Introduction
A comprehensive guide to Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) encompasses various critical aspects, particularly in its application to accounts payable processes. EDI revolutionizes the way businesses exchange documents, automating transactions between trading partners in a standardized electronic format. Understanding EDI begins with grasping its historical evolution, tracing back to its roots in the 1960s and its subsequent development into standardized formats like ANSI X12 and EDIFACT, alongside more contemporary options like XML. In the realm of accounts payable, EDI plays a pivotal role in streamlining processes. It significantly reduces costs associated with manual paper-based systems by eliminating the need for printing, mailing, and manual data entry. Moreover, EDI enhances accuracy by automating data exchange and validation, leading to fewer errors and discrepancies. Its efficiency is evident in accelerating invoice processing and payment cycles, ultimately improving cash flow management for businesses.
Implementing EDI in accounts payable involves several key steps. Vendor onboarding is crucial, requiring effective communication, testing, and setup to ensure seamless integration with trading partners. Integration with existing ERP or accounting software is another critical consideration, ensuring compatibility and smooth data exchange. Additionally, compliance with regulatory requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA is essential to safeguard sensitive data transmitted via EDI channels. The core components of an EDI system, including communication protocols, translation software, and security measures, are fundamental to its successful implementation and operation within accounts payable departments.
Within the context of accounts payable, specific EDI transaction sets are particularly relevant. Purchase orders (850), invoices (810), and remittance advice (820) are among the key transaction types that streamline the procurement-to-payment process. These transaction sets facilitate efficient exchange of crucial documents between buyers and suppliers, enhancing transparency and accuracy throughout the supply chain.
Despite its numerous benefits, implementing EDI in accounts payable comes with its challenges. Adapting to diverse trading partner requirements and formats can be complex, requiring careful coordination and flexibility. System compatibility issues may arise when integrating EDI systems with existing infrastructure, necessitating thorough testing and troubleshooting. Adequate training and support for staff are vital to ensure smooth adoption and ongoing maintenance of EDI systems.
Real-world case studies and best practices provide valuable insights into successful EDI implementations in accounts payable. By examining examples of businesses that have effectively leveraged EDI to streamline processes and enhance efficiency, organizations can glean practical strategies for optimizing their own accounts payable operations. Through continuous improvement and innovation, businesses can harness the full potential of EDI to drive productivity and profitability in the accounts payable domain.
How Its Work?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a sophisticated system facilitating seamless exchange of business documents between trading partners. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how EDI works:
1. Data Translation: The process begins with the conversion of internal electronic data from a company’s format (like CSV or XML) into a standardized format compatible with EDI standards (such as ANSI X12 or EDIFACT). This translation ensures uniformity across different systems and facilitates smooth communication between partners.
2. Transmission: Once the data is translated, it is transmitted securely over a network using various communication protocols like FTP (File Transfer Protocol), AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), or HTTP/S. This transmission can occur in real-time or batch mode, depending on the requirements of the trading partners.
3. Intermediary Processing: In some cases, intermediary services such as Value-Added Networks (VANs) may be utilized to facilitate EDI transactions. VANs act as intermediaries between trading partners, providing added security, data validation, and protocol conversion services.
4. Receipt and Acknowledgment: Upon receiving the transmitted EDI documents, the recipient’s system processes the data and generates acknowledgment messages confirming successful receipt or indicating any errors encountered during the transmission. These acknowledgment messages, such as Functional Acknowledgment (997), help ensure data integrity and provide feedback to the sender.
5. Integration with Business Processes: After successful transmission and receipt, the EDI data is integrated into the recipient’s internal systems and business processes. This integration often involves automatic updating of databases, inventory systems, and other relevant applications, minimizing manual intervention and reducing processing time.
6. QR Code Scanner Integration: Incorporating QR code scanning capabilities into the EDI process adds an extra layer of efficiency and convenience. For example, QR codes containing shipping information or product details can be scanned directly into the EDI system, streamlining data entry and reducing the risk of manual errors. This integration enhances the overall speed and accuracy of information exchange between trading partners.
How Does Edi Differ From Traditional Document Exchange for Purchase Orders?

Certainly! Here are six detailed descriptions differentiating EDI from traditional document exchange for purchase orders, incorporating the keyword “receipt scanner” into the content:
1. Speed and Efficiency: Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) facilitates the instantaneous exchange of purchase orders between trading partners in a standardized digital format. This contrasts with traditional document exchange methods, such as postal mail or fax, which are slower and prone to delays. Additionally, with EDI, there’s no need for manual data entry, reducing the risk of errors and streamlining the procurement process. Integrating a receipt scanner into the EDI system further enhances efficiency by quickly digitizing paper documents, such as invoices or receipts, and seamlessly incorporating them into the electronic workflow.
