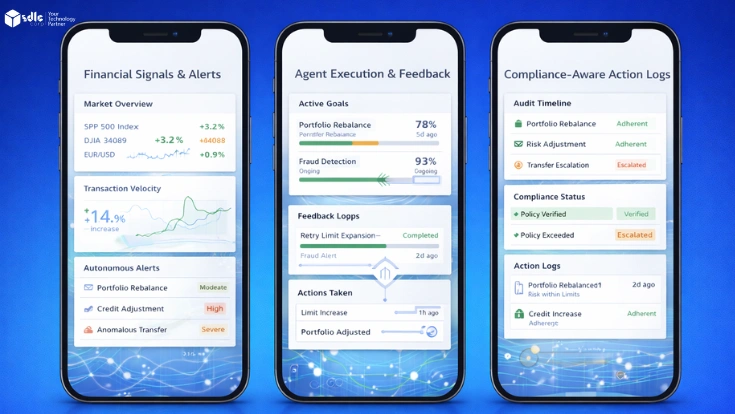
Introduction
AI for Finance helps financial teams manage growing data volumes, reduce risk, and improve decision-making. As transactions, forecasts, and compliance demands increase, manual processes struggle to keep pace. Artificial intelligence enables faster analysis, pattern detection, and more consistent outcomes across finance functions.
This blog explains how artificial intelligence works in finance, where it delivers value, and how teams can apply it responsibly across risk management, forecasting, accounting, and compliance. For a broader technical foundation, you can review our AI development services overview explaining how enterprise finance teams adopt AI responsibly.
The Role of AI in Modern Finance
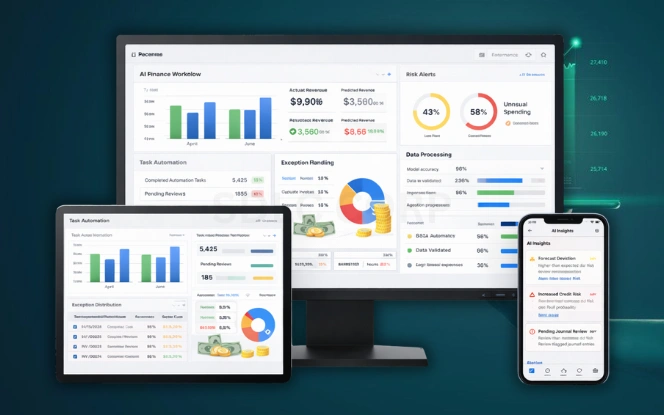
Finance has always depended on accuracy and timing. Artificial intelligence in finance improves both by automating data-heavy tasks and supporting better judgment. AI systems analyze large datasets, learn from patterns, and produce consistent outputs.
Financial organizations use AI to:
- Process transactions at scale
- Detect anomalies in real time
- Support compliance and reporting
- Improve forecasting accuracy
AI in financial services works best when paired with human oversight. Machines handle volume and speed. Humans handle context and accountability. This balance defines successful adoption.
A deeper breakdown of enterprise adoption models is available in our AI implementation strategy guide for regulated industries.
How AI Systems Process Financial Data
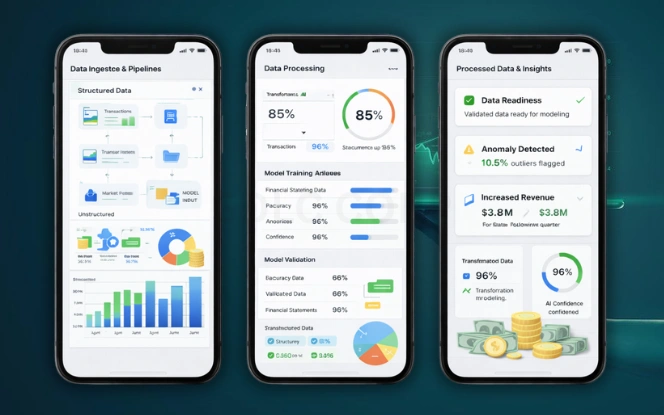
AI systems rely on structured and unstructured financial data. This includes ledgers, invoices, market feeds, customer behavior, and historical performance. Machine learning models in finance train on this data to identify relationships that are not visible through traditional analysis.
