Introduction
The Buying Department plays a pivotal role within the organizational structure of companies, particularly those involved in retail, manufacturing, or any business requiring procurement of goods and services. This department is primarily responsible for sourcing, purchasing, and acquiring the necessary materials, products, or services to support the organization’s operations and meet its strategic objectives.
Within the organizational hierarchy, the Buying Department typically falls under the umbrella of the Operations or Supply Chain division, although its placement may vary depending on the company’s size, industry, and structure. The department is often led by a Director or Manager of Procurement, who oversees a team of buyers, purchasing specialists, and procurement professionals.
The key functions of the Buying Department encompass various activities such as vendor selection and evaluation, negotiation of contracts and pricing, inventory management, order processing, and supplier relationship management. These functions are essential for ensuring the organisation obtains quality goods and services at competitive prices, while also maintaining optimal inventory levels to meet demand and minimise excess or obsolete stock.
Effective management of the Buying Department requires collaboration with other departments such as Finance, Operations, and Marketing to align procurement strategies with overall business objectives. For example, close coordination with the Finance Department is necessary to ensure adherence to budgetary constraints, optimise cash flow, and manage accounts payable effectively.
Speaking of financial metrics, the accounts receivable turnover is a vital indicator that measures how efficiently a company collects payments from its customers. It is calculated by dividing the total credit sales by the average accounts receivable balance during a certain period. A high accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates that the company is collecting payments quickly, which is favourable for cash flow management and liquidity. Conversely, a low turnover ratio may suggest issues with credit policies, collection processes, or customer creditworthiness, warranting further analysis and potentially corrective actions.
The Buying Department plays a critical role in the organisational structure by managing the procurement process to acquire necessary goods and services efficiently. Collaboration with other departments, such as Finance, is essential for aligning procurement strategies with overall business objectives. Additionally, monitoring financial metrics like accounts receivable turnover provides valuable insights into the company’s financial health and operational efficiency.
How Its Work?
In an organizational structure, the Purchasing Department plays a critical role in managing the acquisition of goods and services necessary for the operation of the business. This department is responsible for sourcing suppliers, negotiating contracts, and ensuring timely delivery of materials while adhering to budgetary constraints. Let’s delve into how the Purchasing Department operates within the organizational framework, particularly in conjunction with the Accounts Payable function.
Firstly, the Purchasing Department typically falls under the umbrella of the Operations or Supply Chain Management division within a company. Its primary function is to support various departments by procuring the necessary resources efficiently and cost-effectively. This involves identifying the needs of different departments, evaluating potential suppliers, and selecting the most suitable ones based on factors like quality, price, reliability, and compliance with regulations.

What is a Purchasing Department?
The Purchasing Department, also known as the Procurement Department in some organizations, is a critical component of businesses across various industries. Its primary function is to manage the acquisition of goods and services required for the organization’s operations. Here’s a detailed description of what a Purchasing Department entails:
1. Strategic Sourcing: The Purchasing Department is responsible for strategically sourcing suppliers and vendors who can provide the required goods and services at the best possible value in terms of price, quality, and delivery. This involves conducting market research, supplier evaluation, and negotiation to secure favourable contracts and agreements.
2. Supplier Relationship Management: Developing and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is essential for the Purchasing Department. This includes communication, performance evaluation, and addressing any issues or concerns that may arise during the procurement process.
3. Vendor Selection and Evaluation: The department evaluates potential vendors based on various criteria such as price competitiveness, product quality, reliability, and reputation. This involves conducting supplier assessments, audits, and sometimes site visits to ensure that vendors meet the organisation’s standards and requirements.
4. Purchase Order Processing: Once vendors are selected, the Purchasing Department is responsible for processing purchase orders. This involves generating purchase orders based on approved requisitions from other departments, ensuring accuracy in terms of quantities, specifications, and pricing, and sending them to the respective vendors.
5. Contract Negotiation and Management: Negotiating contracts and agreements with suppliers is a key responsibility of the Purchasing Department. This includes defining terms and conditions, pricing structures, delivery schedules, and any other relevant clauses to protect the interests of the organisation and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
6. Inventory Management: Inventory management involves overseeing the sourcing, storing, and tracking of a company’s goods and materials. With tools like Power Automate, businesses can automate inventory-related tasks such as stock updates, reorder notifications, and inventory level monitoring. By integrating Power Automate with inventory management systems, companies can streamline workflows, reduce manual errors, and ensure optimal stock levels, enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
7. Cost Reduction Initiatives: Continuously seeking opportunities to reduce costs without compromising quality is another important function of the Purchasing Department. This may involve consolidating purchases, negotiating volume discounts, exploring alternative suppliers or sourcing regions, and implementing cost-saving measures such as value engineering or standardisation.
8. Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with procurement activities is crucial for the Purchasing Department. This includes assessing supplier financial stability, geopolitical risks, supply chain disruptions, quality control issues, and compliance risks to ensure continuity of supply and minimise potential disruptions to operations.
9. Compliance and Ethics: Ensuring compliance with internal policies, industry regulations, and ethical standards is a priority for the Purchasing Department. This includes adhering to procurement policies and procedures, promoting fair and transparent bidding processes, and preventing conflicts of interest or unethical practices in supplier relationships.
10. Continuous Improvement: Lastly, the Purchasing Department is involved in continuous improvement initiatives aimed at enhancing procurement processes, optimising supplier performance, and driving efficiency gains throughout the supply chain. This may involve implementing technology solutions, streamlining workflows, and fostering innovation in procurement practices.
Overall, the Purchasing Department plays a critical role in optimising the organisation’s procurement activities to ensure the timely acquisition of goods and services at the best possible value, thereby contributing to the organisation’s competitiveness and overall success.
"Structural Integration: The Purchasing Department's Position"
What is the role of a purchasing department?
Here are six detailed descriptions outlining the role of a purchasing department:
1. Strategic Sourcing and Supplier Management: The purchasing department plays a critical role in strategic sourcing, identifying, evaluating, and selecting suppliers who can provide goods and services at competitive prices while maintaining quality standards. They negotiate contracts, establish relationships with suppliers, and manage supplier performance to ensure timely delivery, quality assurance, and cost-effectiveness.
2. Cost Control and Budget Management: A key responsibility of the purchasing department is to control costs and manage budgets effectively. They analyse market trends, monitor prices, and negotiate favorable terms with suppliers to optimise purchasing decisions and maximise cost savings. By implementing cost-effective procurement strategies and leveraging economies of scale, they contribute to the overall financial health of the organisation.
3. Inventory Management and Stock Control: The purchasing department is responsible for managing inventory levels and ensuring adequate stock levels to meet demand while minimising excess inventory costs. They monitor inventory turnover rates, forecast demand, and coordinate with other departments to maintain optimal stock levels. By implementing efficient inventory management practices, they reduce carrying costs, minimise stockouts, and improve overall operational efficiency.
4. Compliance and Risk Management: Ensuring compliance with regulations and mitigating risks associated with procurement activities are essential functions of the purchasing department. They stay updated on relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards, ensuring that procurement practices adhere to legal and ethical requirements. Additionally, they assess supplier risks, implement risk mitigation strategies, and establish contingency plans to address potential disruptions in the supply chain.
5. Streamlining Processes and Improving Efficiency: The purchasing department continuously seeks opportunities to streamline procurement processes and improve operational efficiency. They leverage technology, such as procurement software and e-procurement systems, to automate routine tasks, streamline workflow processes, and enhance collaboration with suppliers. By eliminating inefficiencies and optimising processes, they reduce cycle times, lower transaction costs, and enhance overall productivity.
6. Cross-functional Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Effective collaboration with internal stakeholders, such as finance, operations, and inventory management, is essential for the purchasing department to fulfil its role successfully. They work closely with other departments to understand their procurement needs, align purchasing activities with organisational objectives, and facilitate communication to ensure the timely and accurate fulfilment of orders. By fostering strong relationships with internal stakeholders and promoting a collaborative culture, they enhance organisational agility and responsiveness to changing business requirements.
What are the key functions of purchasing departments?
The purchasing department plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of a company’s supply chain. One of its primary functions is to source and select suppliers that offer the best value proposition in terms of quality, price, and reliability. This involves thorough market research, supplier evaluations, and ultimately, contract negotiation to secure favourable terms and conditions. Once contracts are in place, the department is responsible for effective contract management to ensure compliance and resolve any disputes that may arise. Additionally, purchasing departments are tasked with managing inventory levels to optimise availability while minimising excess inventory costs. They continuously seek opportunities for cost reduction through strategies like bulk purchasing and value analysis. Furthermore, they oversee quality assurance processes to ensure that purchased goods and services meet established standards and regulatory requirements. Building and nurturing positive relationships with suppliers is also a key aspect of their role, as it fosters collaboration, resolves issues, and drives continuous improvement and innovation in the supply chain.
