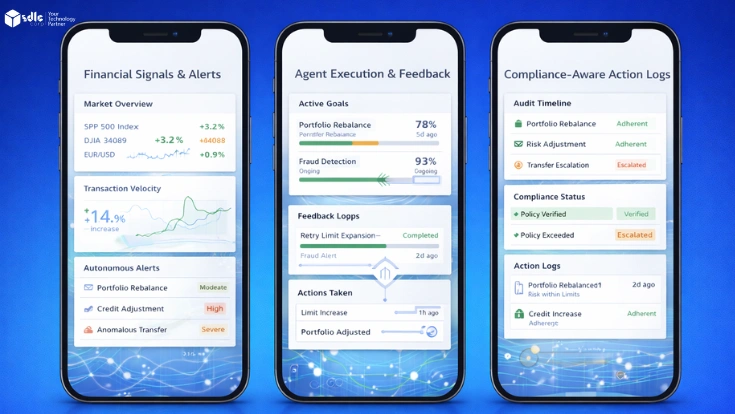
Introduction
Modern supply chains face constant disruption from geopolitical tensions, unexpected demand surges, and sustainability pressures. Traditional planning systems and forecasting tools, while valuable, often fall short when events move faster than models can adapt. Companies need solutions that can anticipate, simulate, and recommend strategies in real time.
This is where Generative AI in Supply Chain steps in. Unlike traditional predictive tools, generative AI goes beyond analyzing the past. It creates new pathways, scenarios, and recommendations tailored to live data. From AI-powered supply chain optimization to supply chain automation with generative AI, organizations are beginning to see how this technology reduces risk, improves performance, and supports growth.
Role of Generative AI in Supply Chain Management
Supply chain systems handle data across sourcing, production, logistics, and distribution. Generative AI can support these processes by summarising operational data, generating planning reports, and assisting with communication across stakeholders. Many organisations explore Generative AI development services to build models that work with structured and unstructured supply chain data.
Why Traditional AI Struggled in Supply Chains
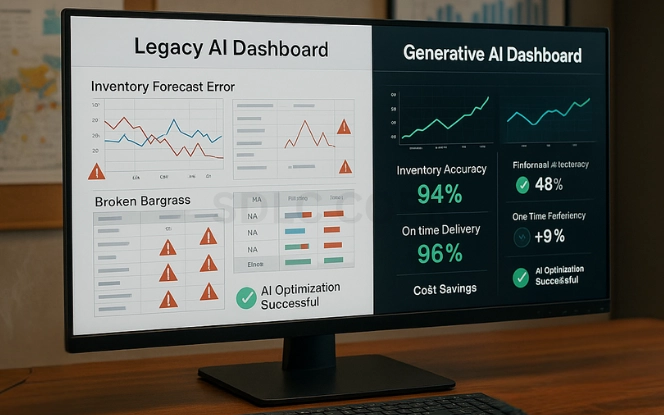
For over a decade, companies invested in AI for supply chain analytics, yet results were often underwhelmed.
Why it fell short:
- Process gaps: Legacy workflows lacked flexibility.
- Data fragmentation: Quality and consistency issues limited insight.
- Human adoption: Tools were complex, and planners resisted adoption.
Generative AI resets these limitations. Instead of static outputs, it adapts to incomplete data, integrates unstructured sources, and generates decisions in natural language that teams can act on immediately.
Key Benefits of Generative AI in Supply Chain
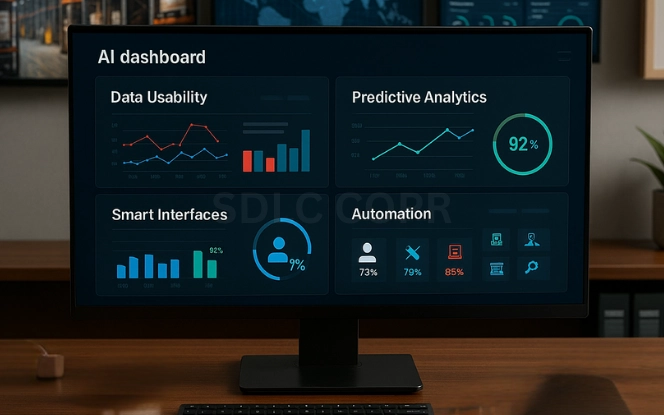
Generative AI strengthens the backbone of supply chains in several ways:
- Improved Data Usability
- Harmonizes fragmented datasets into a single usable model.