Key data inputs include:
- Transaction histories
- Financial statements
- Market indicators
- Risk and compliance records
Once trained, models can classify data, predict outcomes, or flag exceptions. However, output quality depends on data quality. Poor data leads to unreliable results.
Strong governance, validation rules, and audit trails remain essential. AI enhances financial workflows but does not replace financial responsibility.
AI for Financial Risk Management
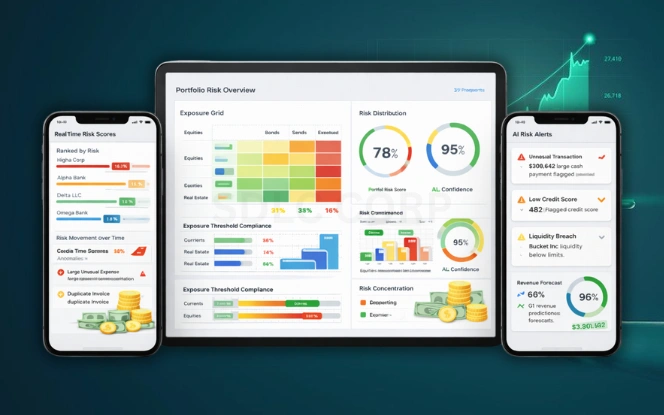
Financial risk evolves constantly. Credit exposure, market volatility, liquidity pressure, and operational failures create ongoing threats. AI in financial risk management improves early detection and response.
AI models monitor patterns across portfolios and transactions. They identify deviations that may signal fraud, credit default, or compliance issues. Unlike static rules, AI adapts as conditions change.
Common risk use cases include:
- Credit scoring and loan risk
- Fraud detection
- Market risk monitoring
- Stress testing
Human review remains critical. AI highlights risk faster, but final decisions must remain explainable and compliant with regulations.
You can also explore our risk analytics and compliance automation framework to understand how AI supports governance requirements.
Machine Learning in Finance Operations
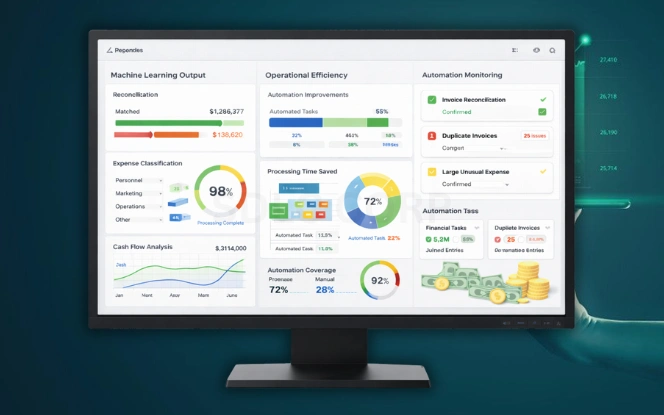
Machine learning in finance focuses on learning from historical patterns to improve operational efficiency. Models adjust as new data arrives. This allows systems to stay relevant even as market behavior shifts.
Finance teams apply machine learning to:
- Expense classification
- Payment reconciliation
- Cash flow analysis
- Customer segmentation
These systems reduce repetitive work and improve consistency. However, transparency matters. Financial institutions must understand how models reach conclusions, especially when outcomes affect customers or regulators. Clear documentation and model governance protect trust.
AI in Accounting and Financial Close

The financial close process demands accuracy under time pressure. AI helps teams complete close cycles faster while reducing errors. Systems match transactions, flag discrepancies, and validate entries automatically.
