Introduction
The rise of tool-using AI agents marks a significant leap in artificial intelligence, shifting from static models to dynamic, action-driven systems. These agents can connect with external tools, APIs, and databases, making them vital in the era of AI automation. Unlike conventional AI, they don’t just analyze data they act on it. For businesses, this means reduced costs, faster decision-making, and seamless scalability.
For developers and technical readers, it opens opportunities to design intelligent AI systems that integrate with real-world workflows and enterprise tools. From automating customer support to optimizing supply chains, tool-using AI agents are quickly becoming the backbone of digital transformation. To explore the foundations behind this shift, check out our detailed guide on AI Development Services.
1. What Are Tool-Using AI Agents?
Tool-using AI agents are autonomous systems that extend beyond static machine learning models by integrating with external tools, APIs, and databases. Instead of only generating predictions or text, they can perform real-world actions by interacting with software environments.
Unlike standalone AI models, which operate only on their training data and built-in algorithms, tool-enhanced AI agents can:
- Access live data from external sources.
- Execute commands across third-party platforms.
- Adapt their reasoning based on real-time feedback loops.
This fundamental difference makes tool-using agents more dynamic, scalable, and context-aware.

Example in Action
Imagine a language model generating a financial report. A standalone AI could only summarize past training data.
But a tool-enhanced AI agent can:
- Connect to a real-time stock market API.
- Fetch live pricing and historical data.
- Query a database to validate past performance.
- Deliver an up-to-date, data-backed financial report.
By combining reasoning capabilities with tool integration, these agents move from being static predictors to active problem-solvers.
Core AI Systems Behind Tool Execution
Tool-using agents rely on core AI systems for intent detection, reasoning, and response synthesis. These foundations are typically built using structured AI development services to ensure reliability and system compatibility.
2. How Do Tool-Using AI Agents Work?
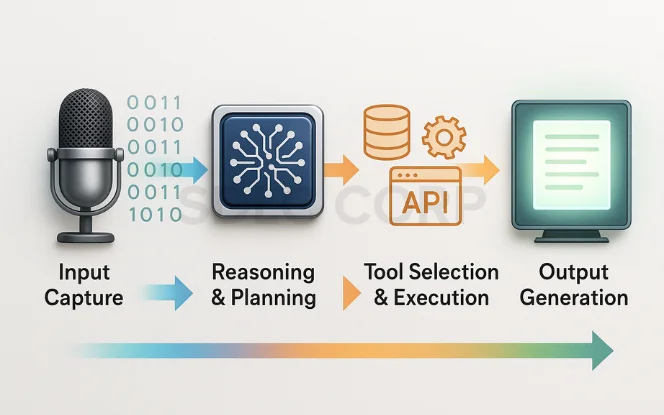
Tool-using AI agents operate through a structured pipeline, often referred to as the AI agent loop. This loop ensures that the agent not only processes inputs but also dynamically selects and executes the right tools for task completion.
Step-by-Step Workflow
- Input Capture
- The agent receives a user query, command, or data stream.
- Example: “Generate a market analysis using the latest financial data.”
- The agent receives a user query, command, or data stream.
- Reasoning & Planning
- The core AI model interprets the input using natural language processing (NLP) and contextual reasoning.
- It maps out the next steps required to fulfill the request.
- The core AI model interprets the input using natural language processing (NLP) and contextual reasoning.
- Tool Selection (Orchestration Layer)
- The agent determines which external tool or API is best suited for the task.
- Keywords: tool orchestration, AI workflow automation.
- The agent determines which external tool or API is best suited for the task.
- Execution
- The selected tool (e.g., API, database, or SaaS integration) is called programmatically.
- The agent retrieves or processes real-time data.
- The selected tool (e.g., API, database, or SaaS integration) is called programmatically.
- Output Generation
- The agent synthesizes results from tools with its own reasoning.
- Final output is optimized for clarity, accuracy, and user intent.
- The agent synthesizes results from tools with its own reasoning.
The Agent Loop Explained
This workflow creates a closed-loop system, often called the AI agent pipeline:
- Sense (Input) → Think (Reasoning) → Act (Tool Execution) → Refine (Output).
- Each cycle allows the agent to self-correct and adapt based on new information.
For instance, if a requested API fails, the agent can retry with fallback tools or reformulate the query demonstrating true autonomy.
By combining reasoning intelligence with tool orchestration, tool-using AI agents unlock the potential for end-to-end AI workflow automation across industries.
