Introduction
Web3 represents the next evolution of the internet, built on decentralized networks using blockchain technology. Unlike traditional Web 2.0, where data is controlled by centralized entities, Web3 allows users to own and control their data, enabling a more transparent, secure, and user-driven digital ecosystem. A Web3 development company plays a vital role in creating decentralized platforms that empower users with true ownership, while a Web3 app development company focuses on building applications that leverage blockchain for enhanced security and transparency.
Additionally, Web3 game development services are transforming the gaming industry by introducing play-to-earn models and true ownership of in-game assets. The foundation of this new era is blockchain development, which ensures that Web3 applications are secure, scalable, and decentralized. Web3 is essential today as it shifts control from corporations to users, creating a fairer, more equitable digital landscape.
Early Web
Since it was made and has been around ever since most people have considered the Internet a regular part of modern life, the creators’ initial vision for the Web has been altered over time. To better understand this, divide the Web’s brief history into Web 1.0 and Web 2.0.
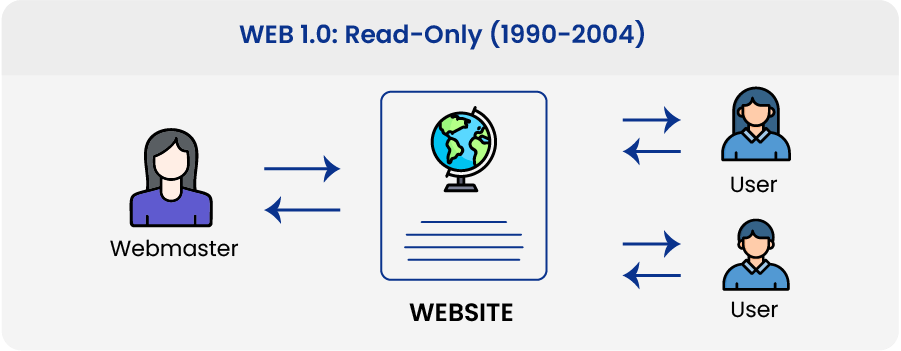
Web 1.0: Read-Only (1990-2004)
Tim Berners-Lee worked at CERN in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1989 on the protocols that would become the World Wide Web. His concept? To develop open, decentralized protocols that allowed information to be shared from anywhere on the planet.
Berners-invention, Lee’s now known as ‘Web 1.0,’ was first implemented between 1990 and 2004. Web 1.0 consisted primarily of static websites owned by businesses, with little to no interaction between users – individuals rarely produced content – leading to it being dubbed the read-only web
Web 2.0: Read and Write (2004-now)
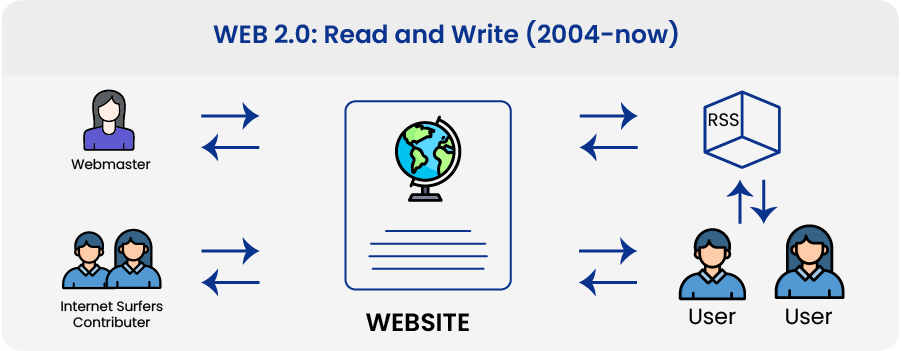
The introduction of social media platforms in 2004 began the Web 2.0 era. Instead of being read-only, the web evolved into a read-write medium. Companies started providing platforms for users to share user-generated content and engage in user-to-user interactions rather than simply delivering content.
As more people went online, a few large corporations began to control a disproportionate amount of the web’s traffic and value. Web 2.0 also gave birth to the revenue model based on advertising. Users could create content but couldn’t own or profit from it.
Web 3.0

Gavin Wood, the co-founder of Ethereum, coined the phrase “Web 3.0” shortly after Ethereum launched in 2014. Gavin articulated a solution to a problem many early crypto adopters perceived: The Web asked for too much faith.
Most of what people know and use on the Internet today is based on trusting a few private companies to act in the public’s best interests.
Build Your Custom Blockchain Today!
A Blockchain development company specializes in building secure, decentralized applications and platforms using blockchain technology.

What is Web3?
Web3, also known as the decentralized web, marks the next step in the evolution of the internet. It offers a more secure, private, and decentralized web experience, powered by blockchain technology. Unlike traditional internet models, Web3 is based on decentralization, meaning no single authority or entity controls the network.
With Web3, users gain enhanced control over their data and digital identities, allowing for more secure and transparent interactions with applications and services. Web3 development companies play a crucial role in building these decentralized platforms, while a Web3 app development company focuses on creating secure, user-centric applications. This shift is enabled by decentralized protocols like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) and the Ethereum blockchain, which serve as the foundation of the Web3 ecosystem.
Exploring the Key Features of Web3: Decentralized Applications and Web3 Wallets
The ability to develop decentralized applications (dApps) that operate on the blockchain is one of Web3’s key features. People can use these dApps to create new types of digital assets, such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which represent unique digital assets for anything from art to virtual real estate.
Another critical aspect of Web3 is the concept of Web3 wallets, which are digital wallets that allow users to securely store their cryptocurrencies and interact with dApps on the blockchain. Web3 wallets differ from traditional wallets because they enable users to access and interact with multiple dApps without needing various logins and passwords.
Why is Web3 Important?
Although Web3’s killer features are not isolated and do not fit neatly into neat categories, we have attempted to separate them for clarity.
Ownership
Web3 gives you unprecedented control over your digital assets. For example, let’s say you’re playing a web2 game—your account links to the in-game item when you purchase it. You will lose these items if the game’s creators delete your account. Alternatively, if you stop playing the game, you will lose the value you have invested in your in-game items.
Web3 enables direct ownership via non-fungible tokens (NFTs). No one, not even the game’s creators, can remove your request. Furthermore, if you stop playing, you can recoup the value of your in-game items by selling or trading them on open markets.
Transform Your Business with Blockchain Solutions!
Blockchain consulting services provide expert guidance on integrating blockchain technology into business models, improving security, and scalability.