Acquiring Goods at the Best Possible Price
1. Procurement: Purchasing departments are responsible for sourcing and acquiring goods and services necessary for the organisation’s operations, ensuring they meet quality standards and are obtained at competitive prices.
2. Vendor Management: They establish and maintain relationships with suppliers, negotiating contracts, terms, and conditions to ensure the reliability, quality, and cost-effectiveness of supplies.
3. Inventory Management: Purchasing departments oversee inventory levels, optimising stock levels to meet demand while minimising carrying costs and avoiding stockouts or excess inventory.
4. Cost Control: They monitor and control expenditures, implementing strategies to reduce costs, such as bulk purchasing, vendor consolidation, and cost-benefit analysis.
5. Compliance: Purchasing departments ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, such as procurement laws, ethical standards, and environmental regulations.
6. Strategic Planning: They contribute to the organisation’s strategic goals by aligning purchasing activities with overall objectives, identifying opportunities for cost savings, and supporting innovation and efficiency initiatives.
Procuring Raw Materials for Sustaining Operations
1. Strategic Sourcing: Procuring raw materials involves strategically identifying and selecting suppliers who offer the best quality, price, and reliability to sustain operations efficiently.
2. Supply Chain Optimization: Ensuring a smooth flow of raw materials from suppliers to production facilities, minimising delays, and optimising inventory levels to prevent disruptions in operations.
3. Quality Assurance: Implementing stringent quality control measures to guarantee that raw materials meet specified standards, thus maintaining product consistency and customer satisfaction.
4. Cost Management: Employing cost-effective procurement strategies, such as bulk purchasing or negotiating favourable contracts, to minimise expenditure while maintaining material quality.
5. Risk Mitigation: Assessing and mitigating potential risks in the supply chain, such as supplier bankruptcies, natural disasters, or geopolitical conflicts, to ensure uninterrupted operations.
6. Sustainability Practices: Incorporating sustainable sourcing practices by prioritising suppliers with environmentally friendly processes and ethically sourced materials, aligning with corporate social responsibility goals.
Procuring Raw Materials for Sustaining Operations
1. Efficient Sourcing: Selecting reliable suppliers and negotiating favourable terms to ensure a steady supply of raw materials is crucial for sustaining operations. This involves assessing supplier capabilities, reliability, and geographic proximity to optimise logistics.
2. Quality Assurance: Implementing stringent quality control measures to maintain the consistency and integrity of raw materials is essential for producing high-quality products. Regular inspections and testing help identify any deviations that could affect production processes.
3. Inventory Management: Striking the right balance between maintaining adequate raw material inventory levels and avoiding excess stockpiles is critical. Utilising inventory management systems can help optimise inventory turnover and minimise carrying costs.
4. Risk Mitigation: Identifying and mitigating potential risks in the supply chain, such as natural disasters, geopolitical instability, or supplier disruptions, is essential for ensuring the continuity of operations. Developing contingency plans and diversifying suppliers can help mitigate these risks.
5. Cost Optimization: Continuously evaluating and optimising procurement processes to minimise costs without compromising quality is imperative. This may involve exploring alternative sourcing options, bulk purchasing, or renegotiating contracts to achieve cost savings.
6. Sustainability Initiatives: Incorporating sustainable sourcing practices into procurement strategies not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also helps mitigate environmental risks and ensures the long-term availability of resources. This includes sourcing from eco-friendly suppliers and promoting recycling and waste reduction initiatives throughout the supply chain.
Purchasing Department Staff
The Purchasing Department Staff encompasses a diverse range of roles crucial for the smooth operation of procurement activities within an organisation. Procurement Specialists play a pivotal role in sourcing and negotiating contracts with vendors, ensuring optimal value and quality for the company’s purchases. Inventory Managers diligently track inventory levels, analyse usage patterns, and coordinate with suppliers to maintain optimal stock levels and prevent shortages or excess. Cost Analysts contribute their expertise in cost estimation and analysis, identifying opportunities for cost-saving measures and enhancing the department’s overall efficiency. Supply Chain Coordinators manage logistics and coordinate the flow of goods, ensuring timely delivery and minimising disruptions in the supply chain. Vendor Relationship Managers focus on fostering strong partnerships with suppliers, communicating company needs, and negotiating favourable terms to drive mutual success. Compliance Officers oversee adherence to regulations, policies, and ethical standards, mitigating risks and ensuring accountability in procurement processes. Together, these dedicated professionals form a cohesive team driving the Purchasing Department’s success in meeting organisational objectives.
