Blockchain Technology Complete Guide
Introduction
Blockchain technology is a groundbreaking innovation that offers a decentralized, secure, and transparent method for recording and managing data across various industries. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain enhances efficiency and trust in digital transactions. Blockchain development is at the core of creating and maintaining these decentralized systems, allowing businesses to leverage this powerful technology for various use cases.
One of the key components of blockchain is smart contract development, which automates processes such as payments or agreements when specific conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries. For businesses with unique needs, custom blockchain development provides tailored solutions that fit specific operational requirements. Additionally, blockchain wallet development ensures users can securely store and manage digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies or NFTs, further enhancing the usability of blockchain networks. This guide will explore the essential aspects of blockchain and its diverse applications across industries.
Get Started with Secure Blockchain Wallet Solutions Today!
Blockchain wallet development enables secure storage and management of digital assets, allowing users to send, receive, and track cryptocurrencies.

How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Blockchain technology operates as a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers, known as nodes. Each transaction is grouped into a “block” and added to a chain of previous transactions, creating a secure, chronological record. The blocks are connected using cryptographic hashes, ensuring that no block can be altered without altering all subsequent blocks, making the data tamper-proof. Blockchain development enables this structure, allowing for transparency and security in various applications. Smart contract development can automate processes by executing predefined agreements without intermediaries. The entire system is decentralized, removing the need for central authorities, and is maintained by consensus algorithms across the nodes.
Here are the Most Essential Segments of the Blockchain:
distributed Ledger
A blockchain is basically distributed Ledger a distributed ledger that keeps track of transactions in a way that doesn’t require a central location. This means that the ledger is not kept in one place. Instead, it is kept on a network of computers. Each node on the network keeps a copy of the ledger, and all of the nodes work together to verify transactions and keep the ledger’s integrity.
Cryptography
Cryptography is a set of methods used to make sure that data and communications are safe. Several cryptographic methods are used by blockchain technology to protect the data it stores. Hashing is one of the most important techniques. It turns data of any size into data of a fixed size. Hashing is used to give each block in the blockchain a unique digital signature. This makes sure that any changes to the data will be noticed right away.
Consensus Mechanism
It’s the process by which nodes on the network agree on how the blockchain is doing. For example, (PoW) Proof of Work, (PoS) Proof of Stake, and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) are all ways that blockchain technology reaches a consensus. These mechanisms make sure that all nodes on the network agree on the validity of the transactions and stop bad people from messing with the blockchain.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts enable the automation of specific tasks, such as executing payments when predefined conditions are met. These contracts are written in specialized programming languages and are securely stored on the blockchain in an immutable format. Smart contract development ensures that these agreements are self-executing and cannot be altered, providing a reliable and efficient way to automate processes without the need for intermediaries.
Decentralized Applications (dApps)
Decentralized applications, or dApps, are programmes that run on a decentralised network, like a blockchain. They are made to be open source, easy to understand, and not controlled by a single group. dApps can be used for a lot of different things, from financial apps to social media sites.
Tokens
Tokens are digital assets that are made available on a blockchain. They can be used as money or as a way to show things like real estate or stocks. Tokens are stored on the blockchain, which makes it safe and easy to move them from one address to another.
In short, blockchain technology is a complicated system made up of a lot of different segments. Together, these parts make a secure, open, and decentralized network that can be used for a lot of different things. From distributed ledgers to smart contracts, every part of the blockchain is important for keeping it honest and safe.
Transform Your Business with Blockchain Solutions!
Blockchain consulting services provide expert guidance on integrating blockchain technology into business models, improving security, and scalability.

Let's Understand the Workings of Blockchain Technology with the Help of an Image
Let’s Understand the Workings of Blockchain Technology with the Help of an Image
The image shows how a blockchain works in a visual way. The blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores information in a way that is not controlled by one person or group. The picture shows a chain of blocks, with each block representing a transaction or piece of data that has been added to the blockchain. The first block in the chain is called the “genesis block,” and it is the first block that starts the chain. The genesis block doesn’t have a previous block hash, which is a unique identifier that links each block to the one before it. After the genesis block, other blocks are added to the chain in the order in which they happened.