Read This : Personal AI Agents Explained
3. Technical Architecture of Tool-Using AI Agents
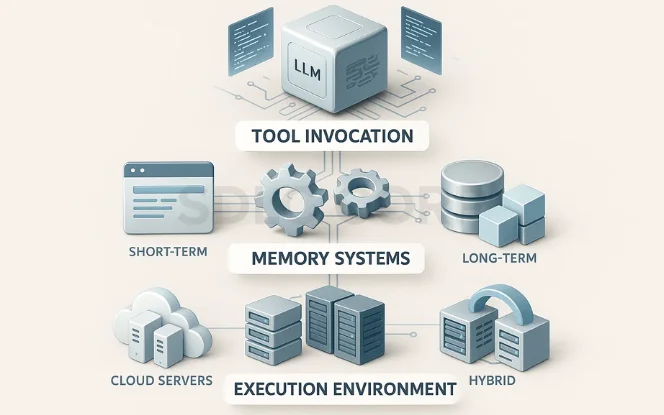
The strength of tool-using AI agents lies in their modular architecture, where each layer contributes to intelligent decision-making, tool orchestration, and seamless integration with external systems. This design enables scalable AI workflow automation and AI tool integration across industries.
LLM Backbone
- Acts as the cognitive engine of the agent.
- Powered by advanced large language models (LLMs) such as GPT, Claude, or LLaMA.
- Handles natural language reasoning, contextual understanding, and plan generation.
- Example: GPT interprets “fetch current sales metrics” and breaks it into structured actions.
Tool Invocation Layer
- Functions as the execution bridge between the AI and external systems.
- Handles API calls, database queries, and third-party app interactions.
- Example: An AI agent invokes a payment API to process a transaction or a CRM database to fetch customer records.
- Core to AI orchestration, ensuring the right tool is triggered at the right time.
Memory Systems
- Enable agents to maintain context persistence across tasks.
- Short-term memory: Holds conversation prompts and recent context.
- Long-term memory: Stored in vector databases (e.g., Pinecone, FAISS) for knowledge retrieval.
- Example: Remembering a client’s last query or pulling historical data for trend analysis.
Execution Environment
- Determines where the agent runs and scales.
- Cloud runtimes: Offer elasticity, high availability, and API accessibility.
- Local runtimes: Provide more security and privacy, suitable for sensitive industries.
- Hybrid execution allows balancing performance, compliance, and cost-efficiency.
Why This Matters
By combining the LLM backbone, tool orchestration layer, memory systems, and execution environments, AI agents achieve:
- Dynamic reasoning beyond static models.
- Seamless tool integration for enterprise workflows.
- Adaptive automation powered by both short-term interactions and long-term intelligence.
This layered AI architecture ensures that agents are not only responsive but also scalable, secure, and industry-ready.
4. Benefits of Tool-Enhanced AI Agents
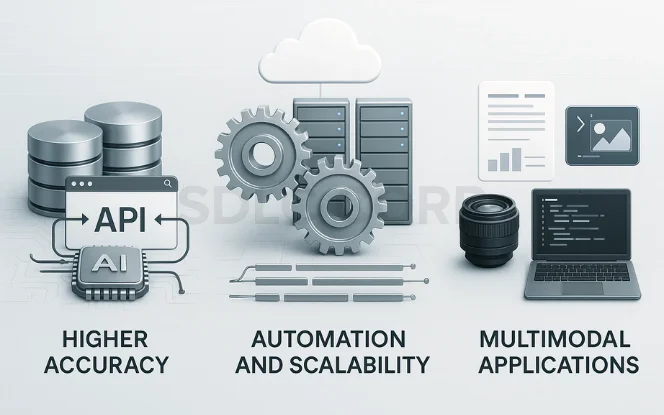
Tool-enhanced AI agents go beyond static models by integrating with external systems, enabling business AI automation at scale. Their architecture unlocks powerful capabilities that drive productivity, accuracy, and adaptability across industries.
Higher Accuracy via External Knowledge
- Standalone models rely only on training data, which can become outdated.
- Tool-enhanced agents query live APIs, databases, and knowledge graphs for real-time accuracy.
- Example: A customer-support AI pulling the latest order status directly from an ERP system.
Improved Automation and Scalability
- By orchestrating multiple tools, agents can automate complex workflows without human intervention.
- Enables enterprises to streamline supply chain management, financial reporting, and IT operations.
- Scaling becomes effortless since agents can run parallel tasks across cloud environments.
- SEO term: business AI automation.
Multimodal Applications
- Agents are not restricted to text they integrate with vision models, code interpreters, and data analytics tools.
- Example:
- Text: Drafting compliance reports.