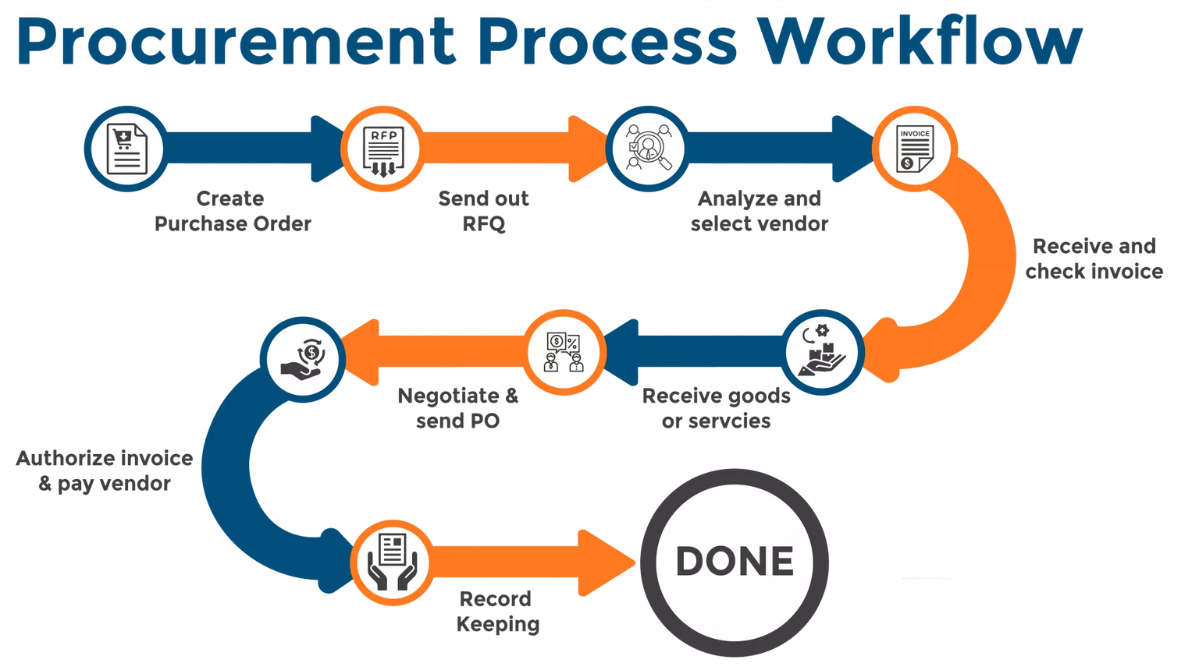
How Procurement Policy and Procedure Work?
1. Guiding Principles: Procurement policies outline the fundamental principles governing purchasing decisions, such as transparency, fairness, and accountability. Procedures detail the steps to ensure adherence to these principles.
2. Vendor Selection: Policies establish criteria for selecting vendors, including factors like quality, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with regulations. Procedures outline the process for soliciting bids, evaluating proposals, and awarding contracts.
3. Budget Management: Procurement policies set guidelines for budget allocation and expenditure. Procedures specify how to track spending, obtain necessary approvals, and ensure purchases align with available funds.
4. Risk Mitigation: Policies address risks associated with procurement, such as fraud, corruption, and supply chain disruptions. Procedures include measures to mitigate these risks, such as conducting due diligence on vendors and implementing internal controls.
5. Compliance: Procurement policies ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, such as anti-corruption laws and ethical standards. Procedures detail how to document transactions, maintain records, and report any irregularities.
6. Continuous Improvement: Procurement policies encourage continuous improvement by fostering innovation, streamlining processes, and seeking feedback from stakeholders. Procedures include mechanisms for evaluating performance, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing best practices.
"Embedding the Purchasing Department into the Organizational Framework"
What are the duties and responsibilities of a purchasing department?
1. Supplier Management: The purchasing department is responsible for identifying, evaluating, and managing relationships with suppliers to ensure the availability of quality materials or services at the best possible prices.