- Harmonizes fragmented datasets into a single usable model.
- Enhanced Analytics
- Supports predictive analytics for supply chain by not only forecasting but also simulating responses to changes.
- Supports predictive analytics for supply chain by not only forecasting but also simulating responses to changes.
- Smarter Interfaces
- Provides conversational answers, helping planners interact naturally with complex models.
- Provides conversational answers, helping planners interact naturally with complex models.
- Deeper Automation
- Powers supply chain automation with generative AI, from purchase orders to logistics scheduling.
AI-Powered Supply Chain Optimization

Optimization is the heart of competitive supply chains. With generative AI, optimization shifts from one-time problem solving to continuous, dynamic adjustment.
Example: A global manufacturer uses generative AI to evaluate multiple shipping routes in real time. It generates options that balance delivery speed, fuel costs, and sustainability metrics.
Impact: Reduced operating costs, improved on-time-in-full delivery, and greater flexibility during disruptions.
By embedding AI-powered supply chain optimization into core planning processes, companies move from reactive firefighting to proactive orchestration.
Demand Forecasting with Generative AI
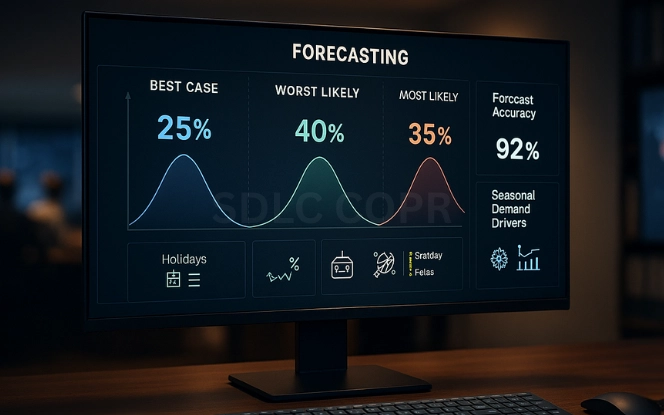
Traditional forecasting often fails during volatile markets. Generative AI builds adaptive, multi-scenario forecasts that integrate real-world signals.
Demand Planning and Risk Analysis: Supply chains face constant uncertainty from demand shifts, delays, and external disruptions. Generative AI can help analyse historical data, generate scenario summaries, and support decision-making. In these cases, a Generative AI consulting company may assist organisations in evaluating feasibility, selecting use cases, and defining guardrails for responsible model use.
How it works: It incorporates external data such as social media sentiment, economic indicators, and supplier health.
Benefit: Forecasts are not just single-number outputs but a range of demand forecasting with generative AI scenarios, each with probabilities and suggested responses.
This helps avoid costly errors in overstocking or understocking.
Predictive Analytics for Supply Chain
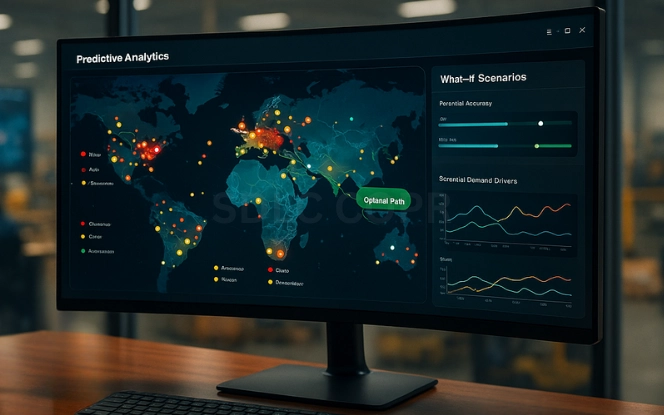
While forecasting addresses “what demand might look like,” predictive analytics for supply chain covers broader risk and performance issues. Generative AI enhances this by simulating “what-if” scenarios:
- Predicting supplier failures and generating backup sourcing plans.
- Anticipating bottlenecks and recommending alternate routes.
- Assessing cost impacts of raw material volatility.
These predictive insights give supply chain leaders foresight and flexibility, supporting resilience against shocks.