- Vision: Analyzing product defects via image recognition.
- Code: Debugging scripts by connecting with developer toolchains.
- Text: Drafting compliance reports.
- Expands their role as AI productivity tools in diverse sectors.
Why Businesses Should Care
By combining real-time accuracy, scalable automation, and multimodal adaptability, tool-using AI agents deliver:
- Reduced operational costs through workflow automation.
- Enhanced decision-making with up-to-date insights.
- Future-ready AI productivity tools capable of adapting to evolving business needs.
Check Out : Task-Oriented AI Agent
5. Challenges in Deploying Tool-Using AI Agents
While tool-using AI agents deliver significant advantages, their deployment introduces AI deployment challenges that organizations must address. These challenges primarily stem from performance bottlenecks, external dependencies, and security concerns.
Latency and Performance Issues
- Every tool invocation (API call, database query, or external function execution) adds latency.
- High-complexity workflows involving multiple tools may slow down response times.
- Example: An AI pipeline fetching data from multiple financial APIs may experience network delays that affect real-time reporting.
- Optimization strategies: asynchronous execution, caching, and load balancing.
API Reliability and External Dependencies
- Tool-using agents depend on third-party APIs and SaaS integrations, which may suffer outages or version changes.
- An unreliable API can break the agent’s workflow, leading to incomplete or inaccurate results.
- Example: A CRM integration failing during customer query resolution.
- Mitigation: fallback mechanisms, redundancy layers, and monitoring tools.
Security, Compliance, and Hallucination Control
- Agents often handle sensitive business data, making secure AI integration critical.
- Risks include:
- Data leaks during API calls.
- Unauthorized access to enterprise systems.
- Hallucinations (fabricated or misleading outputs) amplified when combined with external tools.
- Data leaks during API calls.
- Solutions:
- Zero-trust security models.
- Audit trails and access logging.
- Reinforcement techniques to minimize hallucinations.
- Compliance alignment (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Zero-trust security models.
Scaling Agents Across Enterprise Systems
In enterprise settings, agents may operate across multiple departments and systems. An enterprise AI development company can help design scalable architectures that maintain access control and auditability.
Key Takeaway
To unlock the full potential of tool-using AI agents, businesses must balance innovation with governance. Robust monitoring, redundancy, and secure AI integration practices are essential to build trust and ensure sustainable deployment.
6. Real-World Applications of Tool-Using AI Agents
Tool-using AI agents are rapidly transforming industries by embedding intelligence into workflows. By combining reasoning with tool orchestration, they unlock powerful AI automation applications across SEO, customer engagement, software delivery, and data intelligence.
SEO Automation
- AI agents streamline SEO workflows by integrating with keyword APIs, rank trackers, and analytics platforms.
- Capabilities include:
- Keyword research at scale using live search data.
- SERP analysis to track competitor performance.
- Content clustering for topic authority and semantic SEO.
- Keyword research at scale using live search data.
- Example: An AI agent fetching keyword volumes from Google Ads API, clustering them via vector similarity, and generating a ready-to-publish content map.
- SEO term: AI in SEO.
Customer Service
- AI chatbots become context-aware support agents when connected to CRMs, ticketing systems, and payment APIs.
- Benefits:
- Resolve real-time queries such as billing, order tracking, or refunds.
- Reduce dependency on human agents.
- Resolve real-time queries such as billing, order tracking, or refunds.
- Example: A chatbot pulling order history from Shopify API to provide personalized support instantly.
DevOps and Software Delivery
- Tool-using AI agents act as AI DevOps tools, automating critical steps in the CI/CD pipeline.
- Applications:
- Running automated test suites.
- Deploying code via orchestration tools (e.g., Kubernetes, Docker).
- Monitoring logs for anomaly detection.
- Running automated test suites.
- Example: An AI agent detecting a failed build, re-running automated tests, and pushing a fix to GitHub Actions without manual intervention.
Data Analysis & Insights
- Agents integrate with databases, BI tools, and unstructured sources for real-time decision-making.
- Capabilities include:
- Querying SQL databases for structured insights.
- Using vector search for semantic queries in unstructured datasets.
- Generating dashboards and predictive analytics.
- Querying SQL databases for structured insights.
- Example: An AI agent querying Snowflake for sales data and combining it with social media sentiment analysis to predict market demand.
Key Insight
By embedding AI into SEO, customer service, DevOps, and data pipelines, organizations gain a competitive advantage through scalable, automated, and intelligent workflows. These AI automation applications are paving the way for the next wave of enterprise productivity.