2. Procurement Process Oversight: They oversee the entire procurement process, from requisition to payment, ensuring compliance with company policies, legal requirements, and ethical standards.
3. Cost Analysis and Negotiation: Conducting cost analysis to identify cost-saving opportunities and negotiating contracts with suppliers to secure favorable terms and prices for the organization.
4. Inventory Management: Monitoring inventory levels to ensure adequate stock levels while minimising excess inventory and associated costs.
5. Risk Management: Identifying potential risks in the supply chain, such as supplier disruptions or quality issues, and implementing strategies to mitigate these risks.
6. Budget Management: Developing and managing budgets for purchasing activities, optimising spending to achieve cost-efficiency while meeting operational needs.
What are the benefits of having purchase departments?
1. Cost Efficiency: Purchase departments leverage their expertise to negotiate favourable terms with suppliers, ensuring the best prices for goods and services, thus optimizing the company’s budget and reducing overall costs.
2. Supplier Relationship Management: Purchase departments foster strong relationships with suppliers, enhancing communication and collaboration. This leads to better reliability, quality control, and potential for future partnerships and discounts.
3. Streamlined Processes: Through meticulous planning and coordination, purchase departments streamline procurement processes, minimizing delays and ensuring timely delivery of materials or services essential for uninterrupted operations.
4. Risk Mitigation: By conducting thorough vendor assessments and implementing robust quality assurance measures, purchase departments mitigate risks associated with unreliable suppliers, counterfeit products, or supply chain disruptions, safeguarding the company’s reputation and financial interests.
5. Compliance and Ethics: Purchase departments adhere to legal and ethical standards in sourcing practices, ensuring compliance with regulations and promoting transparency in procurement activities. This fosters trust among stakeholders and mitigates the risk of legal or reputational damage.
Conclusion
The purchasing department plays a crucial role in the organizational structure by serving as the linchpin between suppliers and internal stakeholders. Through its strategic sourcing initiatives, meticulous vendor management, and adherence to ethical and legal standards, the purchasing department contributes significantly to cost efficiency, risk mitigation, and streamlined operations within the organization. By integrating technologies such as QR code scanners into their processes, purchasing departments can further enhance efficiency and accuracy in inventory management, procurement, and quality control. As businesses navigate an increasingly complex global marketplace, the purchasing department remains a vital component, driving value and competitive advantage through its proactive approach to supply chain management.
FAQs
1. What is the role of the purchasing department in the organizational structure?
The purchasing department plays a crucial role in sourcing goods and services essential for the organization’s operations. It is responsible for identifying suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing relationships to ensure timely and cost-effective procurement while adhering to quality standards and compliance requirements.
2. How does the purchasing department interact with other departments within the organization?
The purchasing department collaborates closely with various departments such as finance, operations, and inventory management. It gathers input from these departments to understand their procurement needs, coordinates purchasing activities to fulfill those needs efficiently, and communicates updates regarding supply availability, delivery schedules, and budget allocations.
3. What criteria are used to select suppliers and vendors by the purchasing department?
The purchasing department employs various criteria to select suppliers and vendors, including price competitiveness, quality standards, reliability, delivery capabilities, financial stability, and ethical business practices. Supplier evaluations may also consider factors like geographical proximity, sustainability initiatives, and compatibility with the organisation’s values and goals.
4. How does the purchasing department ensure cost-effectiveness and efficiency in procurement processes?
The purchasing department utilises strategic sourcing techniques, such as vendor consolidation, bulk purchasing, and negotiation of favourable terms and pricing agreements, to achieve cost savings. Additionally, it employs efficient procurement workflows, leverages technology for automation and data analysis, and continually evaluates and optimises procurement strategies to enhance efficiency and reduce unnecessary expenditures.
5. What measures does the purchasing department take to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with regulatory standards in procurement activities?
The purchasing department implements robust supplier vetting processes to assess reliability, quality, and adherence to ethical and regulatory standards. It conducts due diligence on potential vendors, establishes clear contractual agreements with suppliers outlining performance expectations and compliance requirements, and monitors supplier performance regularly. Additionally, the department stays abreast of regulatory changes, conducts internal audits, and provides training to staff to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Share a few details about your project, and we’ll get back to you soon.
Let's Talk About Your Project
- Free Consultation
- 24/7 Experts Support
- On-Time Delivery
- sales@sdlccorp.com
- +1(510-630-6507)