2. Accuracy and Precision: EDI ensures greater accuracy and precision in purchase order processing compared to traditional methods. Through EDI, purchase orders are transmitted electronically, eliminating the need for manual transcription and reducing the likelihood of errors associated with human data entry. Moreover, by integrating a receipt scanner into the EDI system, businesses can automatically capture and digitize information from physical documents, minimizing discrepancies and enhancing the accuracy of order fulfillment and invoicing processes.
3. Cost Savings: Implementing EDI for purchase order exchange offers significant cost savings over traditional document exchange methods. With EDI, businesses can eliminate expenses associated with paper-based processes, such as printing, postage, and document storage. Additionally, the automation and efficiency provided by EDI reduce labor costs by minimizing the need for manual intervention in order processing. By incorporating a receipt scanner into the EDI infrastructure, organizations can further reduce costs by digitizing paper receipts and invoices, reducing reliance on physical storage and manual data entry.
4. Integration and Compatibility: EDI enables seamless integration with existing enterprise systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, Inventory Management Systems, and Supply Chain Management solutions. This integration ensures that purchase orders flow seamlessly throughout the organization’s workflow, from procurement to fulfillment. In contrast, traditional document exchange methods often require manual intervention to input data into multiple systems, leading to compatibility issues and data discrepancies. By incorporating a receipt scanner into the EDI ecosystem, businesses can extend this integration to include digitized paper documents, ensuring comprehensive data visibility and consistency across the supply chain.
5. Security and Compliance: EDI offers enhanced security features compared to traditional document exchange methods. EDI transmissions are encrypted, protecting sensitive purchase order data from interception or tampering during transit. Moreover, EDI adheres to strict industry standards and protocols, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). By integrating a receipt scanner into the EDI system, businesses can further enhance security by digitizing paper documents and storing them in secure, centralized repositories, reducing the risk of loss or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
6. Scalability and Flexibility: EDI provides scalability and flexibility to accommodate the evolving needs of businesses and their trading partners. As transaction volumes increase or new trading partners are onboarded, EDI systems can easily scale to handle growing demands without significant infrastructure investments. Additionally, EDI supports a wide range of document types beyond purchase orders, including invoices, shipping notices, and payment remittances, making it a versatile solution for electronic document exchange. Integrating a receipt scanner into the EDI framework further enhances flexibility by enabling businesses to capture and digitize various types of paper documents, adapting to the diverse requirements of supply chain management and financial processes.
Dive into EDI: Explore Our Comprehensive Guide Now!

What Types of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Implementations Exist?
Certainly! Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) implementations can vary based on factors such as business needs, industry standards, and technological capabilities. Here’s a brief overview of the types of EDI implementations:
1. Direct/Point-to-Point EDI: In a direct EDI implementation, trading partners establish a direct connection between their respective EDI systems. This setup requires partners to agree upon communication protocols and data formats beforehand. Direct EDI is suitable for large organizations with well-established trading relationships and a high volume of transactions.
2. Value-Added Network (VAN) EDI: Value-Added Networks act as intermediaries between trading partners, providing additional services such as message routing, translation, and monitoring. VANs offer enhanced security, reliability, and scalability compared to direct connections. This approach is suitable for businesses looking to outsource EDI infrastructure management and gain access to value-added services.
3. Web-Based/Cloud EDI: Web-based or cloud-based EDI solutions leverage internet technologies to facilitate document exchange between trading partners. These solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and accessibility, as they can be accessed from any location with an internet connection. Web-based EDI is particularly well-suited for small to medium-sized businesses looking for a cost-effective and easy-to-implement EDI solution.
4. Mobile EDI: Mobile EDI solutions enable users to exchange business documents using mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. These solutions provide flexibility and convenience, allowing users to access and manage EDI transactions on the go. Mobile EDI is beneficial for field sales representatives, remote workers, and businesses operating in dynamic environments where traditional desktop access may be limited.
5. Integrated EDI: Integrated EDI solutions are tightly integrated with existing enterprise systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, Inventory Management Systems, and Supply Chain Management solutions. Integration eliminates the need for manual data entry and streamlines business processes by automating the exchange of documents between internal and external systems. Integrated EDI solutions enhance data accuracy, visibility, and efficiency across the organization.
6. AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) EDI: AS2 is a widely adopted protocol for secure and reliable EDI communications over the internet. AS2 provides encryption, digital signatures, and message integrity verification, ensuring the confidentiality and authenticity of transmitted data. AS2 EDI implementations are suitable for businesses requiring high levels of security and compliance with industry regulations.