In the chain, each block is made up of a block header and the block body. The block header has information like the block number, the time the block was made, and the hash of the block before it. The data that is being stored on the blockchain is in the block body. When a new block is added to a chain, the network of nodes on the blockchain verifies the block. These nodes do complicated calculations to make sure that the data in the block is correct and that the block is valid. After the block is verified, it is added to the chain, and a new block is made.
Types of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has different forms. Each kind of blockchain has its own features and ways to use it.
1. Public Blockchain
A public blockchain is a decentralised network in which anyone can be a node. The transactions on the public blockchain are open to the public and can be seen by anyone. The records of the transactions are also kept forever on the blockchain. The best-known use of the public blockchain is in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Some of the benefits of public blockchains are that they are very safe, easy to understand, and there is no one in charge of the network. But public blockchains have some problems, like slow transaction speeds, a lot of energy use, and problems with scaling.
How Does Walmart Uses Public Blockchain Technology?
Walmart, one of the biggest stores in the world, has been looking into how public blockchain technology could help improve the way it manages its supply chain. Using IBM’s Food Trust blockchain platform, the company has set up a pilot project to track where fresh food comes from and how it gets from the farm to the store shelves. In the pilot project, a public blockchain is used.The blockchain keeps track of important information, like where food products come from, how they are made, and where they are sent. This lets Walmart keep track of how the food gets from the farm to the store shelves in real time.
This system for managing the supply chain is made better in many ways by the use of blockchain technology. First, it makes things clearer and easier to track, which makes food safer and helps keep it from getting contaminated or going bad. If a problem is found with a certain batch of fruit or vegetables, the blockchain can quickly find the source and let Walmart take the right steps.
Second, using blockchain technology can help cut down on waste and make things run more smoothly. By giving Walmart real-time information about where the produce is and how it got there, the company can improve its supply chain management and reduce the amount of food that is being wasted because it spoils or gets damaged while being shipped. Third, the use of blockchain technology can also make the supply chain more accountable and trustworthy. Everyone in the network can see the same information, which helps build trust and lowers the risk of fraud.
2. Private Blockchain
A private blockchain is a network that only nodes with permission to join can join. Businesses and organisations often use private blockchains to keep sensitive data safe and private. In a private blockchain, all of the people who take part know each other, and the transactions are checked by a set of nodes that have already been chosen. Private blockchains have some benefits, such as more privacy, faster transaction speeds, and better scalability. But because the validation process is centralised, private blockchains are less safe than public blockchains.
How Does JPMorgan Use Private Blockchain Technology?
JPMorgan is one among the biggest banks in the whole world, and it has been looking into how private blockchain technology could help it improve the way it handles payments and settlements. In 2019, JPMorgan launched its own blockchain-based payment system called JPM Coin. It is built on a private blockchain. The JPM Coin is a digital currency that is meant to make international payments faster and more efficient and to cut down on settlement times. Because the coin is backed by the US dollar, its value is stable and easy to predict.
The JPM Coin is built on a private blockchain, which means that JPMorgan and the other people who are allowed to use it control it. The network is permissioned, which means that only people who have been given permission can join it and take part in reaching a consensus. Using a private blockchain is good for JPMorgan in a number of ways. First of all, it gives the bank more control over the network and makes sure that only people with permission can use it. This makes the network safer and more reliable, which is important for transactions involving money.
Second, using a private blockchain lets JPMorgan speed up and make it easier to send money across borders. With the JPM Coin, transactions can be settled in real-time, which cuts down on the need for middlemen and speeds up the payment process. Third, using a private blockchain lets JPMorgan cut down on the cost of making payments across borders. By using a digital currency backed by the US dollar, like fiat currency, the bank can lower the costs of currency conversion and other transactions.
Overall, JPMorgan’s use of private blockchain technology in the JPM Coin shows the potential benefits of using blockchain technology in real-world financial applications. Even though the platform is mostly used for cross-border payments right now, it could be used for other kinds of financial services in the future. If that happens, it could change how financial transactions are done around the world.
3. Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain combines the best parts of both public and private blockchains. It lets people see some parts of the blockchain but keeps other parts secret. For example, a hybrid blockchain can be used to store public data, like a cryptocurrency ledger, and a private blockchain can be used to store private data, like medical records. The hybrid blockchain has the best features of both public and private blockchains, such as security, privacy, scalability, and openness.
4. Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain is a type of private blockchain where transactions are verified by a group of organisations working together. Consortium blockchains are often used in fields like supply chain management, finance, and healthcare, where multiple parties need to access and verify the data. In a consortium blockchain, the organisations that are involved have a say in the validation process, and a group of pre-determined nodes run the network.
5. Permissionless Blockchain
A permissionless blockchain is a type of public blockchain in which anyone can join the network as a node. Permissionless blockchains are often used for decentralised applications, where users can create, deploy, and use applications without the need for middlemen. Permissionless blockchains have a lot of benefits, such as being very open, decentralised, and safe. Permissionless blockchains, on the other hand, tend to be slower and less scalable than private blockchains. Access control is the main difference between permissionless blockchain and public blockchain. A public blockchain is a blockchain where anyone can join the network if they want to. A permissionless blockchain, on the other hand, is a type of blockchain where only authorised users can access the information.
Blockchain technology comes in many different forms, such as public, private, hybrid, consortium, and permissionless blockchains. Each type of blockchain has its own unique features and uses, so it’s important to choose the right type based on what the application needs.
Boost Your Earnings with NFT Staking Now!
Leading NFT staking platform development company offering secure, scalable, and customizable staking solutions.

How Does a Public Blockchain Work (Step-by-Step)
As a society, we made ledgers to keep track of information, and they can be used in many different ways. For example, ledgers are used in real estate to keep track of when changes were made to a house or when it was sold. In bookkeeping, we also use ledgers to keep track of everything a company buys or sells. Most transactions are kept track of with double-entry accounting. Even though this is better than single-entry accounting, which is not transparent and doesn’t hold people accountable, double-entry accounting has its own problems: Because each entry is recorded separately, it is hard for one party to check the records of the other.
Traditional ledgers also make it easy to change, remove, or add records. Due to this, you are less likely to believe that the information is true. Public blockchains solve both of these problems, as well as the way we trust each other, by changing the way we keep records from double-entry to triple-entry. This means that transactions on a blockchain are cryptographically sealed by a third entry. This makes a record of transactions that can’t be changed. This record is stored in blocks and checked by a distributed consensus mechanism.
These ways of reaching a decision also make sure that new blocks are added to any blockchain. Proof-of-work (PoW), which is also called “mining,” is one type of consensus mechanism. Mining isn’t the only way to reach a consensus on a blockchain. Bitcoin and Ethereum use it, but by 2022, Ethereum plans to switch to proof-of-stake (PoS), which is a different method.
Proof of Work (PoW) vs. Proof of Stake (PoS)
Consensus mechanisms are what make a public blockchain work. This is the process for validating transactions without a third party like a bank. PoW and PoS are two examples of such ways. Their goal, which is to agree that a transaction is valid, doesn’t change, but how they get there does.
What Does PoW Mean?
PoW, which is the technical term for mining, was the first way to reach a consensus. As of this writing, Bitcoin and Ethereum are still using it, but as was already said, Ethereum will switch to PoS by 2022. Many investors diversify their cryptocurrency portfolios by holding both Ethereum and various altcoins. Cryptography is the basis for PoW. Cryptography uses maths equations that only computers can solve. This system is shown by the example of how blocks are added to the Bitcoin Blockchain in the section before this one.
PoW has two major problems: it uses a lot of electricity and can only handle a certain number of transactions at once (seven for Bitcoin). Most transactions take at least ten minutes to finish, and when the network is busy, this time gets longer. Even so, Bitcoin’s ten-minute delay is pretty amazing when you think about how long it takes to send money across the world or even to clear a check. To solve these problems with PoW, other ways to reach a consensus were made, with PoS being the most popular.
What is PoS?