AI supports:
- Automated reconciliations
- Journal entry validation
- Exception reporting
- Audit preparation
Artificial intelligence in finance does not eliminate accountants. Instead, it shifts their focus from manual checks to review and analysis. This improves control and accountability across reporting cycles.
AI for Financial Forecasting
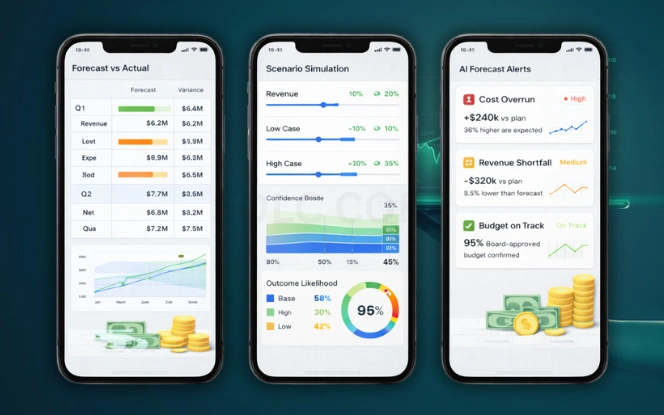
Forecasting relies on assumptions. AI for financial forecasting improves forecasts by learning from historical performance and external signals. Models consider seasonality, trends, and correlations that static spreadsheets miss.
AI-driven forecasting supports:
- Revenue projections
- Budget planning
- Demand estimation
- Scenario analysis
Forecast accuracy improves when models use clean historical data and defined business logic. AI does not predict the future perfectly. It improves probability estimates and highlights risk ranges.
AI in Banking and Lending
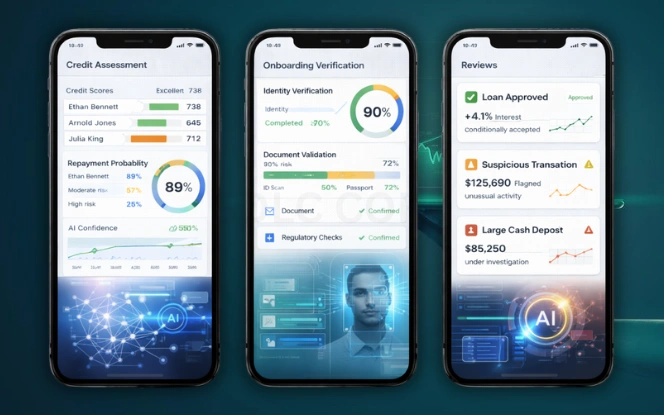
Banks process millions of transactions daily. AI in financial services supports customer onboarding, credit evaluation, and transaction monitoring. These systems reduce friction while improving compliance.
Key applications include:
- Customer verification
- Credit risk assessment
- Transaction monitoring
- Personalized financial offers
Banks must ensure fairness and transparency. Biased data can lead to biased outcomes. Responsible AI governance remains critical in lending decisions.
Fraud Detection and Compliance

Fraud patterns change quickly. Static rules often fail to detect new threats. AI systems learn from behavior rather than fixed thresholds. This improves detection without increasing false positives.
AI strengthens:
- Payment fraud detection
- Identity misuse monitoring
- Compliance reporting
- Regulatory audits
Regulators expect explainable systems. Financial institutions must document how AI flags activity and how teams respond. Transparency protects both customers and institutions.
AI in Investment and Portfolio Management

Investment teams use AI to analyze market data, news feeds, and historical trends. Models support portfolio optimization and risk balancing.
AI assists with:
- Asset allocation analysis
- Risk-adjusted returns
- Market sentiment analysis
AI does not replace investment judgment. Markets respond to human behavior and unexpected events. AI provides structured insights that support, not replace, decision-making.
