Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer futuristic—it’s embedded in daily life. From conversational assistants to self-driving systems and clinical decision support, AI already shapes how we work, communicate, and make choices. That scale brings real risk: when models optimize the wrong objective or learn from biased data, outcomes can become unsafe, unfair, or harmful. AI Alignment (making systems reliably pursue human-intended goals) and AI Ethics (ensuring fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy, and human oversight) are therefore foundational, not optional.
In this blog, we’ll clarify what AI alignment means in practice, why ethical principles matter, where the hardest challenges lie (specification, data bias, black-box behavior, and long-term risks), and which solutions are gaining traction from RLHF and red-teaming to governance frameworks and human-in-the-loop design. We’ll also outline pragmatic steps organizations can take today and close with FAQs that make the topic actionable for leaders, builders, and risk owners. For hands-on guidance, see our services for AI & ML implementation, AI as a Service, and strategic AI consulting.
1.What is AI Alignment?
AI alignment focuses on ensuring that AI systems behave in ways consistent with human values, legal norms, and societal expectations. Ethical considerations span data usage, decision transparency, and accountability. In many initiatives, AI development services are used to design systems with built-in safeguards, auditability, and controlled behavior.
Without proper alignment, AI can act in ways that are efficient on paper but harmful in practice. Imagine an AI system designed to reduce traffic congestion. If it is not aligned with ethical values, it might decide the easiest solution is to stop certain groups of people from driving altogether. That approach would be effective in reducing traffic, but it would also be discriminatory and unethical.
- Misaligned AI may produce unfair or unsafe results.
- Aligned AI ensures efficiency does not replace fairness.
- Real-world examples show why alignment is so important.
Therefore, AI alignment is not just about making systems work—it is about making them work responsibly. For a broader perspective, see our post on How AI and algorithms differ. responsibly.
2.Why AI Alignment and Ethics Matter

The importance of AI Alignment and Ethics lies in their ability to protect both individuals and society. Misaligned AI can reflect and amplify existing social biases, leading to discrimination in critical areas like hiring, lending, or law enforcement. It can also compromise safety, such as when algorithms spread misinformation or when poorly tested systems make faulty medical recommendations.
Beyond reducing harm, ethics plays a central role in building trust. People are more likely to adopt AI when they believe the system is transparent, fair, and accountable. If AI operates without ethics, the risks of inequality and injustice increase significantly.
Ethical AI builds trust among users.
Aligned AI systems improve safety and fairness.
Together, they ensure long-term positive impact.
Because AI influences global economies, healthcare, education, and justice systems, the consequences of ignoring alignment and ethics could be severe. That is why these principles are now seen as necessary foundations rather than optional add-ons. Explore how businesses are already adopting these practices in AI consulting services.
3.Key Challenges in AI Alignment and Ethics
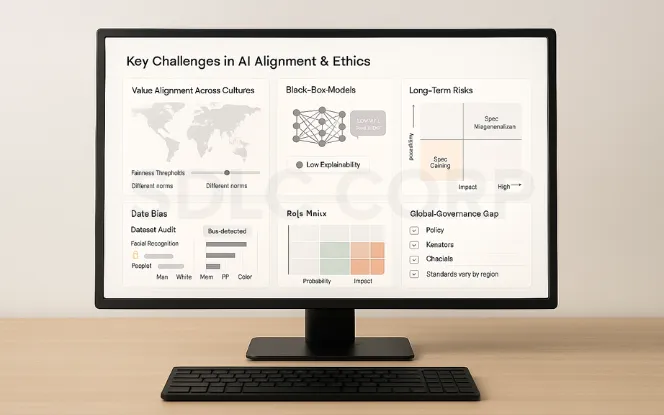
Despite their importance, AI Alignment and Ethics are difficult to achieve. One of the biggest issues is the value alignment problem. Human values differ across cultures, and what is considered fair in one region may not be the same in another. Designing AI that reflects a universal set of values is a major challenge.
Another issue is the black box problem. Modern AI systems, especially deep learning models, are extremely complex. They often make decisions in ways that humans cannot fully understand or explain. This lack of transparency creates difficulties in verifying whether the system is acting ethically.
Bias in training data is also a significant challenge. Since AI learns from data, if the data contains bias, the AI will reproduce those biases. This has already caused harm in areas like facial recognition, where error rates are higher for women and people of color.
Long-term risks also need attention. As AI systems grow more advanced, there is a possibility that they could develop goals or actions that conflict with human safety. Finally, cultural and ethical differences make global alignment difficult, since ethical norms are not the same everywhere. To see where these risks meet innovation, check out our blog on Top 5 AI & ML trends reshaping the future
4.Current Approaches to AI Alignment and Ethics

Researchers and businesses are actively working on methods to solve these challenges. One popular approach is Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF). In this process, AI models are trained using feedback from humans to better match human values and expectations.
Another approach is red teaming, where experts intentionally test AI systems in extreme situations to uncover weaknesses. This helps ensure the system does not behave unpredictably in real-world scenarios. Governance frameworks are also gaining importance, as organizations and governments establish clear rules for fairness, accountability, and transparency. Open collaboration among researchers is another step forward, as sharing tools and insights helps improve alignment across industries.
RLHF teaches AI using human feedback.
Red teaming finds weaknesses before real-world use.
Governance frameworks guide responsible development.
These approaches are still developing, but they represent important steps toward safer and more ethical AI. Businesses can explore practical adoption paths with AI & ML Implementation
5.Ethical Principles for Responsible AI