PoS still uses cryptographic algorithms to verify transactions, but a validator is chosen based on how many coins they hold, which is also called their stake. People aren’t really mining, and there’s no reward for each block. Blocks are instead “forged.” In this process, those who take part lock up a certain number of coins on the network. The bigger someone’s stake, the more mining power they have and the more likely they are to be chosen as the next block’s validator.
So that the person with the most coins doesn’t always win, other ways of picking winners are used. These include random block selection (forgers with the highest stake and lowest hash value are chosen) and coin age selection (forgers are chosen based on how long they’ve held their coins). As a result, transactions take less time and cost less. For example, transactions can be sent and received in seconds with NEO and Dash.
Comparison of Blockchain over Traditional Finance
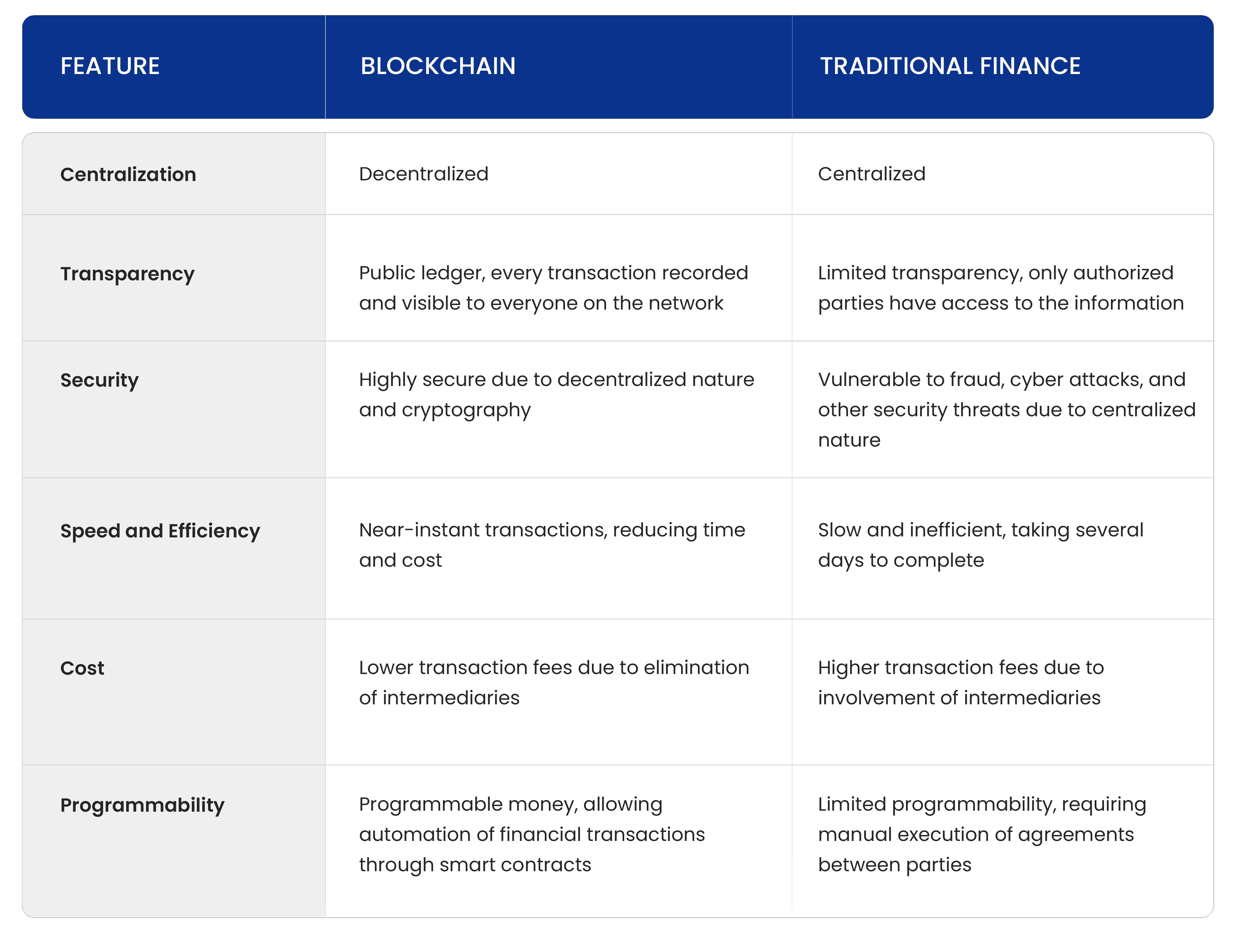
The way that money is transferred has changed a lot because of blockchain technology. In traditional finance, banks, payment processors, and other financial institutions are used as middlemen to make transactions possible. On the other hand, blockchain technology gets rid of middlemen by making a decentralised system where transactions can be checked and processed without trust. Here are some ways that blockchains are better than traditional financial systems:
Decentralisation
Decentralization is one of the best things about blockchain technology. In traditional finance, transactions are processed and verified by centralised institutions, which can lead to mistakes and fraud. Blockchain technology gets rid of the need for middlemen. Instead, transactions are checked by a decentralised network of nodes. This decentralised system makes things clearer and makes fraud less likely.
