Introduction
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are essential tools for modern organizations looking to streamline operations, improve decision-making, enhance data accuracy, and scale efficiently. Among ERP software solutions, Odoo ERP stands out due to its modular, open-source architecture, extensive functionalities, and adaptability for businesses of various sizes and industries. However, the implementation process plays a pivotal role in determining the overall success of the ERP system.
This comprehensive guide explores the best practices for Odoo ERP implementation, offering actionable strategies, expert recommendations, and lessons from real-world case studies to ensure your ERP deployment delivers long-term value.
2. Understanding Odoo ERP
Odoo ERP is a powerful, all-in-one business management suite that integrates essential business functions into a single, unified platform. The system includes core modules such as CRM, sales, eCommerce, finance, warehouse management, production planning, HRM, and project tracking. It offers both a free community edition and a feature-rich enterprise version.
Key features:
Modular Design: Activate only the ERP modules you need and scale seamlessly.
Integrated Applications: Achieve unified reporting and automation across departments.
Customization & Scalability: Adapt modules to meet evolving business needs.
Open Source & Cloud-Based Options: Choose between local hosting and Odoo.sh or third-party cloud services.
3. Pre-Implementation Planning
Effective ERP implementation begins with strategic planning. Failure to properly define scope, goals, and expectations can lead to delays, budget overruns, and system underutilization.
Steps to follow:
Business Process Mapping: Evaluate existing workflows and pinpoint inefficiencies.
Gap Analysis: Compare current processes against best practices and Odoo capabilities.
Stakeholder Alignment: Define roles and get buy-in from leadership and end-users.
Objective Setting & KPIs: Establish benchmarks for ERP performance and adoption.
Budget and Timeline Framework: Align project cost with complexity and ROI expectations.
4. Choosing the Right Implementation Partner
Selecting a skilled Odoo implementation partner can significantly impact your ERP project’s success. A qualified partner offers technical, functional, and domain-specific expertise to accelerate deployment and reduce risks.
Evaluation checklist:
Odoo Certified Partner: Prefer Gold or Silver partners with certified consultants.
Industry Experience: Look for successful ERP implementations in your vertical.
Customization and Development Capabilities: Ensure ability to build or modify modules.
Training and SLA-Based Support: Choose a partner who provides end-user training and long-term support packages.
5. Data Migration and System Configuration
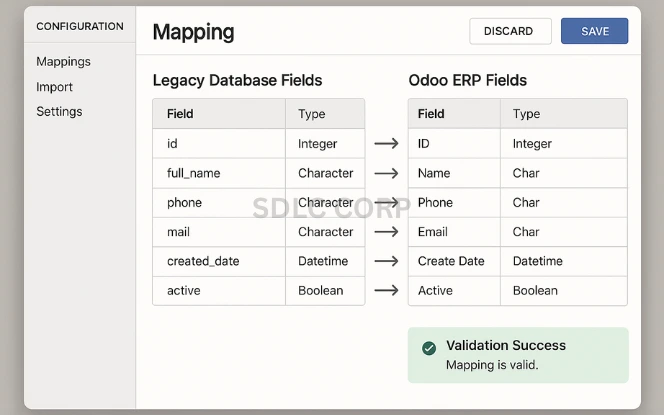
Data migration is a high-risk activity in ERP projects. Accurate data transfer is vital to maintain reporting accuracy and operational continuity.
Best practices:
Legacy Data Audit: Remove obsolete or duplicated records.
Mapping and Transformation: Ensure compatibility between legacy system fields and Odoo schema.
Automation Tools: Use migration scripts and Odoo’s built-in import features.
System Configuration: Customize modules to reflect your business logic, workflows, and localization requirements.
6. Customization vs. Standardization
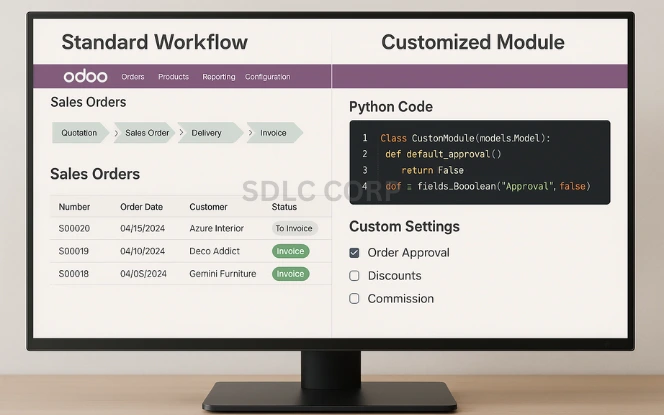
Customizing Odoo can provide a competitive edge, but excessive customization leads to complex upgrades and higher maintenance costs.
Recommendations:
Process Standardization: Use standard Odoo workflows when possible.
Justifiable Customization: Customize only where there is a clear business need.
Scalable Architecture: Follow modular development practices for custom apps.
Upgrade-Friendly Coding: Stick to Odoo’s guidelines to ensure version compatibility.
7. User Training and Change Management
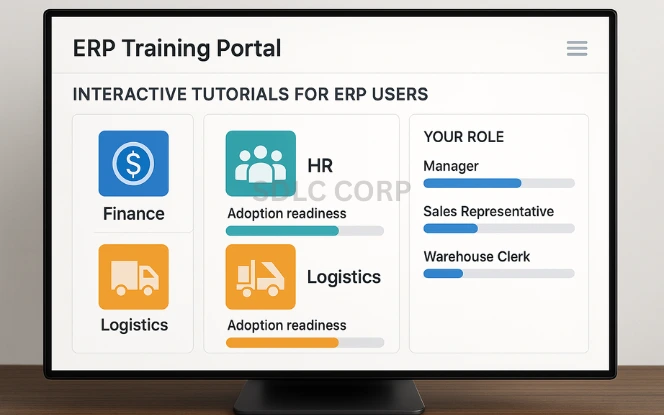
A robust change management plan and user training framework are essential to ensure ERP system adoption and minimize resistance.