Digital Twins in Supply Chain Management
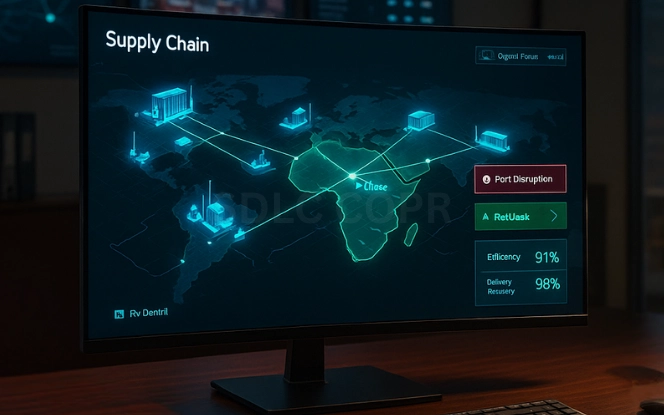
Digital twins in supply chain management create virtual replicas of operations such as factories, warehouses, and transport lanes that mirror real-world performance.
Generative AI supercharges these twins by simulating multiple future outcomes. Companies can test:
- What happens if a port closes unexpectedly?
- How would a supplier bankruptcy affect production?
- What strategies minimize carbon footprint while maintaining service levels?
By running these simulations in a risk-free digital twin environment, businesses reduce uncertainty and prepare for challenges before they strike.
Four Levels of GenAI Adoption in Supply Chains
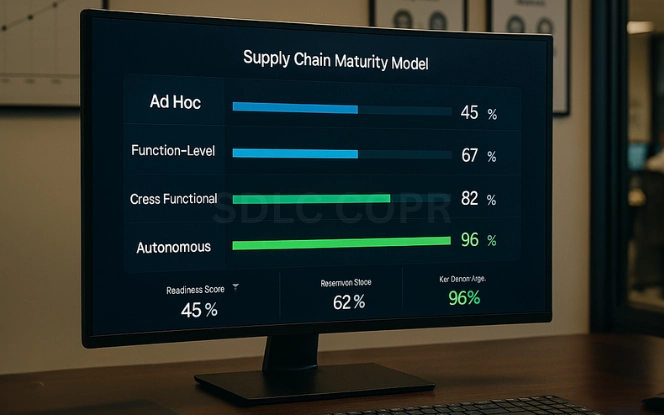
Based on industry research, organizations typically progress through four adoption stages:
- Ad hoc experiments – Limited pilots in forecasting or automation.
- Function-level deployment – GenAI embedded in planning or sourcing teams.
- Cross-functional orchestration – Integration across procurement, production, and logistics.
- End-to-end autonomous supply chain – Digital agents coordinate decisions across the network.
Each stage requires stronger data infrastructure, clearer governance, and increased trust from decision-makers.
A Five-Step Implementation Playbook

Adopting generative AI is not a simple exercise. Leaders can follow a structured path:
- Set ambition: Define measurable outcomes such as forecast accuracy improvement or reduced cost-to-serve.
- Map key decisions: Identify where generative AI can have the most impact, such as inventory, routing, or sourcing.
- Prioritize use cases: Focus on pilots with quick wins to build momentum.
- Redesign workflows: Introduce AI copilots into daily planner tasks.
- Build partnerships: Develop an ecosystem of data, cloud, and AI technology partners.
Deployment and Model Implementation:
Turning generative AI concepts into working systems requires careful deployment and ongoing evaluation. This includes model testing, monitoring, and updates as supply chain conditions change. Some teams use AI/ML implementation services to manage rollout, validation, and integration within complex operational environments.
Challenges and Risks
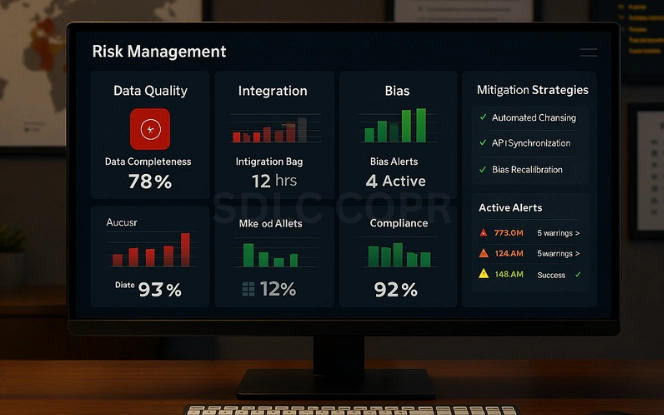
Despite its promise, generative AI requires careful management.