Translucency
The blockchain ledger is a public ledger, so everyone on the network can see and record every transaction. This level of openness makes it easier to have faith in the financial system. In traditional finance, transactions are kept track of in a central database that only people with permission can access. This lack of openness can make it hard for people to trust each other.
Explore our other insights!

How will Blockchain and NFTs Change the Software Industry?
Introduction The software industry is no stranger to innovation, but few technologies have had as profound an impact

How Much Does it Cost to Build a Blockchain App?
Introduction Blockchain technology has become a driving force of innovation, transforming industries such as finance, healthcare, logistics, and

Revolutionizing Last-Mile Delivery with Blockchain Technology
Introduction The last-mile delivery process is often the most complex and costly part of the logistics and supply
Security
Because Blockchain technology is decentralised, it is inherently safe. Transactions on the blockchain are checked by many nodes on the network. This makes it hard for bad people to mess with the system. Also, blockchain uses cryptography to make sure that transactions are safe. This makes it almost impossible to hack or change the system. Due to how centralised the system is, fraud, cyberattacks, and other security risks are more likely to happen in traditional finance.
Speed and Effectiveness
Transactions in traditional finance can be slow and ineffective, taking several days to finish. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, makes it possible to make transactions almost instantly. This makes financial transactions much faster and cheaper. Blockchain technology is great for cross-border transactions, which can be costly and take a long time with traditional finance. This is because it is faster and more efficient.
Lower Costs
Costs are lower because blockchain technology gets rid of middlemen like banks, payment processors, and other financial institutions. Transactions on the blockchain are processed at a lower cost than in traditional finance. This makes it great for small businesses and individuals who want to save money on transaction fees.
Programmability
Blockchain technology makes it possible to programme money, which means that financial transactions can be done automatically. Smart contracts can be made on the blockchain, which makes it possible for agreements between parties to be carried out automatically. This level of automation cuts down on the need for middlemen and makes financial transactions faster.
Finally, blockchain technology has many advantages over traditional finance, such as decentralisation, transparency, security, speed and efficiency, lower costs, and the ability to be programmed. Because of these benefits, blockchain technology is a great way to do financial transactions, and it may change the way money is handled in the future.
How to Invest in Blockchain Technology - Step By Step Guide
1. Research and Educate Yourself
Do some research and learn about blockchain technology before you put money into it. You need to know what it is and how it works. Research different blockchain projects and how they can be used, read up on news and trends in the industry, and learn about the risks and possible rewards of investing in this technology.
2. Choose a Blockchain Investment Strategy
Choose a way to invest in the blockchain: There are different ways to invest in blockchain technology, such as buying cryptocurrencies, buying blockchain stocks, or buying blockchain-focused funds. Choose a strategy that fits with your investment goals and how much risk you are willing to take.
3. Set Up a Cryptocurrency Wallet
If you decide to invest in cryptocurrencies, you will need to set up a cryptocurrency wallet to store your digital assets safely. Wallets come in different forms, like software wallets, hardware wallets, and paper wallets. Choose the one that fulfills your needs and set it up by following the directions.
4. Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchange
You will need to use a cryptocurrency exchange to buy cryptocurrencies. Look into and compare the different exchanges, paying attention to things like fees, security features, and the cryptocurrencies they support. Set up an account and prove who you are according to the requirements of the exchange.
5. Buy Cryptocurrencies or Blockchain Stocks
Once your account is set up then you can buy cryptocurrencies or blockchain stocks. Choose the cryptocurrency you want to invest in, type in the amount you want to buy, and finish the transaction. If you want to buy blockchain stocks, you will need to do research and pick the stocks you want to invest in. You will then need to enter the amount you want to invest and finish the transaction.
6. Keep Track of Your Investments
Keep track of your investments in blockchain and keep up with news and trends in the industry. Be ready to change your investment plan if the market changes or if something new happens in the blockchain industry.
7. Stay Secure
Protect your investments by using strong passwords, turning on two-factor authentication, and keeping your cryptocurrency wallet and exchange accounts safe.
Investing money into blockchain technology can be a risky but potentially profitable move. It is essential to do your due tasks, invest only the amount that you can afford to lose, and stay informed and aware of market capitalization fluctuations and potential security risks.
Join the Future of Gaming with Web3 Tech!
Web3 game development leverages blockchain for decentralized gaming, enabling player ownership of assets and NFTs.

10 Major Investment Strategies
Growth investing
Growth investing is when people look for companies that are growing faster than average. Most of the time, investors who use this strategy will still buy shares even if they seem expensive. Focus on industries that are doing well now or have done well in the past to narrow down your search. Since the market for blockchain technology is expected to grow, there will likely be a number of companies with strong growth potential.
Samsung
The South Korean tech giant has invested a great deal of capital into blockchain technology. It has built its own blockchain platform and put money into startups that use blockchain. Samsung made this investment by looking at its rapid and dynimic growth. This is Growth invetsent stragergy.
Value Investing
Value investing is when investors look for companies whose prices don’t fully reflect how much they are worth. For value investing to work, you often have to keep your shares for a long time.
Berkshire Hathaway
Berkshire Hathaway is an investment company run by Warren Buffet. Through its subsidiary, Berkshire Hathaway Energy, it has made a number of investments in blockchain technology whose prices were not high in those time. But they had the potential to grow. Looking at these potential Berkshire made these investments.
Dividend Growth Investing
Investors put their money into companies that have a history of paying dividends. You can find out if a company pays dividends by looking at its financial statements. Look for a return of 2% to 6%.
Indexing
This is more of a cautious and passive way to invest, but investors who do this often do better than those who are more active. Most of the time, these investors put their money in an index fund. An index fund is a group of investors’ money that is managed by a fund manager. It invests automatically in the companies in a certain index, like the S&P 500, so that its performance matches that of the index. Index funds are different from ETFs because you can only buy or sell them at the end of the day. The Bitwise 10 Crypto Index Fund is an example of a crypto index fund (BITW).
Investors often trade throughout the day to make money off of small changes in the market. Day traders will use technical analysis to figure out how the market will move and come up with trade ideas based on that. Day trading cryptocurrency is equally lucrative and risky due to highly volatile assets.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, also called “automatic trading,” is a way to invest that uses computer programmes to make trades based on instructions like price, time, etc. that have already been programmed. Algorithmic trading makes up a big part of the American market. AlgoTrader is a programme that you can use to trade Bitcoins automatically.
Contrarian Investing
Contrarian investing means going against what the market is doing on purpose. When people are selling, they buy, and when people are buying, they sell. By watching the Bitcoin Fear and Greed Index, you can get a glance at how people feel about the Bitcoin market. Then, you can do the opposite: buy when people are scared and sell when they are excited (see Fear & Greed Index below).
Arbitrage
Arbitrage is a way to take advantage of price differences between markets for the same asset. You buy the asset in one market and sell it in another for a higher price. Because the price of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin can vary from country to country, this is a great way to make money. In a nutshell, traders will buy cryptocurrency on an overseas exchange (where the price is lower) and then move it to a local exchange and sell it for a higher price. Business Tech says that if you use the right investment platform, you can make 2-4% on each trade. Just make sure to follow local exchange control laws, because there are usually limits to how much local currency you can take across borders.
