Introduction
Shadow AI risks are becoming a growing concern as businesses adopt artificial intelligence tools at speed. Shadow AI refers to the use of AI applications, platforms, or services without official approval from IT or compliance teams. Employees often use these tools to solve problems faster, but doing so without oversight exposes the business to significant challenges.
Shadow AI is not always malicious. In many cases, employees simply adopt tools such as generative AI chatbots, coding assistants, or online analytics platforms to meet deadlines. A marketing team might upload customer data into a free text generator to speed up campaigns, or a developer might test an unapproved AI code assistant. While these actions feel harmless, the lack of oversight creates significant exposure to compliance and security risks.
This blog explains what shadow AI means, the issues it creates, and how businesses can adopt structured approaches to reduce risks. It also outlines shadow AI mitigation strategies, introduces the importance of business AI governance, and emphasizes why protecting the security of shadow AI should be a priority.
Learn how enterprises are adopting AI responsibly in our guide on AI in Enterprise Solutions by SDLC Corp.
Shadow AI in Business Explained
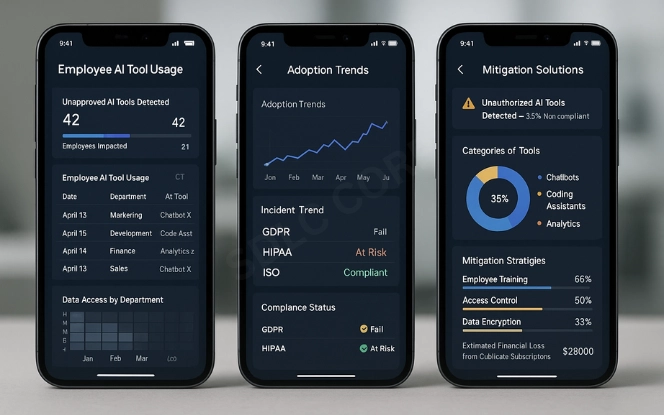
Shadow AI describes artificial intelligence tools adopted by employees or departments without authorization. This could be anything from free chatbot applications to advanced generative AI services accessed directly via the cloud.
Why shadow AI emerges:
Employees look for shortcuts to meet deadlines.
Public AI services are widely available with no barriers to entry.
Department leaders may prioritize convenience over compliance.
Impacts of shadow AI in business:
Data exposure: Staff may feed confidential information into unverified systems.
Siloed adoption: Different departments rely on tools that don’t integrate with core systems.
Compliance risks: Organizations cannot guarantee adherence to legal or regulatory standards.
Financial inefficiency: Duplicate licenses and wasted costs across business units.
When shadow AI scales, organizations risk losing control over their data, workflows, and even decision-making processes. This makes oversight and proactive management essential.
Shadow AI Risks Every Business Should Know
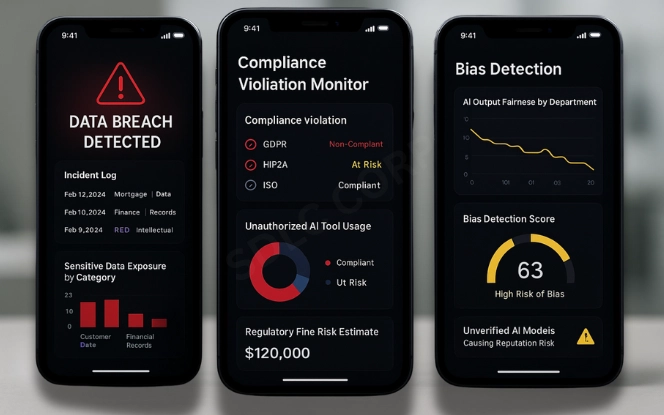
Unchecked use of artificial intelligence introduces a variety of shadow AI risks. These span security, regulatory, and operational domains.
Key categories of risk:
Data breaches: Sensitive corporate data can leak when input into external AI systems.
Regulatory violations: Use of unauthorized AI could breach GDPR, HIPAA, or other global data laws.
Bias and ethics: AI systems adopted without checks may deliver biased outputs, damaging reputation.
Operational inefficiencies: Siloed usage creates rework, duplicate processes, and poor integration.