Effective practices:
Customized Training Modules: Design sessions based on user roles (e.g., finance, operations, HR).
Training Delivery Tools: Use learning management systems, walkthrough videos, and live demos.
Change Management Framework: Incorporate communication plans, feedback loops, and milestone tracking.
Ongoing Support: Provide refresher training and Q&A sessions post-launch.
Keywords focused: ERP user training, change management, Odoo training, ERP adoption strategy, ERP onboarding
8. Testing and Quality Assurance
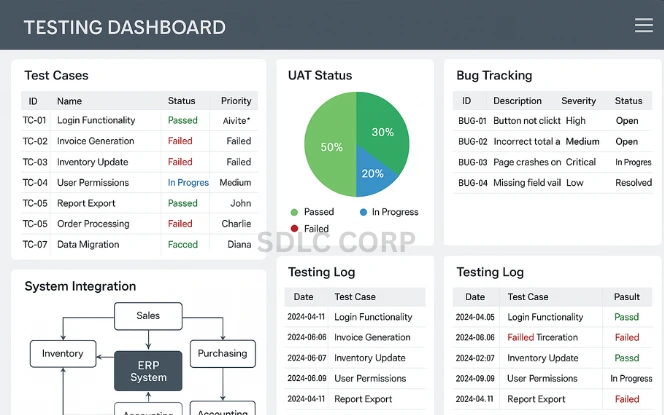
Comprehensive testing ensures your Odoo ERP solution is reliable, scalable, and aligned with business processes.
Testing phases:
Functional Testing: Validate individual modules (e.g., accounting, inventory).
System Integration Testing (SIT): Ensure modules work together seamlessly.
Load Testing: Assess system performance under peak usage.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Gather validation and approval from end-users.
9. Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support
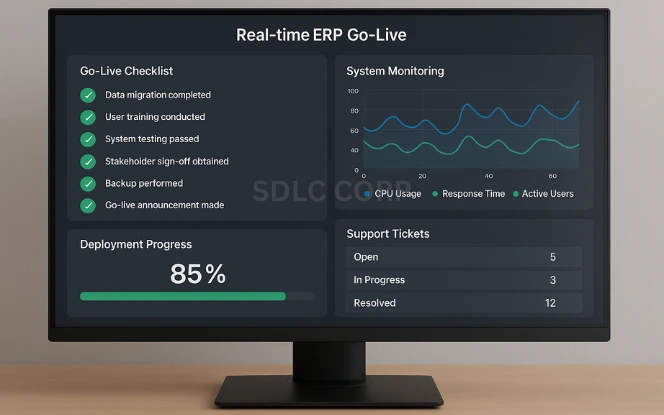
Go-live is just the beginning. Structured support ensures business continuity and system optimization.
Go-live checklist:
Final QA Sign-Off: Confirm readiness across all business units.
Role-Based Access Configuration: Secure and control module access.
Monitoring Tools Deployment: Track performance, errors, and user behavior.
Helpdesk Setup & SLA: Provide multichannel support with response time guarantees.
Review and Optimization Cycles: Plan monthly reviews and system health checks.
10. Case Studies
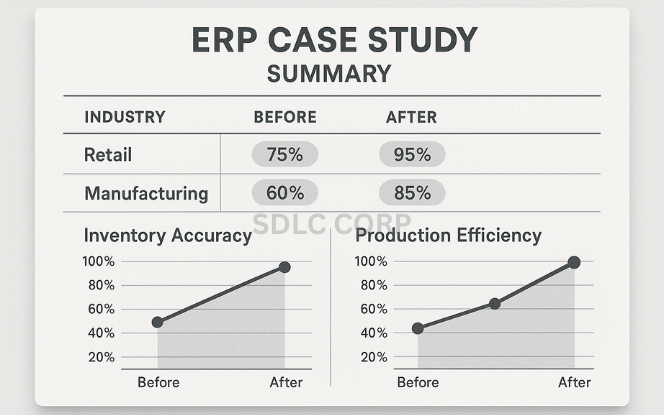
Retail Business Transformation: A multi-store retail chain implemented Odoo POS, inventory, and accounting. Standard workflows and tailored dashboards resulted in a 35% improvement in inventory accuracy and real-time financial reporting.
Manufacturing Optimization: A custom machinery manufacturer replaced legacy tools with Odoo MRP and procurement modules. The ERP implementation reduced production planning errors by 40% and streamlined procurement lead times.
Conclusion
Implementing Odoo ERP can be transformative when approached with a solid roadmap and skilled execution. Every phase from discovery to go-live and beyond demands attention to detail, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Organizations that follow these ERP best practices position themselves for long-term efficiency, scalability, and innovation.
FAQ's
Is Odoo suitable for small businesses?
Yes, Odoo is scalable. Small teams can use its core features, while larger organizations can integrate additional modules as needed.
Can I use Odoo for Agile project management?
Absolutely. Odoo supports Kanban views, task stages, and burndown charts—ideal for Agile workflows.
Does Odoo Project Management support billing?
Yes. You can track time with timesheets and bill clients directly through the Invoicing module.
Can clients access projects?
Yes. You can share access with external users or clients and limit what they see.
Is Odoo cloud-based or on-premise?
It offers both. You can choose between Odoo Online (cloud) or deploy it on your own servers.