Yield Farming
Yield farming is an investment strategy that only works on the blockchain. It involves using smart contracts to lend your cryptocurrency to someone else. The person who borrows the money pays you for your help. Yield farmers often move their cryptocurrency from one lending platform to another to get the most money back. Compound Finance, Aave, and MarketDAO are just a few platforms for yield farming. Find out more about how to farm with DeFi yield.
Diversification
Diversification means spreading your risk across a variety of assets and companies to limit your overall loss and give you more chances to make money. Diversification is more than just a way to invest; it’s also a smart way to invest, which is why most financial experts and brokers recommend it. This plan works well for both regular money and cryptocurrency. In traditional markets, you can spread risk across bonds, money markets, and stocks, and you can even diversify your stock portfolio by investing in different industries. When it comes to cryptocurrencies and blockchain, you can invest in both public blockchain companies and cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Monero, and XRP that can be used for different things (cross border payments). If you really want to put diversification first, you should invest in both traditional markets and crypto markets and rebalance your portfolio as needed.
Importance of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is an innovative idea that could change many different industries and applications. Here are some of the important things about blockchain technology:
One of the most essential things about blockchain technology is that it is not centralised. Blockchain is a distributed ledger that is stored up by a network of nodes. This is different from traditional centralised systems, where data is controlled by a single entity. This makes it safer and less likely to be hacked, stolen, or blocked.
Translucency
Another important thing about blockchain technology is that it is open to everyone. Because every transaction is tracked on blockchain and can be seen by anyone with access, it creates a level of transparency that is hard to get with traditional systems. This can be especially helpful in applications like supply chain management, where people need to be able to track where goods are going and make sure they are real.
Security
Because Blockchain technology is decentralised and can’t be changed, it is very safe. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it can’t be changed or deleted without the agreement of the whole network. Because of this, it can’t be hacked or used for fraud or other bad things.
Efficiency
Blockchain technology could make a lot of different things more efficient. Because it gets rid of the need for middlemen, transactions can be done faster and for less money. This can be very helpful in fields like finance and logistics, where delays and inefficiency can cost a lot of money.
Trust
Trust is important in many fields, and blockchain technology could make it easier for people to trust each other. Because transactions are written down on an unchangeable ledger and can be checked by anyone with access, it creates a level of trust that is hard to reach with traditional systems.
Innovation
Blockchain technology has given a lot of different industries new ways to come up with new ideas. With the ability to build decentralised applications (dApps) on top of the blockchain, developers now have a new set of tools they can use to bring new ideas to solve complex problems.
Accessibility
Blockchain technology could make financial services and other applications easier for more people to use. Because it gets rid of the need for middlemen, it can give people who might not have had the access before to those services. This can be especially helpful in developing countries that may not have access to traditional financial systems.
In short, blockchain technology is important because it is decentralised, open, safe, and efficient. It also has the potential to increase trust and accessibility while allowing innovation in a wide range of industries and applications.
uild a Secure and User-Friendly Blockchain Wallet Today!
Blockchain wallet development involves creating secure, user-friendly digital wallets that enable users to store, manage, and transfer cryptocurrencies and other digital assets.

Advantages of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a game-changing innovation that is quickly changing many industries. It is a distributed ledger that keeps a record of transactions in a way that is clear and can’t be changed. The data on the blockchain is protected by cryptography, which makes it hard to change or hack. This new technology has a lot of benefits, which we will talk about in detail in this article.
Decentralization
One of the best things about blockchain technology is that it doesn’t have a single point of control. Blockchain is not like traditional centralised systems, where one entity controls all the data. Instead, the data is spread out over a network of nodes. This means that no one person or group can change or control the data. This makes the data more secure and open.
Transparency
Transparency is another good thing about blockchain technology. Since all of the transactions on the blockchain are written down in a public ledger, anyone can check them out. This makes it easier to keep a record of the movement of assets and stops fraud and other bad things from happening.