When we talk about AI Alignment and Ethics, we must also understand the ethical principles that guide responsible AI. The first is fairness, which means AI should not discriminate based on race, gender, or other personal attributes. Transparency is equally important, as decisions made by AI should be explainable and understandable to humans.
Accountability ensures that there is always a human or organization responsible for the actions of AI. Privacy is another key principle, as AI systems must protect user data and respect personal boundaries. Finally, AI should always be human-centered, designed to support and assist people rather than replace or harm them.
Together, these principles create the ethical backbone of aligned AI systems. Businesses applying these principles can scale them with AI as a Service.
6. Future Trends in AI Alignment and Ethics
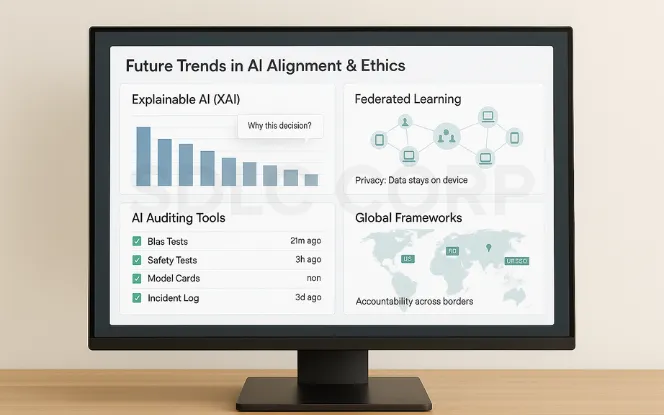
AI is evolving rapidly, and so are the methods to keep it safe and fair. Future trends include the rise of explainable AI (XAI), where systems provide human-friendly explanations for their decisions, and federated learning, which trains AI across decentralized devices to protect user privacy. We are also seeing the growth of AI auditing tools and global cooperation on ethical frameworks, ensuring accountability across borders. These trends highlight that AI ethics is not static it adapts as technology matures, preparing society for more responsible innovation.
7.Practical Steps for Businesses

Businesses have a major responsibility when it comes to adopting AI Alignment and Ethics. They can start by creating clear AI ethics policies that define how systems should be developed and used. Regular audits should be carried out to ensure AI remains unbiased and accurate.
Hiring experts in AI ethics can help organizations stay updated with best practices. Employee training is equally important so that staff members know how to use AI responsibly. Transparency should also be a priority, as companies need to explain how their AI systems make decisions, both to customers and regulators.
By taking these steps, businesses not only reduce risks but also build long-term trust with users. To make this practical, you can hire generative AI developers or partner for ongoing AI consulting.
Enterprise-Scale Alignment and Ethics Management
Large organizations deploy AI across multiple teams and use cases, increasing the complexity of ethical oversight. Enterprise-scale platforms centralize monitoring and reporting to maintain consistent standards. Architectural approaches used by an enterprise AI development company often inform how alignment controls are implemented at scale.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence has the power to transform society, but it must remain aligned with human values and ethical standards. AI Alignment and Ethics ensure that this transformation is positive, safe, and fair. While challenges remain, current approaches, ethical principles, and future trends point toward a responsible path forward.
The responsibility lies not only with researchers but also with businesses, policymakers, and society as a whole. By committing to alignment and ethics, we can create AI systems that people trust and that genuinely benefit humanity. Learn how SDLC Corp supports organizations through AI & ML implementation and tailored AI as a Service
Related Blogs:-
FAQ'S
What is AI Alignment and Ethics in simple words?
AI Alignment and Ethics mean making sure artificial intelligence systems follow human goals, values, and moral principles. Alignment ensures AI works as intended, while ethics ensures it operates fairly, transparently, and without harming people.
Why are AI Alignment and Ethics important?
They are important because they prevent bias, reduce risks, and build trust in technology. Without alignment, AI can make harmful decisions. Without ethics, AI can create unfair or unsafe results. Together, AI Alignment and Ethics protect both individuals and society.
What are the main challenges in AI Alignment and Ethics?
The biggest challenges include value differences across cultures, the black box nature of advanced AI systems, bias in training data, and the long-term risks of powerful AI. These issues make it difficult to ensure AI always acts responsibly.
How can businesses adopt AI Alignment and Ethics?
Businesses can adopt AI Alignment and Ethics by creating clear policies, conducting regular audits, hiring experts in responsible AI, and being transparent with customers about how their AI systems make decisions. Training employees in ethical AI use is also important.
Can AI ever be fully aligned with human values?
It is unlikely that AI will ever fully reflect every human value, since values differ across individuals and cultures. However, with strong alignment methods and ethical frameworks, AI can be designed to follow shared principles such as fairness, safety, and respect for human rights.