Censorship Resistance
A significant power imbalance exists between platforms and content creators. Over a million creators rely on platforms like OnlyFans, with many using it as their primary source of income. When OnlyFans announced plans to ban sexually explicit content, it sparked outrage among creators who felt betrayed by a platform they helped grow. Although the decision was quickly reversed after widespread backlash, it highlighted a common issue with Web 2.0 platforms: creators risk losing their reputation and followers if they leave.
In contrast, with Web3, data is stored on the blockchain, allowing creators to retain their reputation and followers even when moving to a new platform. They can easily plug their identity into an interface that aligns with their values. Additionally, Web3 platforms inherently offer censorship resistance, while Web 2.0 platforms require creators to trust that the platform’s rules won’t suddenly change.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
In addition to owning your data in Web3, you can hold the platform collectively using tokens that function similarly to stock options. DAOs enable you to manage a platform’s decentralized ownership and decide its future.
Smart contracts that automate decentralized decision-making across a pool of resources (tokens) define DAOs as mutually agreed upon. Then, the code automatically executes the voting outcome by users with tokens on how to spend resources.
DAOs refer to many Web3 communities. These communities all have varying degrees of decentralization and code automation. We are currently investigating what DAOs are and how they might evolve.
Identity
Traditionally, you’d set up an account for each platform you use. For example, you may have a Twitter account, a YouTube account, and a Reddit account. Would you like to change your display name or profile picture? Again, you must do this for each account.
Using social sign-ins can sometimes raise the old problem of censorship. These platforms can lock you out of your online life with just one click. Even worse, many websites demand you give them access to your data to create an account.
Web3 solves these issues by giving you control over your digital identity via an Ethereum address and an ENS profile. Using an Ethereum address provides a secure, censorship-resistant, and anonymous single login across platforms.
Native Payments
Web2’s payment infrastructure excludes people who do not have bank accounts or live within the borders of the wrong country, as it is based on banks and payment processors.
Web3 sends money directly to the browser using tokens such as ETH, eliminating the need for a trusted third party.
Web3 Limits
To flourish, the developers of Web3 must resolve several drawbacks, despite the wide range of advantages it currently offers.
Accessibility
Important Web3 features, such as Sign-in with Ethereum, are already accessible to anyone. However, the relative cost of transactions remains prohibitive for many.
Due to high transaction fees, Web3 is less likely to be used in less-affluent developing countries. The Ethereum community is actively addressing these issues through network upgrades and the development of layer 2 scaling solutions. The technology is ready, but higher levels of adoption on layer 2 are required to make Web3 available to everyone.
User Experience
The technical barrier to using Web3 currently needs to be lowered. Users must understand security concerns, navigate unintuitive user interfaces, and comprehend complex technical documentation.
Wallet providers, in particular, are working to address this, but more progress is required before Web3 is widely adopted.
Education
Boost Your Earnings with NFT Staking Now!
Leading NFT staking platform development company offering secure, scalable, and customizable staking solutions.

Centralized Infrastructure
The Web3 ecosystem is new and rapidly evolving. Because of this, it currently depends a lot on centralized infrastructure (GitHub, Twitter, etc.).
Many Web3 businesses scramble to close these gaps, but developing reliable, high-quality infrastructure takes time.
A Decentralized Future
A new and developing ecosystem is called Web3. Although Gavin Wood first used the term in 2014, many of these ideas have just recently come to pass.
For instance, there has been a sharp rise in interest in cryptocurrencies, improvements in layer 2 scaling solutions, extensive testing of novel forms of governance, and revolutions in digital identity just in the past year.
Web3 is still in its infancy, but the future of the Web appears bright as long as we keep enhancing the infrastructure that will support it.
Conclusion
Web3 is a significant change in how we use the internet because it gives us a version of the web that is less centralized, safer, and more open. With the development of new technologies and the growing adoption of blockchain and cryptocurrency, we expect to see Web3 continue to evolve and transform the internet in the future.
How SDLC CORP Can Help with Web3 and why is it so essential Today?
SDLC Corp, as a leading Web3 development company, can help businesses transition to the decentralized web by building secure, scalable platforms that empower users with true ownership of their data. Their expertise as a Web3 app development company enables them to create decentralized applications (dApps) that leverage blockchain and enhance transparency. Additionally, their Web3 game development services allow the creation of play-to-earn models and tokenized in-game assets.
With a strong foundation in blockchain development and smart contract development, SDLC Corp ensures secure, automated transactions for your platform. As pioneers in NFT marketplace development, they help businesses tap into the growing digital asset economy. Moreover, as a leading Web3 consulting company in the USA, SDLC Corp guides clients on how to effectively leverage Web3 technology to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving digital landscape. Web3 is essential today because it decentralizes control, increases security, and enhances user ownership.