These are some common types of EDI implementations, each offering distinct advantages and suitability depending on the specific requirements and preferences of businesses and trading partners.
What Trends Are Driving the Adoption of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Vans Today?
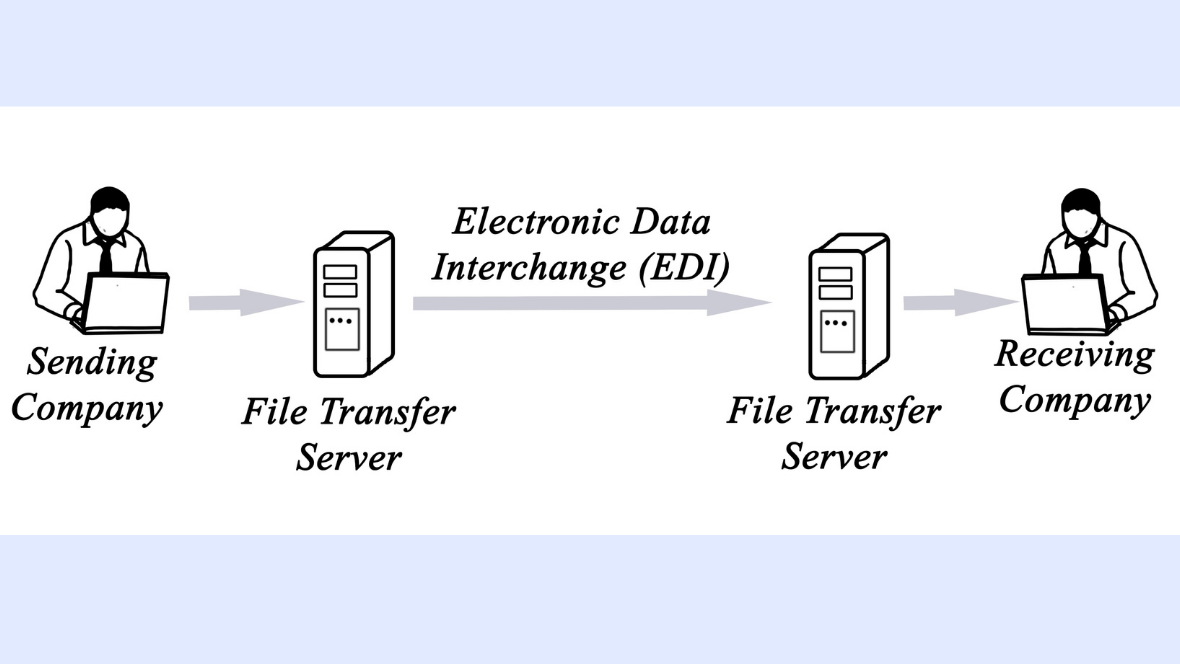
The adoption of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Value-Added Networks (VANs) is being driven by several key trends in today’s business landscape. One significant trend is the increasing globalization of supply chains, with businesses operating across multiple regions and time zones. As companies expand their reach internationally, the need for seamless and standardized communication with trading partners becomes paramount. EDI VANs offer a centralized platform for exchanging electronic documents, enabling businesses to connect with trading partners worldwide efficiently.
Another trend fueling the adoption of EDI VANs is the growing emphasis on supply chain digitization and automation. With the rise of e-commerce and omnichannel retailing, supply chains are becoming more complex and dynamic. Businesses require real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and shipping information to meet customer demands effectively. EDI VANs enable automated exchange of purchase orders, invoices, and other critical documents, streamlining supply chain operations and enhancing overall efficiency.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance requirements are driving businesses to adopt EDI VANs to ensure data security and integrity. Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, are subject to stringent regulations governing the exchange of sensitive information. EDI VANs offer robust security features, including encryption and authentication, to protect data during transmission and storage, helping businesses comply with regulatory mandates and mitigate risk.
Additionally, the rise of cloud computing is accelerating the adoption of EDI VANs by offering scalable and cost-effective solutions. Cloud-based EDI VANs eliminate the need for on-premises hardware and infrastructure, reducing upfront investment costs and enabling rapid deployment. Moreover, cloud-based VANs provide flexibility and scalability to accommodate fluctuating transaction volumes and business growth, making them an attractive option for companies of all sizes.
Overall, the convergence of globalization, supply chain digitization, regulatory compliance, and cloud computing is driving the widespread adoption of EDI VANs today. Businesses recognize the value of these networks in facilitating seamless communication, improving operational efficiency, and staying competitive in an increasingly interconnected and data-driven world.