Financial losses: Overlapping AI subscriptions and untracked expenses drain resources.
Perhaps the most significant issue is the security of shadow AI. Without visibility into how data flows or where it is stored, organizations cannot detect breaches or enforce controls. This lack of transparency weakens trust with customers, regulators, and stakeholders.
Managing Shadow AI in Enterprises
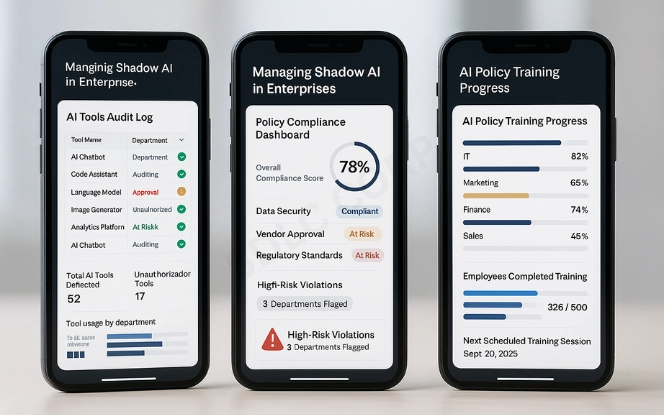
Completely banning AI is often counterproductive. Employees may continue to use tools secretly, making the risks worse. Instead, businesses should focus on managing shadow AI through structured oversight.
Practical steps for management:
Audit existing AI usage: Start by mapping the tools already in use, both approved and unapproved.
Establish clear policies: Set rules for acceptable AI use, data entry, and vendor approval.
Educate employees: Train teams on the dangers of unregulated AI adoption.
Provide approved alternatives: Offer enterprise-grade AI tools that are secure and monitored.
Monitor activity: Implement monitoring systems to flag unusual or unauthorized AI activity.
Why a ban doesn’t work
Consider a company that outright bans employees from using any external AI services. While this reduces short-term risk, it often pushes employees to adopt tools in secret. A developer under pressure may use an AI assistant anyway, leaving IT blind to the activity. This secrecy increases the danger, since data may flow outside controlled systems without any tracking.
When organizations combine education with enforcement, they create an environment where employees are encouraged to innovate within safe boundaries. Structured oversight turns shadow usage into controlled, monitored activity rather than hidden risk.
Shadow AI Mitigation Strategies
Addressing risks requires strong and realistic shadow AI mitigation strategies. These strategies help enterprises retain control while supporting productivity.
- Set up an AI governance framework
- Define roles, approval processes, and oversight mechanisms.
- Involve IT, compliance, and business leaders in decision-making.
- Define roles, approval processes, and oversight mechanisms.
- Centralize procurement
- Prevent duplication by routing all AI subscriptions through a single approval channel.
- Prevent duplication by routing all AI subscriptions through a single approval channel.
- Deploy security controls
- Encrypt data before it is processed by AI systems.
- Monitor traffic to detect unauthorized AI usage.
- Encrypt data before it is processed by AI systems.
- Create usage guidelines
- Communicate clear examples of permitted and restricted use.
- Communicate clear examples of permitted and restricted use.
- Schedule compliance reviews
- Regularly assess tools to ensure alignment with company and regulatory requirements.
- Regularly assess tools to ensure alignment with company and regulatory requirements.
By applying these strategies, companies avoid the worst outcomes of shadow AI and enable employees to work with confidence.
To explore structured governance approaches, see AI Alignment and Ethics
Business AI Governance: Building a Framework
Effective management of shadow AI requires clear policies, communication, and governance mechanisms. Advisory support helps organizations define acceptable AI usage, review processes, and escalation paths. An AI consulting company may assist in establishing governance frameworks that balance innovation with risk control.
Strong business AI governance ensures that all artificial intelligence usage aligns with company values, goals, and compliance obligations.
Core governance elements:
Accountability: Assign ownership of AI decisions to responsible individuals.
Transparency: Document usage logs, data flows, and version history for AI models.
Ethics oversight: Review fairness, bias, and unintended consequences.
Regulatory compliance: Ensure every tool complies with GDPR, HIPAA, and regional data laws.