Learn About Ai Agents : Agentic AI Fundamentals
7. Future of Tool-Using AI Agents
The evolution of tool-using AI agents is set to reshape how businesses adopt automation. With advances in orchestration, reasoning, and collaboration, the future of AI automation points toward more adaptive and enterprise-ready ecosystems.
Rise of Multi-Agent Collaboration
- Instead of a single AI agent handling all tasks, future architectures will feature multi-agent systems.
- Each agent specializes (e.g., data analysis, customer support, DevOps), collaborating to complete workflows.
- Example: One agent extracts market data, another generates a competitive report, and a third designs visual dashboards all in sync.
- Impact: Scalable enterprise AI trends powered by distributed intelligence.
Low-Code Orchestration Platforms
- The next wave of adoption will be driven by low-code and no-code orchestration frameworks.
- Business users without deep technical expertise will be able to:
- Integrate APIs into AI workflows.
- Design drag-and-drop automation pipelines.
- Launch enterprise-ready agents faster.
- Integrate APIs into AI workflows.
- This democratizes AI workflow automation, making it accessible to non-developers.
Neuro-Symbolic Reasoning
- Current LLM-driven agents excel at pattern recognition but often lack deep logical reasoning.
- The future lies in neuro-symbolic AI, which combines:
- Neural networks (for language, vision, and perception).
- Symbolic reasoning (for logic, rules, and structured decision-making).
- Neural networks (for language, vision, and perception).
- Benefit: Agents capable of complex problem-solving with fewer hallucinations and stronger compliance guarantees.
Final Outlook
As enterprise AI trends mature, tool-using agents will evolve into collaborative, low-code, and logically robust systems. This will empower businesses to adopt future-ready AI automation strategies combining scalability, trust, and innovation.
Governance and Oversight of Autonomous Actions
Because tool-using agents can trigger real actions, governance becomes critical. An AI consulting company can assist with policy design, approval flows, and operational oversight frameworks.
Regional Deployment Considerations
Tool-using agents deployed in different regions must comply with local infrastructure and regulations. Teams may rely on AI development services in the US for region-specific deployment practices.
Conclusion
Tool-using AI agents represent the next leap in enterprise AI automation. By combining large language models with real-time tool integrations APIs, databases, and external services they elevate AI from static content generators to dynamic, context-aware agents that drive efficiency, accuracy, and scalability.
For enterprises, the impact is clear:
- Operational efficiency gains through automated, intelligent workflows.
- Higher data accuracy by leveraging external, live knowledge sources.
- Scalable solutions adaptable across functions from marketing and DevOps to customer service and analytics.
To fully harness the potential of AI, organizations should consider partnering with seasoned AI engineering firms. One example is AI Development Expert Solutions, which specializes in end-to-end custom AI solutions ranging from model training and deployment to AI-driven automation to deliver measurable efficiency gains and cost reductions .
FAQs
1. What is a tool-using AI agent?
A tool-using AI agent is an advanced artificial intelligence system that connects with external APIs, databases, or enterprise applications to perform tasks beyond simple text generation. Unlike standalone models, these agents can fetch real-time data, trigger actions, and integrate seamlessly with business workflows.
2. How do tool-using AI agents work?
They follow an AI agent loop consisting of:
- Reasoning: Interpreting the user request.
- Tool Selection: Choosing the right external service or API.
- Execution: Calling the tool to retrieve or process data.
- Result Delivery: Returning the synthesized, context-aware output.
This pipeline is typically powered by large language models (LLMs) that handle natural language understanding and orchestration.
3. What are examples of tool-using AI agents?
- AI chatbots integrated with CRM tools for customer support.
- SEO automation agents for keyword research, SERP analysis, and content clustering.
- AI DevOps tools that automate CI/CD pipelines.
- Data analysis agents that query structured (SQL) and unstructured (text, logs) sources.
4. What are the risks of using tool-enhanced AI agents?
Deploying tool-enhanced agents comes with several AI deployment challenges:
- Dependency on third-party APIs that may be unreliable.
- Latency issues from multiple tool calls.
- Security vulnerabilities if integrations are not properly secured.
- Risk of hallucinations, where the agent generates misleading or incorrect outputs.
5. What industries benefit most from tool-using AI agents?
Industries adopting AI automation applications include:
- Digital marketing (SEO) → automated keyword research and SERP monitoring.
- Finance → real-time risk modeling and compliance checks.
- Healthcare → medical record analysis and patient support chatbots.
- Software development (DevOps) → automated testing, deployment, and monitoring.
- Customer support → context-aware bots with CRM and ERP integrations.