Why Should You Choose Electronic Data Interchange?
Certainly! Here are six brief descriptions outlining reasons to choose Electronic Data Interchange (EDI):
1. Efficiency: EDI streamlines business processes by automating the exchange of documents such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices. This automation reduces manual intervention, speeds up transactions, and minimizes errors, leading to increased operational efficiency.
2. Cost Savings: Implementing EDI reduces costs associated with paper-based document exchange, including printing, postage, and manual data entry. By digitizing and automating processes, businesses can lower operational expenses and improve the bottom line.
3. Accuracy: EDI ensures data accuracy by eliminating the need for manual data entry, which can introduce errors. With standardized electronic formats and automated validation, EDI minimizes discrepancies and improves the reliability of business transactions.
4. Speed: Electronic Data Interchange enables real-time or near-real-time exchange of documents between trading partners. This rapid exchange accelerates order processing, enhances responsiveness to customer demands, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
5. Compliance and Security: EDI systems adhere to strict data security standards and regulatory requirements, ensuring the secure transmission of sensitive information. By encrypting data and implementing authentication measures, EDI helps businesses maintain compliance with industry regulations and protect against data breaches.
6. Scalability: EDI solutions are scalable, allowing businesses to adapt to changing transaction volumes and accommodate growth. Whether expanding operations, adding new trading partners, or integrating with existing systems, EDI can scale to meet evolving business needs without sacrificing performance or reliability.
Unlock EDI Mastery: Dive into Our Complete Guide Today!

What Are the Practical Applications of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
Certainly! Here are six brief descriptions outlining the practical applications of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI):
1. Supply Chain Management: EDI streamlines communication and data exchange between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, facilitating efficient inventory management, order processing, and logistics coordination.
2. Procurement and Purchase Order Automation: EDI automates the exchange of purchase orders, invoices, and other procurement-related documents between trading partners, reducing manual errors, speeding up transaction cycles, and improving supplier relationships.
3. Finance and Accounting Integration: EDI enables seamless integration of financial data between business systems, automating processes such as invoicing, payment processing, and reconciliation, leading to faster payment cycles and improved cash flow management.
4. Healthcare Transactions: In the healthcare industry, EDI is used to exchange patient records, insurance claims, and other medical information electronically, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory requirements like HIPAA.
5. Automotive Manufacturing: EDI is widely adopted in the automotive sector for managing complex supply chains, coordinating production schedules, and exchanging engineering specifications, facilitating just-in-time manufacturing and lean inventory practices.
6. Retail and E-commerce: EDI facilitates electronic transactions between retailers and suppliers, enabling real-time inventory management, order fulfillment, and sales reporting, supporting the seamless operation of online and brick-and-mortar stores.
What Are the Advantages of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?

Certainly! Here are six brief descriptions highlighting the advantages of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), incorporating the keyword “extract data from PDF” into the content:
1. Efficiency: EDI enables the automated exchange of business documents, such as purchase orders and invoices, in a standardized electronic format. This automation reduces manual intervention, streamlines processes, and accelerates transaction cycles. Additionally, EDI facilitates real-time data exchange, enhancing operational efficiency and responsiveness. Integrating tools to extract data from PDFs further boosts efficiency by automating the capture of information from digital documents, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
2. Cost Savings: Implementing EDI leads to significant cost savings by reducing paper usage, postage, and labor associated with manual document processing. With EDI, businesses eliminate the expenses related to printing, mailing, and storing paper documents. Moreover, the automation provided by EDI reduces the need for manual data entry, minimizing labor costs and errors. Incorporating tools to extract data from PDFs enhances cost savings by digitizing paper-based documents and streamlining data capture processes.
3. Accuracy and Data Integrity: EDI ensures greater accuracy and data integrity compared to manual document exchange methods. By electronically transmitting documents in a standardized format, EDI minimizes errors associated with manual data entry, such as typos and transcription mistakes. Furthermore, EDI systems often include validation checks to verify data accuracy and completeness. Integrating tools for extracting data from PDFs enhances data integrity by automating the extraction process and reducing the risk of human error during data entry.
4. Speed and Responsiveness: EDI facilitates rapid exchange of business documents, enabling faster decision-making and response times. Transactions conducted via EDI can be processed and completed in minutes or even seconds, compared to days or weeks required for traditional paper-based processes. This speed enhances overall business agility and responsiveness to market dynamics. Incorporating tools for extracting data from PDFs further accelerates processing times by quickly converting PDF documents into structured data that can be seamlessly integrated into business workflows.