Security
Advanced cryptography is used to protect Blockchain technology, so it can’t be changed or hacked. Every transaction on the blockchain is checked and approved by the network nodes. This makes sure that the transaction is real and not a scam.
Immutable
Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it can’t be changed or taken off. This makes sure that the data is correct and stops fraud and tampering.
Faster and Cheaper Transactions
Transactions can be done faster and for less money with Blockchain technology than with traditional banking systems. Because there are no middlemen, transactions can be done quickly and for less money.
Increased Efficiency
Blockchain technology gets rid of the need for middlemen, so transactions are faster, cheaper, and more efficient. This also cuts down on the chance of mistakes and delays that can happen in older systems.
Trustworthy
Blockchain technology is based on a system that doesn’t require trust between parties, so it’s a safe way to do business. Since all transactions are tracked on the blockchain and verified by the network nodes, there is no need to trust middlemen or counterparties.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology makes it possible to use smart contracts, which are agreements that automatically carry out their terms. Smart contracts can automate many processes and get rid of the need for middlemen. This makes transactions faster, cheaper, and more efficient.
Data Privacy
Blockchain technology protects user data by using sophisticated cryptography to keep it safe. This makes it difficult for hackers to steal or get information that should be kept private.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Blockchain technology enables the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) that operate on the blockchain network. Unlike traditional apps, DApps offer enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency, making them ideal for a wide range of industries. The advantages of blockchain technology include decentralization, transparency, security, immutability, faster and more cost-effective transactions, increased efficiency, reliability, smart contracts, data privacy, and decentralized applications. As blockchain continues to evolve, it has the potential to revolutionize various industries by making them more secure, efficient, and transparent.
Brief History of Blockchain Technology
In 2008, a whitepaper called “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” by an anonymous person or group using the name Satoshi Nakamoto was the first time blockchain was mentioned. The whitepaper suggested a decentralized digital currency system that would fulfill the need for third-party middlemen like banks. The system was based on a distributed ledger called a blockchain, which kept track of transactions in a way that couldn’t be changed.
Bitcoin was the first app based on a blockchain. It came out in 2009. It became popular with early adopters and enthusiasts who saw it as a way to get around the traditional financial system and have more freedom with their money. In the years that followed, more cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based apps came out, each with its own features and ways to use them. When Ethereum came out in 2015, it had smart contracts, which let developers build decentralized applications (dApps) on top of the blockchain.
Since then, blockchain technology has been used in more than just finance. For example, supply chain management, digital identity verification, and voting systems all use blockchain technology. It is decentralized and can’t be changed, which makes it a good choice for applications that need trust, security, and transparency. Even though blockchain technology is still new and changing, it has already changed the way we think about data and trust in a big way. As technology improves, it could change and disrupt many industries and business models.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records transactions across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and security. Blockchain development plays a crucial role in building and maintaining these networks for a wide range of applications, from finance to supply chains. One key feature of blockchain is smart contract development, which automates transactions and processes based on predefined conditions, eliminating intermediaries.
For businesses with specific needs, custom blockchain development offers tailored solutions that fit their unique operational requirements. Another essential aspect is blockchain wallet development, which allows users to securely store, send, and receive digital assets like cryptocurrencies. Blockchain’s immutability, transparency, and decentralized nature make it a transformative technology with potential applications across various industries, offering enhanced security, efficiency, and trustworthiness.
How SDLC CORP Can Help with
Blockchain Development?
SDLC Corp offers comprehensive solutions for blockchain development, providing businesses with secure, scalable, and efficient blockchain networks. Their expertise in smart contract development ensures automation and trust in executing digital agreements without intermediaries. For tailored needs, SDLC Corp excels in custom blockchain development, crafting solutions that align with your business objectives. They also specialize in blockchain wallet development, enabling secure management of digital assets.
Additionally, SDLC Corp provides blockchain consulting services, guiding businesses through the adoption and implementation of blockchain technology. Their proficiency in enterprise blockchain development offers large-scale blockchain solutions to optimize business operations. As experts in Hyperledger development, SDLC Corp delivers permissioned blockchain frameworks, ensuring privacy and scalability for enterprise applications.