Expanding governance in practice
Modern governance goes beyond simple approval checklists. Some industries require detailed reporting to regulators, such as healthcare providers under HIPAA or financial institutions under Basel and GDPR. In these cases, businesses must maintain documentation showing how data is handled, who accessed AI models, and how outputs were validated. This level of oversight prevents fines and builds confidence among regulators and clients.
Good governance requires collaboration across security, compliance, and operational leaders. A proactive stance reduces vulnerabilities and strengthens confidence in enterprise AI use.
Security of Shadow AI
Among all issues, the security of shadow AI is the most urgent. Unauthorized AI systems can introduce vulnerabilities that go undetected until damage occurs.
Recommended security practices:
Access management: Restrict usage of AI systems to authorized personnel.
Data classification: Establish clear rules for what information can and cannot be entered into AI.
Encryption and monitoring: Apply end-to-end encryption and keep detailed logs.
Incident response plans: Prepare procedures for investigating and remediating AI breaches.
Enterprises that focus on security not only reduce immediate risks but also demonstrate responsibility to customers and regulators. This is key to maintaining reputation and trust.
For technical insights on safeguards, visit Responsible AI Development
Practical Solutions for Businesses
Organizations need practical, balanced approaches to shadow AI. The goal is not to restrict innovation but to channel it safely.
Solutions include:
Awareness campaigns: Teach staff the benefits of using approved AI tools.
Monitoring systems: Deploy platforms that detect and track AI usage across the enterprise.
Leadership involvement: Ensure executives lead by example and follow AI governance rules.
Reward programs: Recognize teams that innovate responsibly within established guidelines.
Evolving policies: Update AI governance frameworks regularly to keep pace with new technologies.
Example in practice
A global consulting firm introduced a “safe AI rewards” program where employees were encouraged to disclose unapproved AI tools they were using. Instead of punishment, the IT team reviewed the tool and, if safe, added it to the approved list. This transparency reduced secret adoption and gave employees confidence to innovate without fear.
By blending governance, security, and culture, businesses can reduce hidden risks and unlock the benefits of AI.
Regional Considerations in Shadow AI Governance
Regulatory expectations around AI usage vary by region, affecting how shadow AI risks are addressed. References to AI development services in the US help illustrate how regional regulations influence AI governance, monitoring, and reporting practices.
Conclusion
Shadow AI is no longer an abstract risk. It already exists inside many organizations and grows whenever employees bypass official channels to access AI tools. Left unchecked, it creates data risks, compliance challenges, and operational inefficiencies.
By understanding shadow AI risks, businesses can implement smarter approaches. By focusing on the security of shadow AI, they protect their most valuable data assets. With shadow AI mitigation strategies, leaders can move beyond restriction to proactive management. And with strong business AI governance, organizations can create transparency and accountability across all AI activities.
The future depends on finding balance. Managing shadow AI does not mean stopping employees from using AI. It means giving them secure, governed, and effective tools that help them work smarter.
Businesses that achieve this balance gain more than risk reduction — they gain trust from customers, credibility with regulators, and confidence within their workforce. Proactive organizations turn a hidden liability into a driver of safe innovation.
Contact us SDLC Corp to learn how to protect your enterprise from shadow AI challenges. To accelerate innovation with confidence, Hire AI Development Services with SDLC Corp today.
FAQs
What Are The Biggest Shadow AI Risks For Businesses?
Shadow AI risks include data exposure, compliance failures, bias in outputs, duplicated costs, and vulnerabilities that arise from unapproved AI tools.
How Does Shadow AI In Business Affect Data Security?
Shadow AI in business can compromise sensitive data when employees use unregulated AI platforms. This increases the chance of leaks and weakens security protocols.
What Steps Help In Managing Shadow AI Effectively?
Managing shadow AI requires audits of current tools, clear governance policies, training programs, and offering employees secure, approved AI alternatives.
What Shadow AI Mitigation Strategies Reduce Compliance Risks?
Key shadow AI mitigation strategies include centralized procurement, encryption of sensitive data, compliance reviews, and strict business AI governance practices.
Why Is Security Of Shadow AI A Priority For Enterprises?
The security of shadow AI is crucial because unauthorized systems bypass monitoring. Strong access controls, encryption, and incident response plans protect data.