- Data quality issues can weaken recommendations.
- Integration challenges with ERP or planning systems may slow adoption.
- Hallucinations and bias in AI models demand human oversight.
- Ethical and regulatory risks around data privacy and compliance must be addressed.
A human-in-the-loop approach is the best practice, where AI generates recommendations but humans approve and act.
Future Outlook

In the next five years, generative AI will shift supply chains from reactive networks to self-learning ecosystems. Leaders will rely on:
- Continuous optimization across procurement, production, and delivery.
- Digital twin ecosystems that run thousands of simulations daily.
- End-to-end visibility powered by AI copilots for planners, buyers, and logistics managers.
The result will be faster, leaner, and more sustainable supply chains.
Ongoing Development and System Maintenance
Supply chains evolve due to market shifts, regulatory changes, and new partners. Generative AI systems must adapt accordingly. Some organisations choose to hire generative AI developers to maintain models, update integrations, and ensure systems continue to reflect operational realities.
Conclusion
Generative AI is more than a technological upgrade; it represents a new way of managing complexity in supply chains. By embedding it into forecasting, optimization, predictive analytics, and simulations, companies unlock resilience, agility, and competitive edge.
From AI-powered supply chain optimization to demand forecasting with generative AI and digital twins in supply chain management, the opportunities are vast. The companies that move now will set the standard for the next era of global trade.If you want to explore how these solutions can fit into your organization, Contact us SDLC Corp to design and implement supply chain AI strategies with confidence.
To take the next step, Hire AI Development Services with SDLC Corp and explore how tailored solutions can transform your organization.
Read Related Blogs:
FAQs
How Can Generative AI Improve Supply Chain Efficiency?
Generative AI improves supply chain efficiency by analyzing vast amounts of data and creating optimized strategies for logistics, sourcing, and production. It identifies potential bottlenecks, generates alternative routing models, and balances delivery speed with costs and sustainability goals. Unlike traditional systems, it continuously adapts to real time changes, making operations more resilient. This reduces delays, lowers costs, and increases on-time performance, ensuring companies respond quickly to disruptions while maintaining a lean and agile supply chain.
What Are The Key Use Cases Of Generative AI In Supply Chain Management?
Generative AI is being applied across multiple supply chain functions. In planning, it generates adaptive demand forecasts. In sourcing, it creates backup supplier strategies to reduce risks. In manufacturing, it simulates workflows for efficiency. In logistics, it automates shipment scheduling and route optimization. It also powers digital twins in supply chain management, enabling scenario testing before making real-world decisions. These use cases show how AI-powered supply chain optimization and supply chain automation with generative AI transform operations end to end.
How Does Generative AI Support Demand Forecasting And Predictive Analytics For Supply Chains?
Generative AI enhances both forecasting and predictive analytics by going beyond static models. It incorporates external signals such as market trends, social media sentiment, and economic indicators to create multiple demand scenarios. For demand forecasting with generative AI, businesses can prepare for best-case, worst-case, and most-likely situations. In predictive analytics for supply chain, it simulates supply risks, inventory challenges, and logistics bottlenecks. This dual capability ensures greater accuracy, reduces errors in planning, and improves decision-making across the entire supply chain.
What Are The Risks And Challenges Of Using Generative AI In Supply Chains?
While generative AI offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges. Poor data quality or incomplete information can limit accuracy. Integration with existing ERP and planning systems can be complex. There is also the risk of biased or incorrect outputs, often called hallucinations, which require human oversight. Ethical and regulatory issues around data privacy must be considered as well. To manage these risks, companies should adopt a human-in-the-loop model, ensuring that AI recommendations are always validated by experienced supply chain professionals.
What Is The Future Of Digital Twins And Automation In Supply Chain Management With Generative AI?
The future of supply chains lies in combining digital twins in supply chain management with supply chain automation with generative AI. Digital twins will allow companies to run thousands of simulations daily, testing different scenarios for cost, sustainability, and service impact. Generative AI will then automate decisions such as procurement, inventory allocation, and logistics planning based on these simulations. Together, they will create more autonomous and predictive supply chain ecosystems, reducing uncertainty, improving resilience, and enabling smarter end-to-end operations.