in smartphones and apps expand accessibility beyond formal settings into everyday life.
Because AI models are becoming more adaptable, these speech recognition applications will only continue to expand, creating even more opportunities for automation and inclusion.
6. Benefits of Speech-to-Text Technology
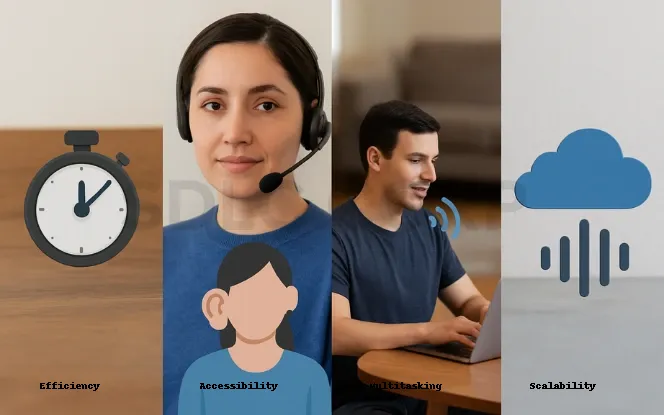

The adoption of automatic speech recognition is driven by clear benefits:
- Efficiency – Speaking can be three times faster than typing.
- Accessibility – Removes barriers for individuals with disabilities.
- Multitasking – Enables hands-free operation while performing other tasks.
- Scalability – Especially with cloud-based transcription services, handling thousands of hours of audio is possible without scaling costs linearly.
According to a Deloitte study, companies using automated transcription tools saw a 25% increase in meeting productivity and a 40% reduction in documentation time.
7.Limitations and Challenges
Even advanced speech recognition technology faces obstacles:
- Background Noise – Busy environments can degrade accuracy.
- Accents & Dialects – Regional variations require targeted model training.
- Specialized Vocabulary – Without domain-specific training, terms can be misinterpreted.
- Latency – Some offline systems process slower than their cloud counterparts.
Ongoing innovation in multilingual speech recognition and adaptive AI models is helping to reduce these issues, but complete perfection remains challenging.
8. Improving Speech-to-Text Accuracy

Best Practices for Users
- Use quality microphones to reduce distortion.
- Record in a quiet, controlled environment.
- Speak at a steady pace with clear enunciation.
Best Practices for Developers
- Train AI models with industry-specific vocabularies.
- Implement noise reduction algorithms in preprocessing.
- Continuously update models with fresh data.
Businesses that follow these steps often see speech-to-text accuracy rise above 95%, making the technology viable even for high-stakes scenarios.
Conclusion
In summary, speech-to-text conversion is revolutionizing how we interact with technology. From real-time transcription in global meetings to secure offline speech-to-text in sensitive environments, the applications are vast and growing.
With machine learning in speech recognition, NLP, and more powerful hardware, the future promises even faster, more accurate, and more intelligent voice-to-text software. For businesses and individuals alike, embracing this technology means gaining efficiency, accessibility, and a competitive edge.
Partnering with an experienced AI development company can help organizations integrate cutting-edge speech recognition solutions tailored to their specific needs, ensuring they stay ahead in an increasingly voice-driven digital world.
FAQ'S
What is the difference between speech-to-text conversion and voice commands?
Speech-to-text converts spoken words into written text, while voice commands interpret specific phrases to trigger actions.
How accurate is speech-to-text conversion?
Accuracy can exceed 95% in ideal conditions, although it depends on audio quality, accents, and background noise.
Can speech-to-text conversion work offline?
Yes, some models run locally on devices for privacy and low-connectivity environments.
Is speech-to-text conversion important for accessibility?
Absolutely, it is vital for individuals with hearing or mobility impairments.
Which industries benefit most from speech-to-text conversion?
Healthcare, legal, education, and corporate sectors gain the most from automated transcription.