Data Governance and Ethics in Financial AI
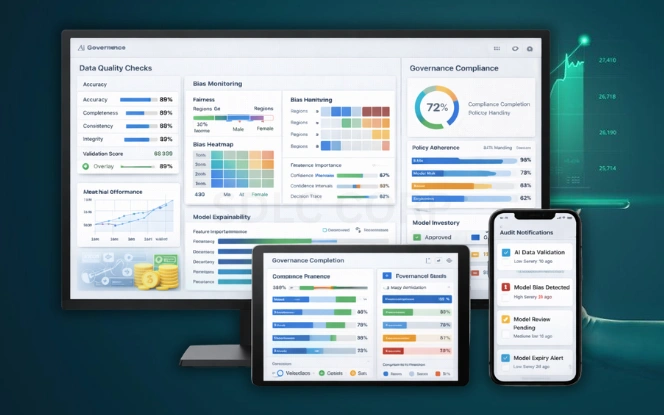
Ethics define trust in finance. AI systems must operate within legal and ethical boundaries. This includes fairness, accountability, and transparency.
Key governance principles include:
- Data quality control
- Bias testing
- Model explain ability
- Audit readiness
Artificial intelligence in finance must align with regulatory expectations. Poor governance creates legal and reputational risk. Responsible AI adoption protects long-term value.
Additional insight into responsible deployment is covered in our Shadow AI Risks and Solutions for Businesses designed for financial organizations.
Integration Challenges in Finance Systems

Legacy systems remain common in finance. Integrating AI requires planning. Data silos, inconsistent formats, and outdated infrastructure slow adoption.
Successful teams:
- Clean and standardize data
- Define clear use cases
- Train staff on AI outputs
- Phase deployments gradually
AI adds value when aligned with business processes. Technology alone does not deliver results.
Measuring ROI from AI in Finance
Finance leaders demand measurable returns. AI projects must show value through efficiency gains, risk reduction, or improved accuracy.
Common metrics include:
- Time saved in close cycles
- Reduction in fraud losses
- Forecast accuracy improvement
- Compliance cost reduction
Clear KPIs ensure AI investments remain accountable.
The Future of AI for Finance

AI adoption will continue across finance functions. Systems will grow more integrated and more regulated. The focus will shift from experimentation to governance and scale.
Future priorities include:
- Stronger model transparency
- Cross-functional data platforms
- Human-AI collaboration
- Regulatory alignment
AI will remain a tool. Financial accountability will remain human.
Conclusion
AI for Finance supports faster analysis, better risk control, and improved decision-making. When implemented responsibly, it strengthens financial operations without compromising trust. Artificial intelligence in finance works best when paired with skilled professionals and strong governance.
Finance leaders should focus on practical use cases, data quality, and compliance readiness. AI in financial services continues to evolve, but fundamentals remain unchanged.
Hire AI Development Services with SDLC Corp to build secure, compliant, and scalable financial AI solutions. Contact us SDLC corp to discuss your finance transformation strategy.
FAQs
What Is AI For Finance And How Is It Used?
AI for Finance refers to the use of intelligent systems to analyze financial data, automate processes, manage risk, and support better decision-making across finance functions.
How Does Artificial Intelligence In Finance Improve Accuracy?
Artificial intelligence in finance improves accuracy by analyzing large datasets consistently, reducing manual errors, and identifying patterns that traditional analysis may overlook.
Where Is AI In Financial Services Most Commonly Applied?
AI in financial services is commonly applied in risk management, fraud detection, forecasting, accounting automation, and compliance monitoring.
How Does AI In Financial Risk Management Work?
AI in financial risk management monitors transactions and market data to detect unusual patterns, assess exposure, and support early risk identification.
What Role Does Machine Learning In Finance Play?
Machine learning in finance enables systems to learn from historical data, improve predictions, and adapt models as financial conditions change.
How Reliable Is AI For Financial Forecasting?
AI for financial forecasting improves projections by using historical trends and external data, but results still require human review and business judgment.
Is AI In Finance Safe And Compliant With Regulations?
AI in finance can be safe and compliant when supported by strong data governance, transparent models, and alignment with regulatory standards.