5. Enhanced Collaboration: EDI fosters seamless collaboration between trading partners by standardizing communication protocols and document formats. This standardization eliminates the need for custom integration solutions and simplifies the exchange of information across disparate systems. Additionally, EDI promotes closer alignment between business processes, reducing misunderstandings and discrepancies. Integrating tools for extracting data from PDFs extends collaboration capabilities by enabling trading partners to exchange information from a variety of document formats, including PDFs, without manual intervention.
6. Compliance and Security: EDI systems adhere to stringent security protocols to protect sensitive business data during transmission and storage. Encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms ensure confidentiality and integrity of transmitted information. Moreover, EDI standards often include built-in compliance requirements, ensuring adherence to industry regulations and standards. Incorporating tools for extracting data from PDFs enhances compliance and security by automating data capture processes while maintaining confidentiality and integrity of extracted information.
Conclusion
A comprehensive guide to Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) serves as an indispensable resource for businesses seeking to understand, implement, and optimize EDI systems. It begins with an overview that clarifies the definition, purpose, and benefits of EDI, laying a solid foundation for readers. Technical standards and protocols, such as ANSI X12, EDIFACT, and XML, are explained to demonstrate how they facilitate structured document exchange and ensure interoperability. The implementation process is outlined, covering steps from assessing organizational readiness to selecting EDI software and establishing connections with trading partners, along with insights into common challenges and best practices.
Integration with existing business systems is a crucial aspect, and the guide delves into how EDI seamlessly integrates with ERP, CRM, and inventory management software, addressing data mapping and synchronization. Security and compliance are paramount considerations, with the guide providing guidance on security measures, encryption techniques, and regulatory requirements like HIPAA and GDPR. It also offers insights into data privacy, access controls, and risk mitigation strategies.
FAQs
1. What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and why is it important?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) serves as the digital backbone for the seamless exchange of business documents among trading partners. It replaces manual, paper-based processes with standardized electronic formats, such as ANSI X12 or EDIFACT, facilitating faster, more accurate communication. EDI is crucial for businesses because it eliminates the inefficiencies and errors associated with traditional methods, streamlining supply chain operations, accelerating transaction processing, and enhancing collaboration between trading partners. By automating document exchange, EDI enables organizations to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment.
2. What are the key components of an EDI system?
A comprehensive EDI system encompasses several essential components to enable seamless electronic communication between trading partners. These components include translation software, which converts data between internal formats and standardized EDI formats, communication protocols such as AS2 or FTP for secure transmission over networks, mapping and integration tools to ensure compatibility with internal systems, compliance validation to adhere to industry standards and regulations, and robust data security measures to protect sensitive information throughout the exchange process.
3. What are the benefits of implementing EDI for businesses?
Implementing EDI offers numerous advantages for businesses across various industries. It enables cost savings by reducing expenses associated with paper-based processes and manual data entry. Additionally, EDI improves efficiency by streamlining transaction processing, minimizing errors, and enhancing order fulfillment accuracy. With increased visibility into supply chain activities and real-time transaction status, businesses can make more informed decisions and respond quickly to market demands, gaining a competitive edge. Furthermore, EDI fosters stronger relationships with trading partners through enhanced collaboration and communication capabilities.
4. How do businesses get started with EDI implementation?
Initiating an EDI implementation involves a systematic approach tailored to the organization’s specific needs and requirements. Firstly, businesses should assess their EDI needs, considering factors like transaction volumes, trading partner relationships, and regulatory compliance obligations. Then, they can select an appropriate EDI solution provider based on features, scalability, compatibility, and cost considerations. Trading partner onboarding is a critical step, involving the establishment of communication protocols, testing processes, and compliance validation. Integration with internal systems, such as ERP or accounting software, is essential for seamless data exchange and process automation. Finally, providing adequate training and support to staff members involved in EDI processes ensures a smooth transition and ongoing success.
5. What are common challenges associated with EDI implementation, and how can they be addressed?
Despite its many benefits, EDI implementation can present challenges for businesses. Managing the complexity of EDI standards and document formats, variability in trading partner requirements, integration with legacy systems, and ensuring compliance and security are common hurdles. To address these challenges, businesses should prioritize proper planning, collaboration with trading partners, leveraging EDI software features for data transformation and validation, and implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive information. Seeking assistance from EDI service providers or consultants can also help navigate complex implementation hurdles and optimize EDI processes for long-term success.
Share a few details about your project, and we’ll get back to you soon.
Let's Talk About Your Project
- Free Consultation
- 24/7 Experts Support
- On-Time Delivery
- sales@sdlccorp.com
- +1(510-630-6507)
